Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome EKG examples: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (left posterior pathway). | |||
[[File:WPWLP.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (Posteroseptal pathway). | |||
[[File:WPW.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | ---- | ||
Shown below is an EKG showing abnormal QRS form with [[delta wave]]s seen best in the V leads. | |||
[[File:Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome9.jpg|center|800px]] | [[File:Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome9.jpg|center|800px]] | ||
---- | |||
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome demonstrating upstroke of the QRS-complex which is 'slurred', resulting in a delta-wave (arrow). | |||
[[File:Rhythm_WPW.png|center|800px]] | |||
---- | ---- | ||
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of delta waves in a patient with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW) | |||
[[File:Wolff-Parkinson-White-syndrome.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome. | |||
[[File:wpw_full_ecg.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome. | |||
[[File:wpw_full_ecg2.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome. | |||
[[File:wpw_full_ecg3.png|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type I. | |||
[[File:Ganseman WPW type 1.1.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type I. | |||
[[File:Ganseman WPW type 1.2.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type I. | |||
[[File:Ganseman WPW type 1.3.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type II. | |||
[[File:Ganseman WPW type 2.1.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type II. | |||
[[File:Ganseman WPW type 2.2.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type II. | |||
[[File:Ganseman WPW type 2.3.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type II. | |||
[[File:Ganseman WPW type 2.4.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type II. | |||
[[File:Ganseman WPW type 2.5.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
WPW syndrome with an [[orthodromic]] circus movement [[tachycardia]]: Narrow complex tachycardia with a rate of 200 bpm (RR interval 320 ms). After 5 cycles, the tachycardia suddenly stops and four multiform complexes are seen without any [[P wave]]s. These complexes should be regarded as a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, which is not uncommon after an [[adenosine]]-terminated [[supraventricular tachycardia]]. A 5th complex is preceded by a [[P wave]]. The subsequent 4 complexes show a widened QRS complex and all are immediately preceded by a [[P wave]]. The initial phase of the [[QRS]] complex is slurred and positive in all available leads. [[Sinus rhythm]] continues thereafter with gradual abbreviation of the [[QRS]] complex until a 120 msec wide QRS complex remains. | |||
[[File:Puzzle_2007_5_198_fig1.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
The same patient's EKG during sinus rhythm. A discrete delta wave is clearly visible. The morphology of the delta wave suggests a left posterior [[Kent bundle]]. | |||
[[File:Puzzle_2007_5_198_fig2.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
---- | |||
==Sources== | ==Sources== | ||
Revision as of 15:00, 16 October 2012
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
For the main page on Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome click here
EKG examples
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.

Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
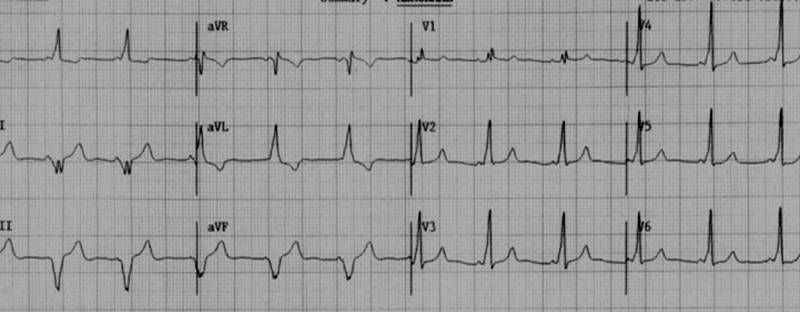
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (antero-lateral pathway).
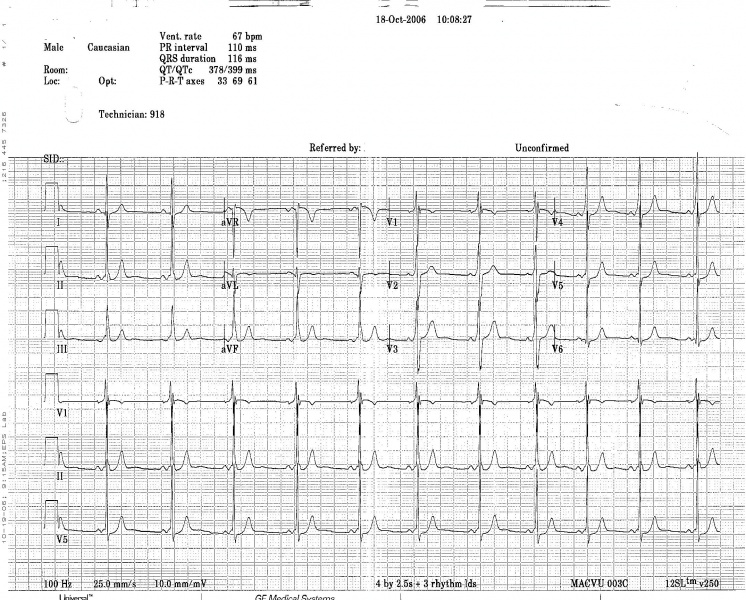
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome depicting delta wave.

Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (antero-septal pathway).
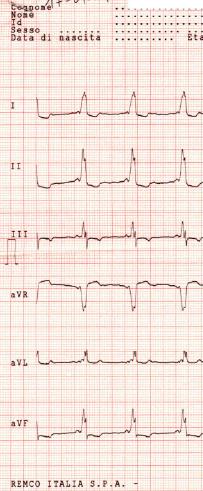
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (antero-septal pathway).
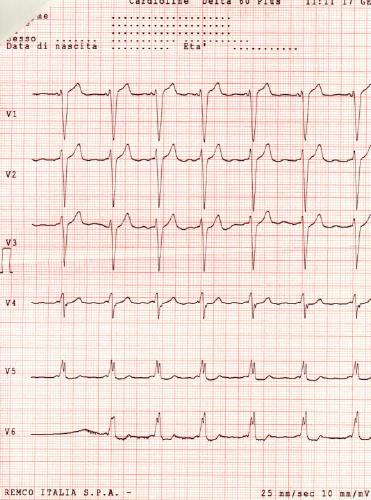
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (epicardial pathway).
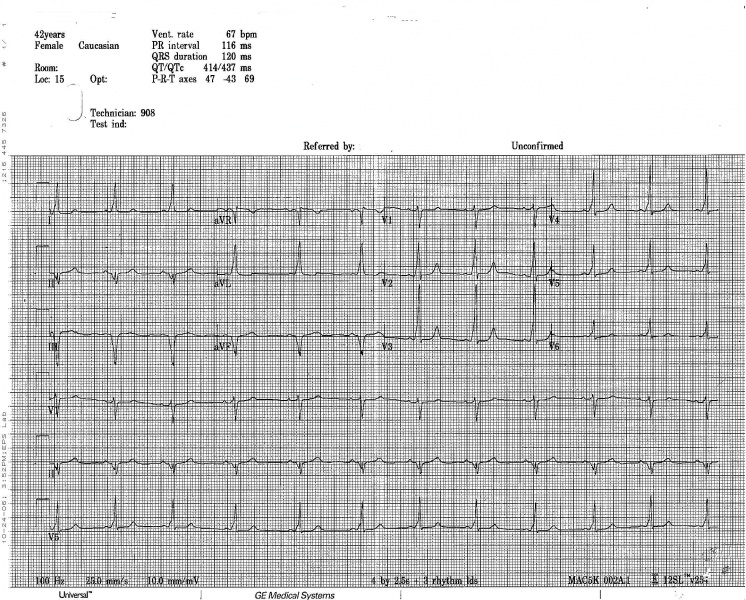
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (left posterior pathway).
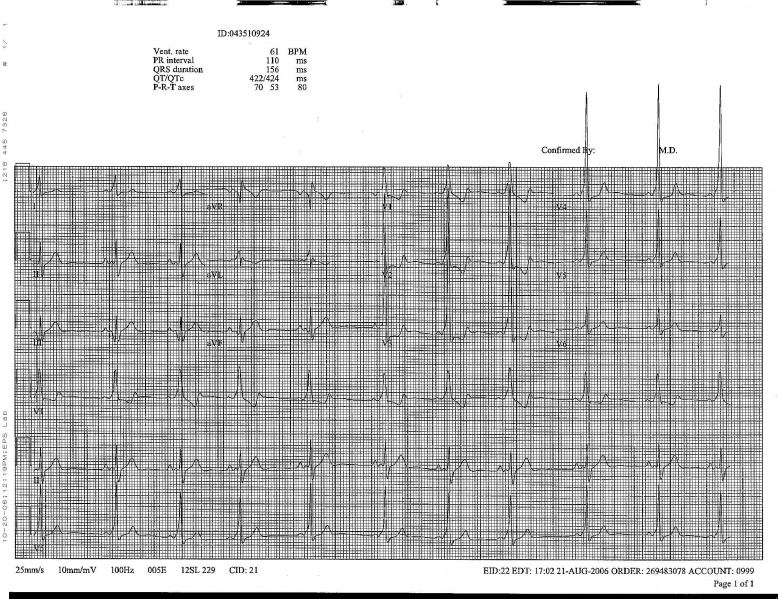
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (Posteroseptal pathway).
Shown below is an EKG showing abnormal QRS form with delta waves seen best in the V leads.

Shown below is an electrocardiogram of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome demonstrating upstroke of the QRS-complex which is 'slurred', resulting in a delta-wave (arrow).
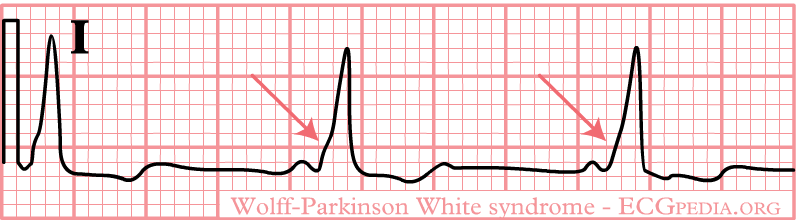
Shown below is an electrocardiogram of delta waves in a patient with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW)
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome.
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome.
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome.
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type I.
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type I.
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type I.
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type II.
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type II.
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type II.
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type II.
Shown below is a 12 lead electrocardiogram of WPW syndrome type II.
WPW syndrome with an orthodromic circus movement tachycardia: Narrow complex tachycardia with a rate of 200 bpm (RR interval 320 ms). After 5 cycles, the tachycardia suddenly stops and four multiform complexes are seen without any P waves. These complexes should be regarded as a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, which is not uncommon after an adenosine-terminated supraventricular tachycardia. A 5th complex is preceded by a P wave. The subsequent 4 complexes show a widened QRS complex and all are immediately preceded by a P wave. The initial phase of the QRS complex is slurred and positive in all available leads. Sinus rhythm continues thereafter with gradual abbreviation of the QRS complex until a 120 msec wide QRS complex remains.
The same patient's EKG during sinus rhythm. A discrete delta wave is clearly visible. The morphology of the delta wave suggests a left posterior Kent bundle.
Sources
Copyleft images obtained courtesy of ECGpedia, http://en.ecgpedia.org/index.php?title=Special:NewFiles&offset=&limit=500