Aortic coarctation (patient information): Difference between revisions
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Aortic coarctation is a congenital heart disease with a narrowing part of the aorta. This condition leads the heart must pump harder to force blood through the narrow part of the narrowing aorta. The cause is not clear. Usual signs and symptoms of aortic coarctation include [[dizziness]] or [[fainting]], [[shortness of breath]], [[headache]], [[chest pain]] and [[hypertension]]. Tests such as [[echocardiography]] and [[chest x-ray]] can show the enlarged left ventricle in patients with aortic coarctation. Treatments include [[medicine]]s used to control [[hypertension]], [[balloon angioplasty]] and [[stenting]], and [[surgery]]. The prognosis of aortic coarction depends on the effect of [[balloon angioplasty]] and [[stenting]] or [[surgery]]. | Aortic coarctation is a congenital heart disease with a narrowing part of the aorta. This condition leads the heart must pump harder to force blood through the narrow part of the narrowing aorta. The cause is not clear. Usual signs and symptoms of aortic coarctation include [[dizziness]] or [[fainting]], [[shortness of breath]], [[headache]], [[chest pain]] and [[hypertension]]. Tests such as [[echocardiography]] and [[chest x-ray]] can show the enlarged left ventricle in patients with aortic coarctation. Treatments include [[medicine]]s used to control [[hypertension]], [[balloon angioplasty]] and [[stenting]], and [[surgery]]. The prognosis of aortic coarction depends on the effect of [[balloon angioplasty]] and [[stenting]] or [[surgery]]. | ||
Revision as of 21:54, 10 November 2009
For the WikiDoc page for this topic, click here
| Aortic coarctation (patient information) | |
 | |
|---|---|
| ICD-10 | Q25.1 |
| ICD-9 | 747.10 |
| OMIM | 120000 |
| DiseasesDB | 2876 |
| eMedicine | med/154 |
| MeSH | D001017 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Jinhui Wu, MD
Please Join in Editing This Page and Apply to be an Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
What is aortic coarctation?
-
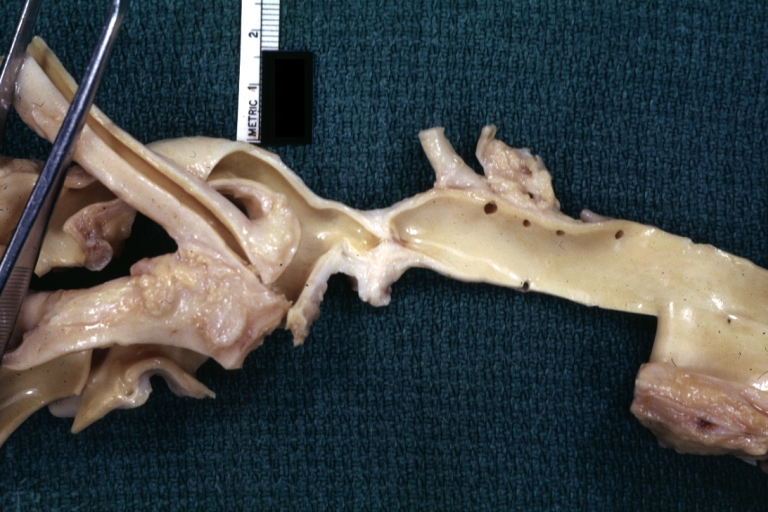
AORTA: Coarctation, Adult: Gross, fixed tissue, an excellent illustration of postductal coarctation
-
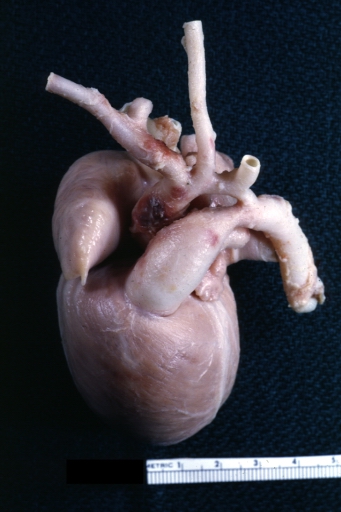
AORTA: Coarctation: Gross, hypoplastic aortic arch and infantile coarctation well demonstrated.
Aortic coarctation is a congenital heart disease with a narrowing part of the aorta. This condition leads the heart must pump harder to force blood through the narrow part of the narrowing aorta. The cause is not clear. Usual signs and symptoms of aortic coarctation include dizziness or fainting, shortness of breath, headache, chest pain and hypertension. Tests such as echocardiography and chest x-ray can show the enlarged left ventricle in patients with aortic coarctation. Treatments include medicines used to control hypertension, balloon angioplasty and stenting, and surgery. The prognosis of aortic coarction depends on the effect of balloon angioplasty and stenting or surgery.
How do I know if I have aortic coarctation and what are the symptoms of aortic coarctation?
The signs and symptoms of coarctation of the aorta depend on how much blood can flow through the artery. Children with serious aortic narrowing tend to show signs and symptoms earlier in life, while mild cases may not be diagnosed until adulthood. Usual symptoms include:
- Pale skin
- Dizziness or fainting
- Shortness of breath
- Headache
- Chest pain
- Nosebleed
- Hypertension
- Muscle weakness
- Leg cramps or cold feet
- Poor growth
Other health problems may also cause these symptoms. Only a doctor can tell for sure. A person with any of these symptoms should tell the doctor so that the problems can be diagnosed and treated as early as possible.
Who is at risk for aortic coarctation?
Like many congenital heart disease, the cause of aortic coarctation is not clear. Clinical studies suggest that the genetic and environmental factors both play an important role during the pregnancy.
- Genetic disorders such as Turner syndrome
- Pregnant woman had viral infection during pregnancy
How to know you have aortic coarctation?
- Echocardiography: Echocardiography is the most commonly used imaging technique for the diagnosis of aortic coarctation. It can assess atrium and ventricle morphology and characteristic anatomic relations, and detect the location and severity of the aortic coarctation and can show other heart defects, such as a bicuspid aortic valve.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) and Holter monitoring: Electrocardiogram and Holter monitoring can tell electric activities of the heart for cardiovascular diseases. They can supply informations about heart rhythm and indirectly, heart size. Patients with aortic coarctation may show ventricular hypertrophy and heart rhythm irregularity sign.
- Chest x-ray: An x-ray image of chest allows the doctor to check the size and shape of the heart to determine whether the heart is enlarged. And it also helps the doctor check the condition of your lungs. Patients with aortic coarctation may show an enlarged heart or a narrowing in the aorta at the site of the coarctation.
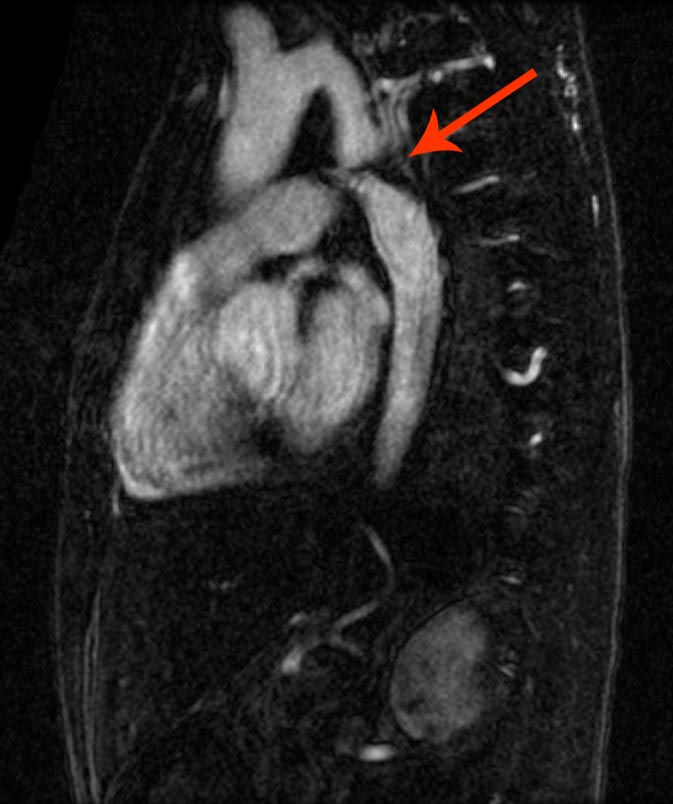
- Cardiac MRI and CT: Cardiac MRI and CT can create pictures of the ventricles, atrium, valves and major blood vessels. It can help doctors analyse the structure and function of the heart and decide the treatment protocols for the patient. Patient with aortic coarctation may reveal the location of the coarctation of the aorta and determine whether it affects other blood vessels in the child's body.
- Cardiac catheterization: In a catheter room, the doctor threads a thin tube through a blood vessel in yourthe patient's arm or groin to an artery in the heart and injects dye to see the heart and the arteries on an x-ray. It can supply detailed information about the severity of the aortic coarctation.
When to seek urgent medical care?
Call your health care provider if your baby has aortic coarctation and symptoms do not improve with treatment, or if new symptoms appear. If your baby experiences either of the following symptoms, seeking urgent medical care as soon as possible:
- Sudden shortnesss of breath
- Severe chest pain
- Fainting
- Unexplained hypertension
Treatment options
Patients with aortic coarctation have many treatment options. The selection depends on the severity of aortic coarctation, symptoms and whether the child occurs the complications or not. The options are medicines, balloon angioplasty and stenting, and surgery. The goal of the treatment is to open the aorta to prevent complications. Before treatment starts, talk to your child's doctor about treatment options and your family's preferences on treatment decisions.
- Medicines: Some anti-hypertension medicines can be used to control blood pressure before or after surgery.
- Balloon angioplasty and stenting: In a catheter room, the doctor threads a thin tube through a blood vessel in your baby's arm or groin to an artery in the heart. Then, an uninflated balloon is placed through the opening of the narrowed aorta and a stent is inserted to keep the narrowed part of the aorta open permanently.
- Surgery: Surgical treatment of aortic coarctation may be performed to repair aortic coarctation. During the surgery, the anesthetist gives medicine to make the child sleepy and comfortable. Then the surgeons make a small cut between the ribs to reach the aorta and repair it. The methods for repairing include resection with end-to-end anastomosis, patch aortoplasty, left subclavian flap angioplasty and bypass graft repair.
Diseases with similar symptoms
Where to find medical care for aortic coarctation?
Directions to Hospitals Treating aortic coarctation
Prevention of aortic coarctation
Although the cause is unknown, the following measures may be helpful to decrease the risk of having a baby with aortic coarctation.
- Screening test and regular check for people with genetic disorders
- Pregnant woman need to avoiding viral infection during pregnancy.
What to expect (Outook/Prognosis)?
The prognosis of aortic coarctation depends on whether balloon angioplasty and stentingor the surgery has been done or not.
Copyleft Sources
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000191.htm
http://www.mayoclinic.com/print/coarctation-of-the-aorta/DS00616/DSECTION=all&METHOD=print