|
|
| (214 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| __NOTOC__ | | __NOTOC__ |
|
| |
|
| ↑↓{{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Trusha}}
| | {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Trusha}} |
| | |
| | ==new== |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | {| align="right" |
| | | |
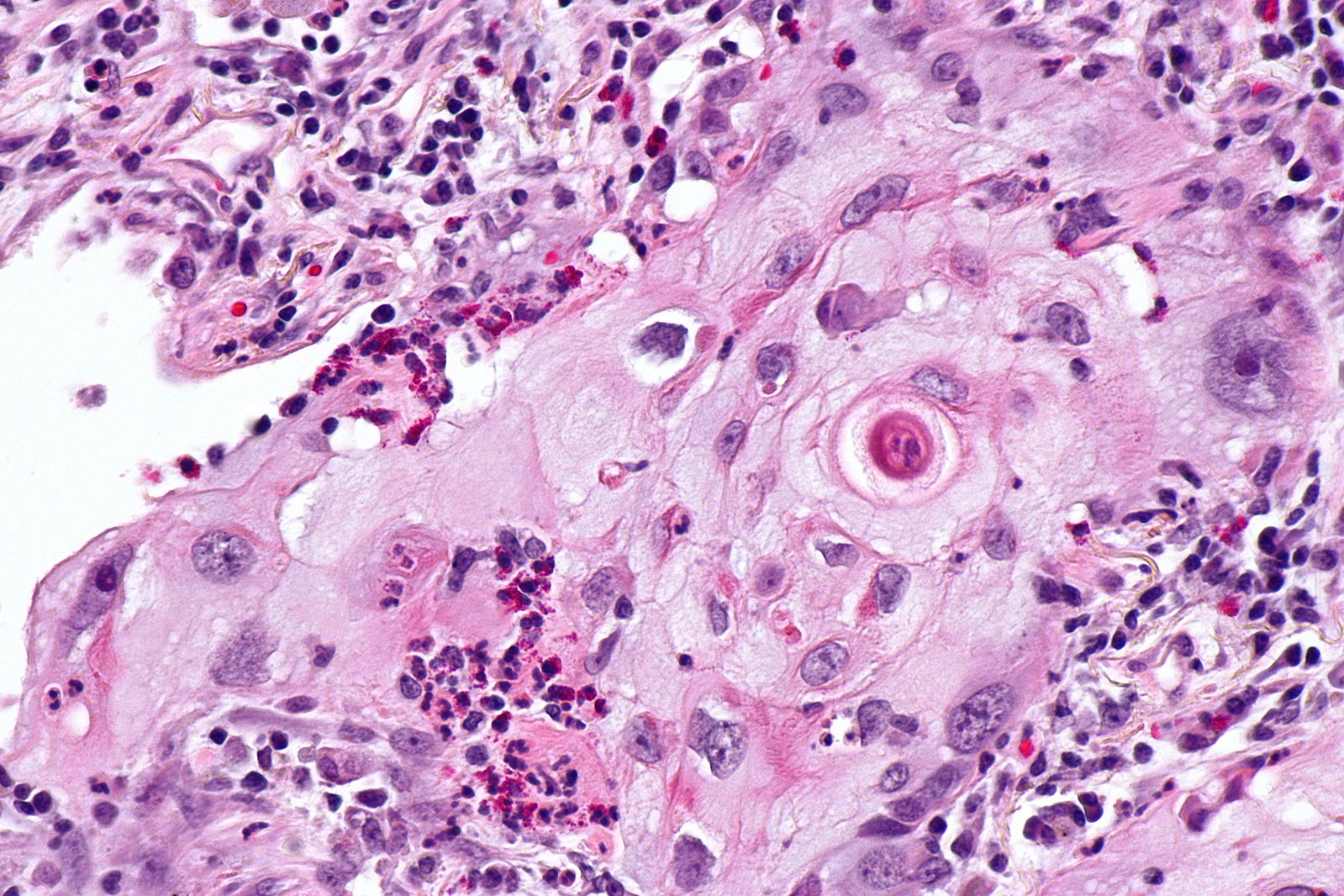
| | [[Image:Squamous cell mircopathology2.jpeg|x200px|thumb| Micropathology: Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. H&E stain, By Nephron [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ALung_squamous_carcinoma_--_high_mag.jpg Wikimedia Commons]]] |
| | |} |
| | {| align="right" |
| | | |
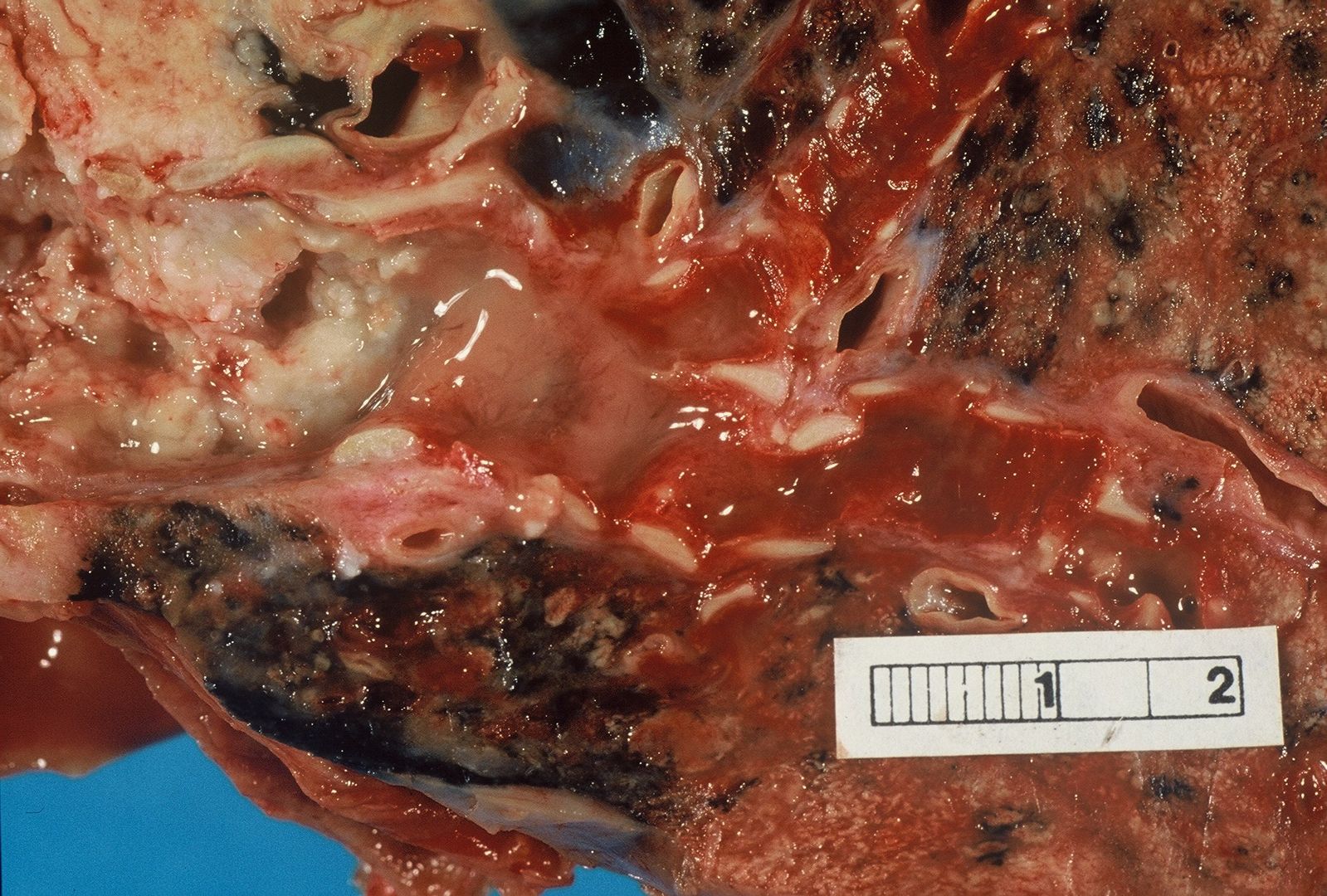
| | [[Image:Bronchial cancer.jpeg|x200px|thumb|Gross pathology: Bronchial squamous lung cell cancer By John Hayman [Public domain], (Image source: [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ACa_bronchus.jpg Wikimedia Commons])]] |
| | |} |
| | |
| | {| |
| | |
|
| |
|
| # [[Endometriosis|Bowel endometriosis]] vs [[Hemorrhoids]] vs [[Diverticular disease|Diverticular diseases]] vs [[Anal fissure]] vs [[Ulcerative colitis]] vs [[Crohn's disease]],
| |
| # [[Superior vena cava obstruction]] | | # [[Superior vena cava obstruction]] |
| # [[Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection]] | | # [[Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection]] |
| Line 29: |
Line 44: |
| # [[Dermoid cyst]] | | # [[Dermoid cyst]] |
| # [[Anthrax]]: | | # [[Anthrax]]: |
| # [[Tularemia]]. | | # [[Tularemia]] |
| | |
| | |
| | [[File:Mediastinal lymohangioma GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows cystic mass which was located on the posterior to the lower esophagus later diagnosed as thoracic duct lymphangioma. [https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2014.47.4.423 Source:Case courtesy of Jin San Bok et al, Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital]]] |
| | |
| | |
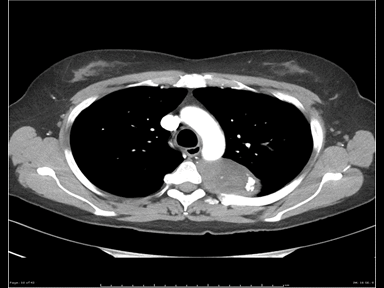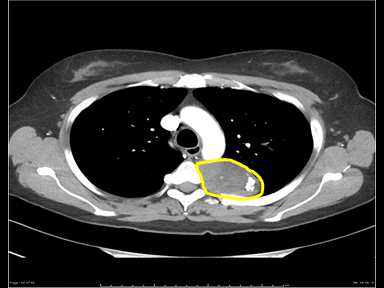
| | [[File:Posterior-mediastinal-schwannoma.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing a soft tissue density lesion within the left posterior mediastinum, in a paravertebral location. The lesion is closely related to the left neural exit foramen, but there is no definite extension into the spinal canal. The lesion does extend into the intercostal space. |
| | Case courtesy of Dr Paul Leong |
| | (Picture courtesy:[https://radiopaedia.org/cases/26625 Radiopedia])]] |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | {{SI}} |
| | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Trusha}}, {{AM}} |
|
| |
|
| {| | | {{SK}} Mediastinal enlargement; mass in the mediastinum |
| |- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;"
| | |
| !'''Class'''
| | ==Overview== |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Disease
| | |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Sign/Symptoms
| | The [[mediastinum]] is a non-delineated group of structures in the thorax (chest), surrounded by loose connective tissue. Since it is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity, and it contains a lot of important structures, it is the site of involvement of various tumors. |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Risk factors
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Gold standard
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Image
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Additional findings
| |
| |-
| |
| | colspan="7" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Anterior mediastinal mass'''
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Tumors
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Thymoma]]
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Facial swelling
| |
| * [[Dysphagia]]
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[wheezing]]
| |
| * [[Chest pain]]
| |
| * [[Muscle weakness]] ([[Myasthenia gravis|MG]])
| |
| * [[Anemia]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Human foamy virus]]
| |
| * [[Epstein-Barr virus]]
| |
| * Human T-cell lymphotropic virus
| |
| * [[MEN 1 syndrome]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Biopsy:
| |
| * Epithelial cells
| |
| * Immature lymphocytes
| |
| * Immature T cells
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |'''Associated condition'''
| |
| * NM
| |
| ** [[Myasthenia gravis]]
| |
| ** [[Neuromyotonia]]
| |
| ** [[Rippling muscle disease]]
| |
| ** [[Polymyositis and dermatomyositis|Polymyositis/dermatomyositis]]
| |
| ** [[Encephalitis]] (limbic, cortical and brain stem)
| |
| ** [[Intestinal pseudoobstruction]]
| |
| * Hematological
| |
| ** [[Anemia]]: [[pure red cell aplasia]], [[pernicious anemia]], [[hemolytic anemia]], [[aplastic anemia]]
| |
| ** Other isolated [[Cytopenia|cytopenias]]: [[eosinophils]], [[basophils]] [[neutrophils]]
| |
| ** Immunodeficiencies: [[Hypogammaglobulinaemia|hypogammaglobulinemia]]/- T-cell deficiencies [[Good syndrome|(Good syndrome)]]
| |
| * Dermatological
| |
| ** [[Pemphigus]] ([[Pemphigus foliaceus|foliaceus]] or [[Paraneoplastic syndrome|paraneoplastic]])
| |
| ** [[Lichen planus]]
| |
| ** [[Alopecia areata]]
| |
| * Endocrine
| |
| ** [[Addison's disease|Addison disease]]
| |
| ** [[Graves' disease|Grave's disease]]
| |
| ** [[Cushing's disease]]
| |
| * Hepato-renal
| |
| ** [[Glomerulonephritis]]
| |
| ** [[Autoimmune hepatitis]]
| |
| * Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
| |
| ** [[SLE]]
| |
| ** [[Sjögren's syndrome]]
| |
| ** [[Systemic sclerosis]]
| |
| ** [[Graft-versus-host disease]]
| |
|
| |
|
| |-
| | ==Causes== |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Fatty mass
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22021525">{{cite journal |vauthors=Molinari F, Bankier AA, Eisenberg RL |title=Fat-containing lesions in adult thoracic imaging |journal=AJR Am J Roentgenol |volume=197 |issue=5 |pages=W795–813 |date=November 2011 |pmid=22021525 |doi=10.2214/AJR.11.6932 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Mostly asymptomatic
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Steroid use
| |
| * Cushing's syndrome
| |
| * Obeses
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |MRI:
| |
| * Well-defined encapsulated mas
| |
| * Extensive fat content
| |
| * Small amounts of solid areas
| |
| * Fibrous septa
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Fatty mass can be:
| |
| * Lipoma
| |
| * Liposarcoma
| |
| * Thymolipoma
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]]
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26174528">{{cite journal| author=Sandlund JT| title=Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children. | journal=Curr Hematol Malig Rep | year= 2015 | volume= 10 | issue= 3 | pages= 237-43 | pmid=26174528 | doi=10.1007/s11899-015-0277-y | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=26174528 }}</ref><ref name="pmid28153383">{{cite journal| author=Armitage JO, Gascoyne RD, Lunning MA, Cavalli F| title=Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. | journal=Lancet | year= 2017 | volume= 390 | issue= 10091 | pages= 298-310 | pmid=28153383 | doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32407-2 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28153383 }}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Painless [[lymphadenopathy]]
| |
| * [[Fever]]
| |
| * [[Weight loss]] and [[Anorexia (symptom)|anorexia]]
| |
| * [[Night sweats]]
| |
| * Constant [[Fatigue (physical)|fatigue]]
| |
| * [[Pruritis|Itchy skin]]
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[Shortness of breath]]
| |
| * [[Abdominal pain]] or swelling
| |
| * [[Constipation]]
| |
| * [[Nausea]]
| |
| * [[Vomiting]]
| |
| * [[Headache]]
| |
| * Personality changes
| |
| * [[Seizures]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Age (above 60 years)
| |
| * Caucasians > African and Asian Americans
| |
| * Positive family history of first degree relative
| |
| * B-cell activating autoimmune disorders
| |
| * Radiation exposure
| |
| * Infections
| |
| (HIV, Hep C, HTLV-1, EBV, HHV-8, H. pylori, psittacosis, Campylobacter jejuni)
| |
| * Previous cancer treatment
| |
| * Exposure to chemicals and drugs
| |
| (pesticides, methotrexate, TNF inhibitors, trichloroethylene)
| |
| * Cigarette smoking for ≥ 40 years
| |
| * BMI ≥30 kg/m2
| |
| * Diet
| |
| * Hair dyes
| |
| * Breast implants
| |
|
| |
|
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Excisional lymph node biopsy with immunohistochemical study
| |
| * CD 20+ cells
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Anemia|Anemia:]]
| |
| **<nowiki/>[[Anemia|I]]<nowiki/>nvolvement of [[bone marrow]]
| |
| ** [[Autoimmune hemolytic anemia|A]]<nowiki/>[[Autoimmune hemolytic anemia|utoimmune hemolysis]] and bleeding.
| |
| * [[Thrombocytopenia]], [[leukopenia]], or [[pancytopenia]]
| |
| * [[Lymphocytosis]] with malignant cells
| |
| * [[Thrombocytosis]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Teratoma]]
| |
| <ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid24426558">{{cite journal |vauthors=Yalagachin GH |title=Anterior mediastinal teratoma- a case report with review of literature |journal=Indian J Surg |volume=75 |issue=Suppl 1 |pages=182–4 |date=June 2013 |pmid=24426558 |doi=10.1007/s12262-012-0569-6 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26251691">{{cite journal |vauthors=No TH, Seol SH, Seo GW, Kim DI, Yang SY, Jeong CH, Hwang YH, Kim JY |title=Benign Mature Teratoma in Anterior Mediastinum |journal=J Clin Med Res |volume=7 |issue=9 |pages=726–8 |date=September 2015 |pmid=26251691 |pmc=4522994 |doi=10.14740/jocmr2270w |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Benign
| |
| * Asymptomatic
| |
| Malignant
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[Dyspnea]]
| |
| * [[Chest pain]]
| |
| * [[Superior vena cava syndrome]]
| |
| * [[Trichoptysis]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Benign equal in men and women
| |
| * Malignant more common in men
| |
| * Pediatric population higher risk
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Chest CT scan:
| |
| * Location
| |
| * Metastasis
| |
| * Intrinsic structure
| |
| * Soft tissue
| |
| * Fat
| |
| * Calcification
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |N/A
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Thyroid disease
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Thyroid cancer]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Lump]] in the neck
| |
| * [[Dysphonia]]
| |
| * [[Dysphagia]]
| |
| * [[Dyspnea]]
| |
| * [[Lymphadenopathy]]
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[Sore throat]]
| |
| * [[Neck pain]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Hx of [[goiter]]
| |
| * Family Hx of thyroid disease
| |
| * Female gender
| |
| * Asian race
| |
| * [[Radiation exposure]]
| |
| * [[Multiple endocrine neoplasia|MEN syndrome]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |US guided biopsy:
| |
| * [[Papillary thyroid cancer]]
| |
| * [[Follicular thyroid cancer]]
| |
| * [[Medullary thyroid cancer]]
| |
| * [[Anaplastic thyroid cancer]]
| |
| * [[Primary thyroid lymphoma|Lymphoma]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |TFT
| |
| * Elevated T3
| |
| * Elevated T4
| |
| * Low TSH
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Goitre|Goiter]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * A visible swelling at the base of your neck
| |
| * Tight feeling in throat
| |
| * [[Cough]]
| |
| * [[Hoarseness]]
| |
| * [[Dysphagia]]
| |
| * [[Dyspnea]]
| |
| * [[Fatigue]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| ** [[Iodine]] deficiency
| |
| ** Female gender
| |
| ** Age over 50 years
| |
| ** Personal or family history
| |
| ** Certain medications
| |
| *** [[Immunosuppressant|Immunosuppressants]]
| |
| *** [[Antiretroviral|Antiretrovirals]]
| |
| *** [[Amiodarone]]
| |
| *** [[Lithium]]
| |
| ** [[Radiation]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Radioactive iodine scan:
| |
| * Nodules
| |
| * Size
| |
| * Function of the gland: ↑ or ↓
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Hyperavtive gland (hyperthyroid):
| |
| * Grave's disease
| |
| Hypoactive gland (hypothyroid):
| |
| * Hashimoto thyroiditis
| |
| Normal functioning gland (euthyroid):
| |
| * Benign thyroid enlargement (non toxic multinodular goiter)
| |
| |-
| |
| | colspan="7" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Middle mediastinal mass'''
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |CVS disease
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Pericardial effusion]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Aortic dissection]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Superior vena cava obstruction]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |GI disease
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Esophageal achalasia]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Esophageal cancer]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Esophageal rupture]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Hiatus hernia]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Pulmonary disease
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Hilar lymphadenopathy]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Pneumomediastinum]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Sarcoidosis]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Mediastinal tumor
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Mediastinal tumor]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Mediastinal germ cell tumor]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Infection
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Mediastinitis]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Anthrax]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Tularemia]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Cystic disease
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Dermoid cyst]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Bronchogenic cyst]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |Chronic
| |
| inflammatory
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Churg-Strauss syndrome]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | colspan="7" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Posterior mediastinal mass'''
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; padding: 5px;" |CNS disease
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Meningocele]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Neurilemmoma]]<ref name="pmid23225215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Juanpere S, Cañete N, Ortuño P, Martínez S, Sanchez G, Bernado L |title=A diagnostic approach to the mediastinal masses |journal=Insights Imaging |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=29–52 |date=February 2013 |pmid=23225215 |doi=10.1007/s13244-012-0201-0 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| |}
| |
|
| |
|
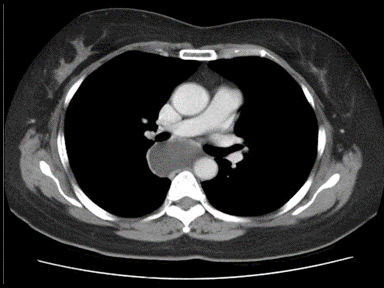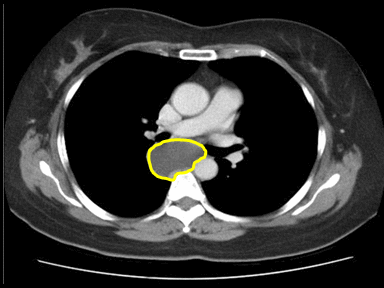
| [[File: Thymoma gif 2.gif|x300px|thumb| CT scan showing a smooth anterior mediastinal mass, with a mixed internal density of containing both enhancing soft tissue and cystic areas. The outline of the mass is relatively well defined. No lymphadenopathy, pleural effusion or infiltration. Case courtesy of Dr. Abdallah Al Khateeb
| |
| (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/43403 Radiopedia])]]
| |
|
| |
|
| | ==Initial Evaluation== |
| | {{familytree/start}} |
| | {{Family tree |border=2|boxstyle=background: WhiteSmoke;| | | | | A01 | | | | |A01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 25em; padding: 1em;">'''Mediastinal Mass'''</div>}} |
| | {{familytree | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | }} |
| | {{familytree | | | | | B01 | | | |B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; padding: 1em; "> '''Workups''' |
| | ---- |
| | ❑ CT chest with contrast <br> ❑ Serum beta-HCG, AFP, if appropriate <br> ❑ CBC, platelets <br> ❑ PET-CT scan (optional) <br> ❑ Pulmonary function tests if clinically indicated <br> ❑ MRI chest if clinically indicated |
| | </div>}} |
| | {{familytree | |,|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|.| | | | | | | }} |
| | {{familytree | C01 | | | | | | C02 | | | |C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em;"> '''Thymic Tumor Likely''' </div> |C02= <div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em;"> '''Thymic Tumor Unlikely''' </div>}} |
| | {{familytree | |!| | | | | | | |!| | | | | }} |
|
| |
|
| [[File: Lipomatosis gif.gif|x250px|thumb| CT scan showing excessive fatty tissue deposition within the posterior mediastinum with anterior displacement of the esophagus. Case courtesy of Dr. Ahmed Abdrabou (Picture courtesy: [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/50447Radiopedia])]]
| | {{familytree | D01 | | | | | | D02 | | | |D01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em; text-size: 85%;">Consider [[Thymoma surgery|surgery]]</div>|D02=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em; text-size: 85%;">Disease-specific management</div>}} |
|
| |
|
| | {{familytree/start}} |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| {{Reflist|2}} | | {{Reflist|2}} |