|
|
| (314 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
| {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Trusha}} | | {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Trusha}} |
|
| |
|
| # [[Endometriosis|Bowel endometriosis]] vs [[Hemorrhoids]] vs [[Diverticular disease|Diverticular diseases]] vs [[Anal fissure]] vs [[Ulcerative colitis]] vs [[Crohn's disease]]
| | ==new== |
| # Colorectal carcinoma ([[Adenocarcinoma]]) vs [[Peutz-Jeghers syndrome]] vs [[Juvenile polyposis syndrome|Juvenile Polyposis Coli]] vs [[Gastrointestinal stromal tumor|Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors]] vs [[Hamartoma]] vs [[MALT lymphoma|Colorectal Lymphoma]]
| | |
| # [[Strangulated hernia]] vs [[Appendicitis]] vs [[Crohn's disease]]
| | |
| # [[Irritable bowel syndrome]] vs [[Crohn's disease]] vs [[Ulcerative colitis]] vs [[Infectious colitis]] vs [[Carcinoid|Carcinoids]]
| | |
| | {| align="right" |
| | | |
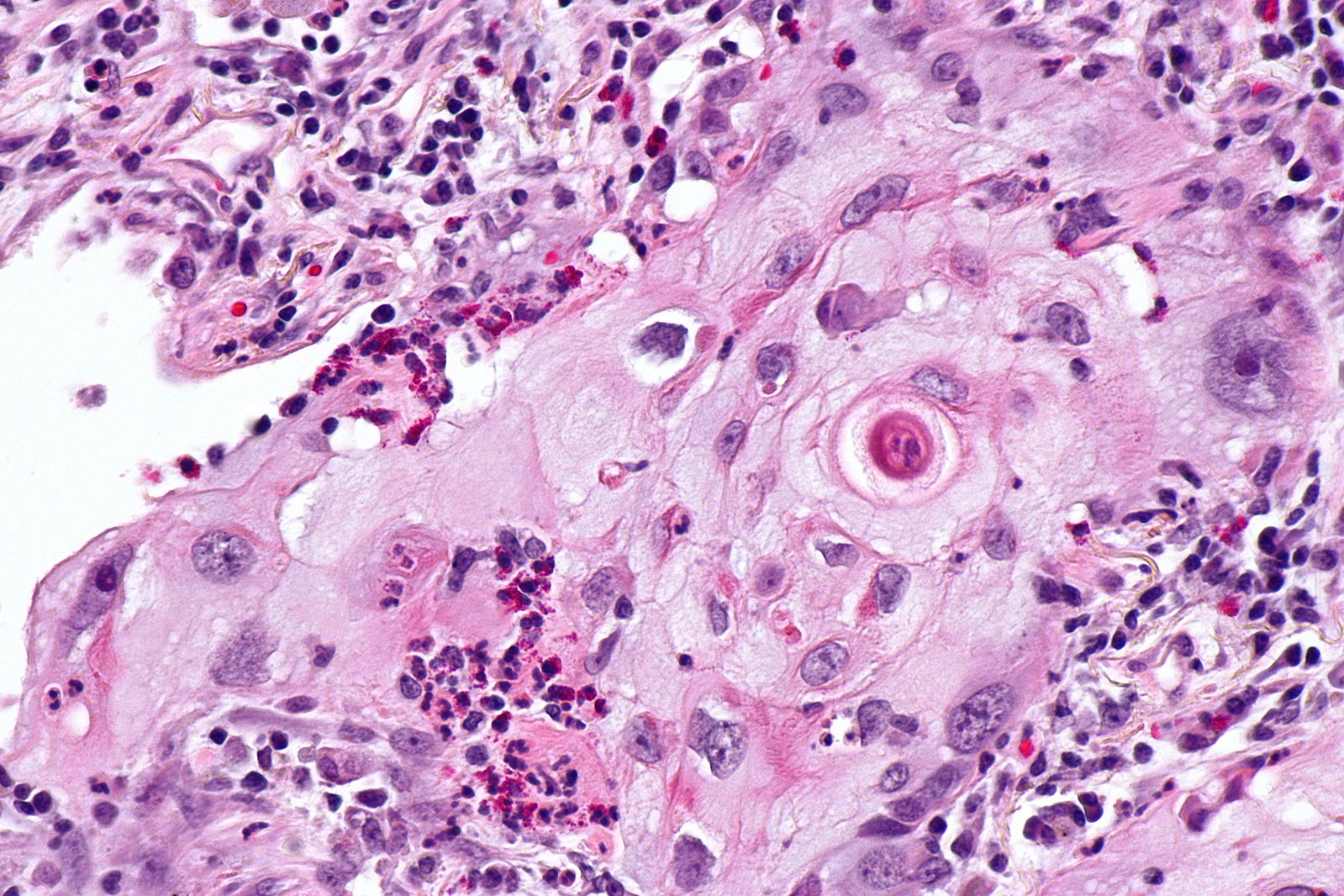
| | [[Image:Squamous cell mircopathology2.jpeg|x200px|thumb| Micropathology: Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. H&E stain, By Nephron [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ALung_squamous_carcinoma_--_high_mag.jpg Wikimedia Commons]]] |
| | |} |
| | {| align="right" |
| | | |
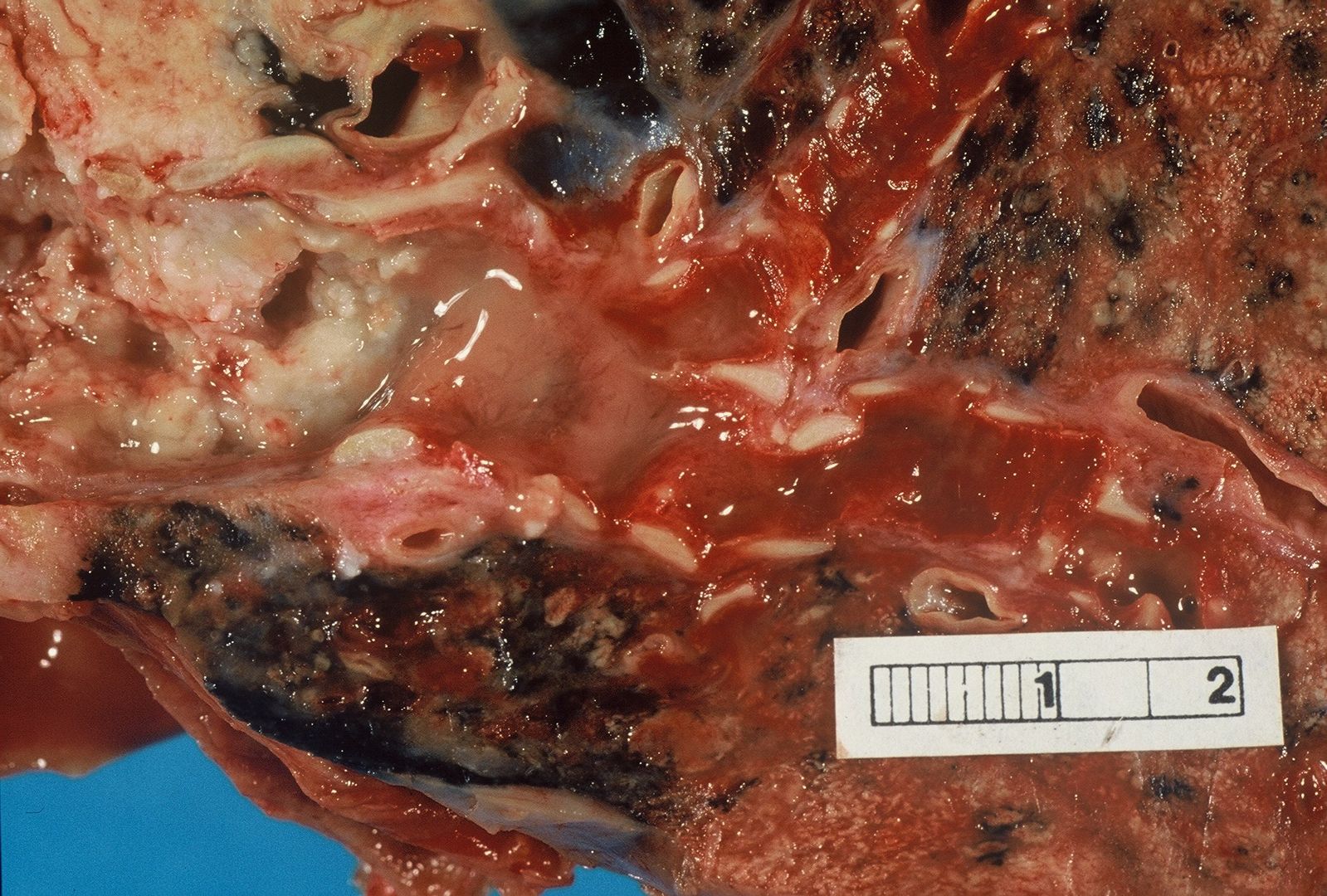
| | [[Image:Bronchial cancer.jpeg|x200px|thumb|Gross pathology: Bronchial squamous lung cell cancer By John Hayman [Public domain], (Image source: [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ACa_bronchus.jpg Wikimedia Commons])]] |
| | |} |
|
| |
|
| {| | | {| |
| |- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;"
| |
| ! rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Diseases
| |
| | colspan="6" rowspan="1" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Clinical manifestations'''
| |
| ! colspan="6" rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Para-clinical findings
| |
| | colspan="1" rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| ! rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Additional findings
| |
| |-
| |
| | colspan="4" rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Symptoms'''
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Physical exam
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Lab Findings
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Radiology
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Histopathology
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Productive cough
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Hemoptysis
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Weight loss
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Other
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Percussion
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Auscultation
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |CBC
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Sputum analysis
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Nodule
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Nodule content
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Other findings
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Pulmonary nodule|Pulmonary Nodule]](benign)
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Asymptomatic
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Hyporesonance
| |
| * Dull percussion
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Normal
| |
|
| |
|
| * Present [[pleural friction rub]]
| |
| * Present [[egophony]]
| |
| * Crackling or bubbling noises
| |
| * Present whispered pectoriloquy
| |
| * Decreased/absent [[breath sounds]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Normal
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Normal
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Single
| |
| * Round, oval
| |
| * <5 mm nodule
| |
| * Ground glass
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Fat in nodule
| |
|
| |
|
| Calcification
| | # [[Superior vena cava obstruction]] |
| * Central dense nidus
| | # [[Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection]] |
| * Diffuse solid
| | # [[Esophageal achalasia]] |
| * Laminated
| | # [[Esophageal cancer]] |
| * Popcorn
| | # [[Esophageal rupture]] |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| | # [[Hiatus hernia]] |
| * well-defined smooth border
| | # [[Hilar lymphadenopathy]] |
| * Growth rate over 18 months
| | # [[Pneumomediastinum]] |
| * Cavity wall thickness of 1 mm
| | # [[Sarcoidosis]] |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| | # [[Lymphoma]] |
| * N/A
| | # [[Neurilemmoma]] |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |N/A
| | # [[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |↓ O2 Sat
| | # [[Teratoma]] |
| |-
| | # [[Thymoma]] |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Pulmonary Nodule (malignant)
| | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | ++
| | # [[Thyroid cancer]] |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | ++
| | # [[Goitre]] |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | ++
| | # [[Mediastinal germ cell tumor]], |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| | # [[Mediastinal tumor]], |
| * [[Dyspnea]]
| | # [[Mediastinitis]] |
| * Non resolving [[pneumonia]]
| | |
| * [[Wheeze|Wheezing]]
| | # [[Churg-Strauss syndrome]] |
| * [[Chest pain]]
| | # [[Bronchogenic cyst]], |
| * [[Cachexia]]
| | # [[Dermoid cyst]] |
| * [[Fatigue]]
| | # [[Anthrax]]: |
| * [[Anorexia|Loss of appetite]]
| | # [[Tularemia]] |
| * [[Dysphonia]]
| | |
| * [[Dysphagia]]
| | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | [[File:Mediastinal lymohangioma GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows cystic mass which was located on the posterior to the lower esophagus later diagnosed as thoracic duct lymphangioma. [https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2014.47.4.423 Source:Case courtesy of Jin San Bok et al, Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital]]] |
| * Hyporesonance
| | |
| * Dull percussion
| | |
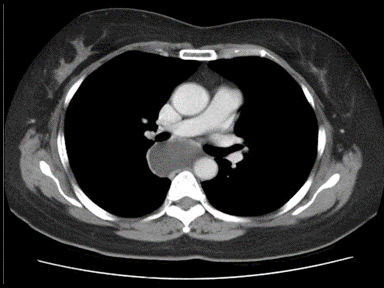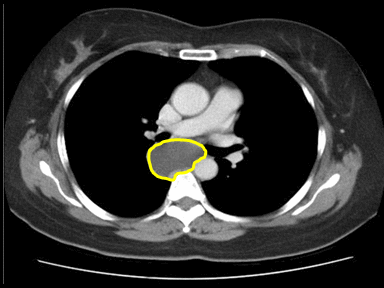
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | | [[File:Posterior-mediastinal-schwannoma.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing a soft tissue density lesion within the left posterior mediastinum, in a paravertebral location. The lesion is closely related to the left neural exit foramen, but there is no definite extension into the spinal canal. The lesion does extend into the intercostal space. |
| * Normal
| | Case courtesy of Dr Paul Leong |
| | (Picture courtesy:[https://radiopaedia.org/cases/26625 Radiopedia])]] |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | {{SI}} |
| | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Trusha}}, {{AM}} |
| | |
| | {{SK}} Mediastinal enlargement; mass in the mediastinum |
| | |
| | ==Overview== |
| | |
| | The [[mediastinum]] is a non-delineated group of structures in the thorax (chest), surrounded by loose connective tissue. Since it is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity, and it contains a lot of important structures, it is the site of involvement of various tumors. |
|
| |
|
| * Present [[pleural friction rub]]
| | ==Causes== |
| * Present [[egophony]]
| |
| * Crackling or bubbling noises
| |
| * Present whispered pectoriloquy
| |
| * Decreased/absent [[breath sounds]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Normal
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Tumor cells
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Multiple small
| |
| * Single > 2 cm of size
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Calcification
| |
| * Amorphous
| |
| * Punctate
| |
| * Reticular
| |
| * Stippled or eccentric
| |
| Cavity
| |
|
| |
|
| Ulceration
| |
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Spiculated border
| |
| * Rapid growth rate (Doubling time 1-18 months)
| |
| * Cavity wall thickness over 15 mm
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * central necrosis
| |
| * Cavity lined by viable cancer cells without necrosis
| |
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Biopsy and histopathological analysis
| |
| |↓ O2 Sat
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;"
| |
| !Diseases
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" |Productive cough
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" |Hemoptysis
| |
| !Weight loss
| |
| !Other symptoms
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" |Percussion
| |
| !Auscultation
| |
| !CBC
| |
| !Sputum analysis
| |
| !Nodule
| |
| !Content
| |
| !Other findings
| |
| !Histopathology
| |
| |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| !Additional findings
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Lung abscess|Abscess]]
| |
| <ref name="pmid26366400">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kuhajda I, Zarogoulidis K, Tsirgogianni K, Tsavlis D, Kioumis I, Kosmidis C, Tsakiridis K, Mpakas A, Zarogoulidis P, Zissimopoulos A, Baloukas D, Kuhajda D |title=Lung abscess-etiology, diagnostic and treatment options |journal=Ann Transl Med |volume=3 |issue=13 |pages=183 |date=August 2015 |pmid=26366400 |pmc=4543327 |doi=10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.07.08 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | ++
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * High [[fever]]
| |
| (> 101' F)
| |
| * [[Pleuritic chest pain|Pleuritic]] [[chest pain]]
| |
| * [[Sputum|Foul smelling sputum]]
| |
| * Night sweats
| |
| * Dyspnea
| |
| * Weight loss
| |
| * Fatigue
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Dull percussion
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Decreased [[Breath sounds|breath sound]]
| |
| * Bronchial [[Breath sounds|breath sound]]
| |
| * [[Crackles|Inspiratory crackles]]
| |
| * [[Crepitations|Localised crepitations]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Pronounced [[leukocytosis]]
| |
| * [[Anemia of chronic disease]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Causative agents
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Vary in size
| |
| * Round in shape
| |
|
| |
|
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Fluid/gas-fluid level
| |
| * Surrounding area consolidation
| |
| * [[Cavity]] persists longer than [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |.
| |
| * The wall of the [[abscess]] is typically thick and the [[luminal]] surface irregular
| |
| * Bronchial vessels and bronchi are truncated
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * In central parts of abscess there are necrotic tissue mixed with necrotic granulocytes and bacteria
| |
| * Neutrophillic granulocytes with dilated blood vessels and inflammatory oedema
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Histopathological analysis
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Clubbing of finger
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Septic pulmonary
| |
| emboli
| |
|
| |
|
| <ref name="pmid21686732">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chang E, Lee KH, Yang KY, Lee YC, Perng RP |title=Septic pulmonary embolism associated with a peri-proctal abscess in an immunocompetent host |journal=BMJ Case Rep |volume=2009 |issue= |pages= |date=2009 |pmid=21686732 |pmc=3029652 |doi=10.1136/bcr.07.2008.0592 |url=}}</ref>
| | ==Initial Evaluation== |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| | {{familytree/start}} |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| | {{Family tree |border=2|boxstyle=background: WhiteSmoke;| | | | | A01 | | | | |A01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 25em; padding: 1em;">'''Mediastinal Mass'''</div>}} |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | | {{familytree | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | }} |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| | {{familytree | | | | | B01 | | | |B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; padding: 1em; "> '''Workups''' |
| * High fever
| | ---- |
| * Dyspnea
| | ❑ CT chest with contrast <br> ❑ Serum beta-HCG, AFP, if appropriate <br> ❑ CBC, platelets <br> ❑ PET-CT scan (optional) <br> ❑ Pulmonary function tests if clinically indicated <br> ❑ MRI chest if clinically indicated |
| * Chest pain
| | </div>}} |
| * Focus of primary infection (Most common, right heart endocarditis)
| | {{familytree | |,|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|.| | | | | | | }} |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| | {{familytree | C01 | | | | | | C02 | | | |C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em;"> '''Thymic Tumor Likely''' </div> |C02= <div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em;"> '''Thymic Tumor Unlikely''' </div>}} |
| * N/A
| | {{familytree | |!| | | | | | | |!| | | | | }} |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |
| * [[S2|Prominent P2 component of second heart sound]]
| |
| * Decreased [[Breath sounds|breath sound]]
| |
| * [[Rales]]
| |
| * [[Crackles]]
| |
| * [[Pleural friction rub]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |
| * Pronounced neutrophilic[[leukocytosis]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |N/A | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |
| * Multiple peripheral nodules
| |
| * Size 0.5– 3.5 cm
| |
| * Variable shapes
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |
| * Central low attenuation
| |
| * Feeding vessels
| |
| * Pleura based wedge-shaped lesions
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * air bronchograms
| |
| * Abscess or infection related changes at the primary focus
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * N/A
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Culture and sensitivity | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |N/A
| |
| |- | |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Fungal | |
| infection
| |
|
| |
|
| <ref name="ChongLee2006">{{cite journal|last1=Chong|first1=Semin|last2=Lee|first2=Kyung Soo|last3=Yi|first3=Chin A|last4=Chung|first4=Myung Jin|last5=Kim|first5=Tae Sung|last6=Han|first6=Joungho|title=Pulmonary fungal infection: Imaging findings in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients|journal=European Journal of Radiology|volume=59|issue=3|year=2006|pages=371–383|issn=0720048X|doi=10.1016/j.ejrad.2006.04.017}}</ref>
| | {{familytree | D01 | | | | | | D02 | | | |D01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em; text-size: 85%;">Consider [[Thymoma surgery|surgery]]</div>|D02=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em; text-size: 85%;">Disease-specific management</div>}} |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |+/-
| | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |+
| | {{familytree/start}} |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |-
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |
| * Fever
| |
| * Dyspnea
| |
| * Chest pain
| |
| * Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions
| |
| * History of travel
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * N/A
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Decreased [[Breath sounds|breath sound]]
| |
| * Rales
| |
|
| |
|
| * [[Crackles]]
| |
| * [[Pleural friction rub]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Eosinophilia
| |
| * Neutropenia or leukopenia
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |KOH stain: Fungi
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Multiple nodules
| |
| * Size 0.5– 3 cm
| |
| * nodules surrounded by ground-glass opacity/halo
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Cavity
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Halo sign in aspergillosis
| |
| * Patchy infiltrate
| |
| * Consolidation
| |
| * Mediastinal adenopathy
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Specific causative agent
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Culture and sensitivity
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |N/A
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Parasites
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Mycobacterial infections
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Chronic inflammatory conditions
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;"
| |
| !Diseases
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" |Cough/Sputum
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" |Cough/Sputum
| |
| !Weight loss
| |
| !Other symptoms
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" |Percussion
| |
| !Auscultation
| |
| !CBC
| |
| !Sputum analysis
| |
| !Chest X-ray
| |
| !CT scan
| |
| !Other imaging
| |
| !Histopathology
| |
| |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| !Additional findings
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Pulmonary AVMs
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Pneumoconioses
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |}
| |
|
| |
|
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| {{Reflist|2}} | | {{Reflist|2}} |