Actinomycosis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
==Causative organism== | ==Causative organism== | ||
Revision as of 22:45, 23 January 2012
For patient information click here
| Actinomycosis | |
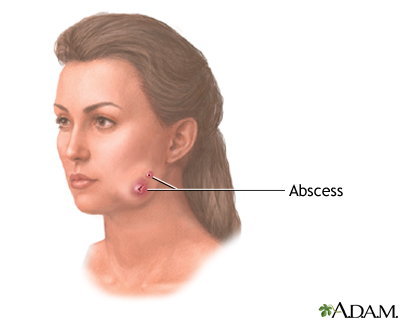 | |
|---|---|
| A patient with Actinomycosis on the right side of the face. | |
| ICD-10 | A42 |
| ICD-9 | 039 |
| DiseasesDB | 145 |
| MeSH | D000196 |
|
Actinomycosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Actinomycosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Actinomycosis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Causative organism
Actinomycosis is primarily caused by any of several members of the bacterial genus Actinomyces. These bacteria are generally anaerobes.[1] Actinomyces spp. normally live in the small spaces between the teeth and gums, causing infection only when they can multiply freely in anoxic environments. The three most common sites of infection are decayed teeth, the lungs, and the intestines.
Since Actinomyces bacteria are generally sensitive to penicillin, it is frequently used to treat actinomycosis.
Pathophysiology & Etiology
- 6 species cause disease in humans:
- A. israelii
- A. Naeslundii
- A. odontolyticus
- A. viscosus
- A. Meyeri
- A. gerencseriae
- Gram positive filamentous rod
- Sulfur Granules
- Actinomyces from within, Nocardia from without
- Generally low pathogenicity and cause disease only in the setting of antecedent tissue injury
Symptoms
- Cervicofacial Actinomycosis (55%)
- Thoracic Actinomycosis
- Lungs
- Pleura
- Mediastinum
- Chest wall (aspiration, extension of cervicofacial disease, transdiaphragmatic or retroperitoneal spread)
- Clinical picture of tuberculosis (TB) or malignancy
- Abdominal and Pelvic Actinomycosis
- Following:
- Penetrating trauma
- Gut perforation
- Surgical manipulation
- Ileocecal predilection
- Confused with:
- TB
- Ameboma
- Chronic appy
- Regional enteritis
- Carcinoma
- Intrauterine devices (IUD’s)
- Confused with:
- Following:
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
Pharmacotherapy
- In vitro susceptible to:
- Penicillin
- Chloramphenicol
- The tetracyclines
- Erythromycin
- Clindamycin
- Imipenem
- Streptomycin
- The cephalosporins
- Prolonged treatment (6-12 months)
Surgery and Device Based Therapy
- Surgery often required for disease of the chest, abdomen, pelvis, and central nervous system (CNS)
References
- ↑ Ryan KJ; Ray CG (editors) (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed. ed.). McGraw Hill. ISBN 0838585299.
External links
Acknowledgements
The content on this page was first contributed by: Dr. Steve Wiviott
Template:Bacterial diseases
Template:SIB
de:Aktinomykose
gl:Actinomicose
hr:Aktinomikoza
nl:Actinomycose
sr:Актиномикоза
fi:Aktinomykoosi
uk:Актиномікоз