|
|
| (347 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) |
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
| {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Trusha}} | | {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{Trusha}} |
|
| |
|
| == tab == | | ==new== |
|
| |
|
| {| class="wikitable"
| | |
| |- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;"
| | |
| ! rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Diseases
| | {| align="right" |
| | colspan="6" rowspan="1" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Clinical manifestations'''
| | | |
| ! colspan="7" rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Para-clinical findings
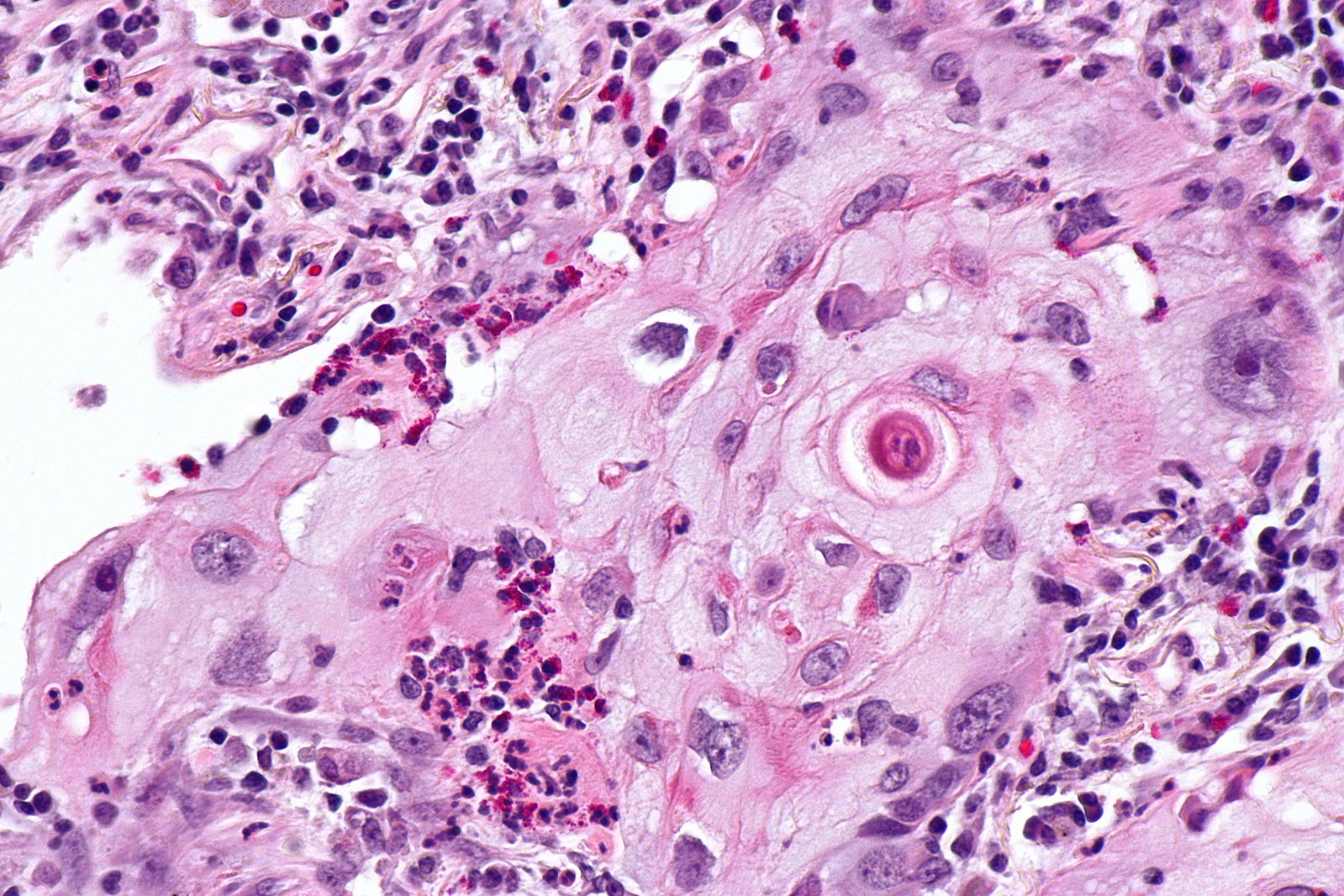
| | [[Image:Squamous cell mircopathology2.jpeg|x200px|thumb| Micropathology: Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. H&E stain, By Nephron [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ALung_squamous_carcinoma_--_high_mag.jpg Wikimedia Commons]]] |
| | colspan="1" rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| | |} |
| ! rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Comments
| | {| align="right" |
| |-
| | | |
| | colspan="6" rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Symptoms'''
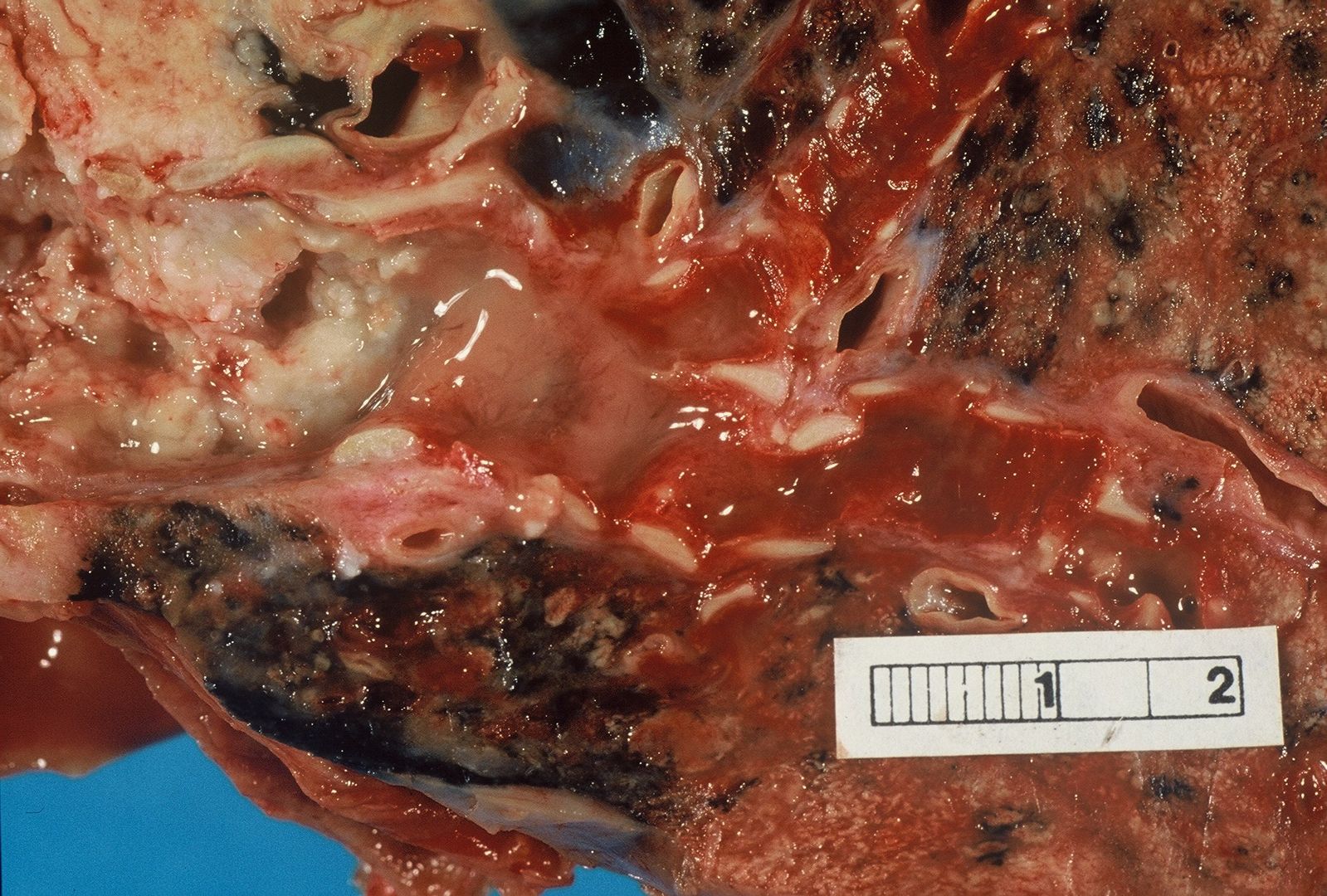
| | [[Image:Bronchial cancer.jpeg|x200px|thumb|Gross pathology: Bronchial squamous lung cell cancer By John Hayman [Public domain], (Image source: [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ACa_bronchus.jpg Wikimedia Commons])]] |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Lab Findings
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Imaging
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Histopathology
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Constipation/Diarrhea
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Blood in stool
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Other symptoms
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Anemia
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Tumor marker
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Endoscopy
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |CT scan
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Other diagnostic study
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Adenocarcinoma
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | colspan="3" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | colspan="2" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Arteriovenous malformation]]<ref name="pmid28139503">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lee HH, Kwon HM, Gil S, Kim YS, Cho M, Seo KJ, Chae HS, Cho YS |title=Endoscopic resection of asymptomatic, colonic, polypoid arteriovenous malformations: Two case reports and a literature review |journal=Saudi J Gastroenterol |volume=23 |issue=1 |pages=67–70 |date=2017 |pmid=28139503 |pmc=5329980 |doi=10.4103/1319-3767.199111 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | colspan="3" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | colspan="2" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Bright red, flat lesions
| |
| * Rarely, polypoid
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Aberrant vessels with thickened, hypertrophic walls in the mucosa and the submucosa.
| |
| * Arteries directly connected to veins without capillary beds
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Diverticulitis]]<ref name="pmid16187597">{{cite journal |vauthors=Shen SH, Chen JD, Tiu CM, Chou YH, Chiang JH, Chang CY, Lee CH |title=Differentiating colonic diverticulitis from colon cancer: the value of computed tomography in the emergency setting |journal=J Chin Med Assoc |volume=68 |issue=9 |pages=411–8 |date=September 2005 |pmid=16187597 |doi=10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70156-X |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Constipation]]/[[Diarrhea]]<ref name="ShenChen2005">{{cite journal|last1=Shen|first1=Shu-Huei|last2=Chen|first2=Jen-Dar|last3=Tiu|first3=Chui-Mei|last4=Chou|first4=Yi-Hong|last5=Chiang|first5=Jen-Huei|last6=Chang|first6=Cheng-Yen|last7=Lee|first7=Chen-Hsen|title=Differentiating Colonic Diverticulitis from Colon Cancer: The Value of Computed Tomography in the Emergency Setting|journal=Journal of the Chinese Medical Association|volume=68|issue=9|year=2005|pages=411–418|issn=17264901|doi=10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70156-X}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +/- | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | + | |
| | colspan="3" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Fever]], [[Rigor|chills]]<ref name="ShenChen2005">{{cite journal|last1=Shen|first1=Shu-Huei|last2=Chen|first2=Jen-Dar|last3=Tiu|first3=Chui-Mei|last4=Chou|first4=Yi-Hong|last5=Chiang|first5=Jen-Huei|last6=Chang|first6=Cheng-Yen|last7=Lee|first7=Chen-Hsen|title=Differentiating Colonic Diverticulitis from Colon Cancer: The Value of Computed Tomography in the Emergency Setting|journal=Journal of the Chinese Medical Association|volume=68|issue=9|year=2005|pages=411–418|issn=17264901|doi=10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70156-X}}</ref>
| |
| * [[Nausea and vomiting|Nausea/vomiting(N/V)]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | colspan="2" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Not recommended <ref name="ShenChen2005">{{cite journal|last1=Shen|first1=Shu-Huei|last2=Chen|first2=Jen-Dar|last3=Tiu|first3=Chui-Mei|last4=Chou|first4=Yi-Hong|last5=Chiang|first5=Jen-Huei|last6=Chang|first6=Cheng-Yen|last7=Lee|first7=Chen-Hsen|title=Differentiating Colonic Diverticulitis from Colon Cancer: The Value of Computed Tomography in the Emergency Setting|journal=Journal of the Chinese Medical Association|volume=68|issue=9|year=2005|pages=411–418|issn=17264901|doi=10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70156-X}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Outpouchings of the colonic wall (Diverticula)<ref name="ShenChen2005">{{cite journal|last1=Shen|first1=Shu-Huei|last2=Chen|first2=Jen-Dar|last3=Tiu|first3=Chui-Mei|last4=Chou|first4=Yi-Hong|last5=Chiang|first5=Jen-Huei|last6=Chang|first6=Cheng-Yen|last7=Lee|first7=Chen-Hsen|title=Differentiating Colonic Diverticulitis from Colon Cancer: The Value of Computed Tomography in the Emergency Setting|journal=Journal of the Chinese Medical Association|volume=68|issue=9|year=2005|pages=411–418|issn=17264901|doi=10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70156-X}}</ref>
| |
| * Inflamed diverticula
| |
| * Abscess formation
| |
| * Intraperitoneal free air (microperforation)
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Barium enema: Circumferential narrowing<ref name="SheimanLevine20082">{{cite journal|last1=Sheiman|first1=Laura|last2=Levine|first2=Marc S.|last3=Levin|first3=Alicia A.|last4=Hogan|first4=Jonathan|last5=Rubesin|first5=Stephen E.|last6=Furth|first6=Emma E.|last7=Laufer|first7=Igor|title=Chronic Diverticulitis: Clinical, Radiographic, and Pathologic Findings|journal=American Journal of Roentgenology|volume=191|issue=2|year=2008|pages=522–528|issn=0361-803X|doi=10.2214/AJR.07.3597}}</ref>
| |
| * Spiculated contour and tapered margins
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Hemorrhoids]]<ref name="JacobsSolomon2014">{{cite journal|last1=Jacobs|first1=Danny|last2=Solomon|first2=Caren G.|title=Hemorrhoids|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|volume=371|issue=10|year=2014|pages=944–951|issn=0028-4793|doi=10.1056/NEJMcp1204188}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Constipation]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | colspan="3" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Perianal Itching
| |
| * Pain with [[defecation]]
| |
| * Painfull, hard lump in anus
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | colspan="2" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Anoscopy]]: Protruding mass from the [[anus]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * DRE: Palpable mass, tender if thrombosed
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Anal fissure]]<ref name="pmid27041801">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schlichtemeier S, Engel A |title=Anal fissure |journal=Aust Prescr |volume=39 |issue=1 |pages=14–7 |year=2016 |pmid=27041801 |pmc=4816871 |doi=10.18773/austprescr.2016.007 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Constipation]]/[[diarrhea]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | colspan="3" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Pain with [[defecation]]
| |
| * [[Itching]]
| |
| * [[Irritation]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +/-
| |
| | colspan="2" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Anoscopy]]: Anal wall laceration
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Infectious colitis]]<ref name="pmid22080825">{{cite journal |vauthors=DuPont HL |title=Approach to the patient with infectious colitis |journal=Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. |volume=28 |issue=1 |pages=39–46 |date=January 2012 |pmid=22080825 |doi=10.1097/MOG.0b013e32834d3208 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Diarrhea]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | colspan="3" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Fever]], [[Rigor|chills]]
| |
| * [[Nausea and vomiting|N/V]]
| |
| * [[Bloating]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | colspan="2" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Patchy or diffuse [[Erythematous|erythematous mucosa]]
| |
| * Edema, [[hemorrhage]], with or without [[ulcers]] of mucosa
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * [[Stool culture|Stool cultures]] in adequate [[culture media]]
| |
| * Stool analysis: Leukocytosis
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Peutz-Jeghers syndrome<ref name="pmid27298573">{{cite journal |vauthors=Zhong ME, Niu BZ, Ji WY, Wu B |title=Laparoscopic restorative proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis for Peutz-Jeghers syndrome with synchronous rectal cancer |journal=World J. Gastroenterol. |volume=22 |issue=22 |pages=5293–6 |date=June 2016 |pmid=27298573 |doi=10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5293 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| |- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;"
| |
| ! rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Diseases
| |
| | colspan="6" rowspan="1" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Clinical manifestations'''
| |
| ! colspan="7" rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Para-clinical findings
| |
| | colspan="1" rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| ! rowspan="4" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Comments
| |
| |-
| |
| | colspan="6" rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |'''Symptoms'''
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Lab Findings
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Imaging
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Histopathology
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Constipation/Diarrhea
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Blood in stool
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Other symptoms
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Anemia
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Tumor marker
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Colonoscopy
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |CT scan
| |
| ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Other diagnostic study
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Carcinoids<ref name="pmid20011309">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chung TP, Hunt SR |title=Carcinoid and neuroendocrine tumors of the colon and rectum |journal=Clin Colon Rectal Surg |volume=19 |issue=2 |pages=45–8 |date=May 2006 |pmid=20011309 |pmc=2780103 |doi=10.1055/s-2006-942343 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Juvenile Polyposis Coli
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST)<ref name="pmid24778074">{{cite journal |vauthors=Niazi AK, Kaley K, Saif MW |title=Gastrointestinal stromal tumor of colon: a case report and review of literature |journal=Anticancer Res. |volume=34 |issue=5 |pages=2547–50 |date=May 2014 |pmid=24778074 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Hamartoms
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Colorectal Lymphoma<ref name="pmid20011310">{{cite journal |vauthors=Quayle FJ, Lowney JK |title=Colorectal lymphoma |journal=Clin Colon Rectal Surg |volume=19 |issue=2 |pages=49–53 |date=May 2006 |pmid=20011310 |pmc=2780105 |doi=10.1055/s-2006-942344 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Kaposi's sarcoma
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Ulcerative colitis]]<ref name="pmid25075198">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fakhoury M, Negrulj R, Mooranian A, Al-Salami H |title=Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments |journal=J Inflamm Res |volume=7 |issue= |pages=113–20 |date=2014 |pmid=25075198 |pmc=4106026 |doi=10.2147/JIR.S65979 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Diarrhea]] | |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |<big>+</big>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |LLQ<ref name="pmid25075198">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fakhoury M, Negrulj R, Mooranian A, Al-Salami H |title=Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments |journal=J Inflamm Res |volume=7 |issue= |pages=113–20 |date=2014 |pmid=25075198 |pmc=4106026 |doi=10.2147/JIR.S65979 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | colspan="3" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | colspan="2" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Continuous lesions<ref name="pmid25075198">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fakhoury M, Negrulj R, Mooranian A, Al-Salami H |title=Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments |journal=J Inflamm Res |volume=7 |issue= |pages=113–20 |date=2014 |pmid=25075198 |pmc=4106026 |doi=10.2147/JIR.S65979 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| * [[Erythema]] (or redness of the [[mucosa]]) and friability of the [[mucosa]]
| |
| * Crypts, formation of residual mucosal tissue
| |
| * [[Polyp (medicine)|Pseudopolyps]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Mucosal and submucosal inflammation<ref name="pmid25075198">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fakhoury M, Negrulj R, Mooranian A, Al-Salami H |title=Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments |journal=J Inflamm Res |volume=7 |issue= |pages=113–20 |date=2014 |pmid=25075198 |pmc=4106026 |doi=10.2147/JIR.S65979 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| * Hemorrhage or inflammatory polymorphonuclear cells aggregate in the lamina propria
| |
| * Distorted crypts
| |
| * Crypt abscess
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Endoscopy and a mucosal biopsy<ref name="pmid16902215" />
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Crohn's disease]]<ref name="pmid25075198">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fakhoury M, Negrulj R, Mooranian A, Al-Salami H |title=Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments |journal=J Inflamm Res |volume=7 |issue= |pages=113–20 |date=2014 |pmid=25075198 |pmc=4106026 |doi=10.2147/JIR.S65979 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Diarrhea]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |LRQ<ref name="pmid25075198">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fakhoury M, Negrulj R, Mooranian A, Al-Salami H |title=Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments |journal=J Inflamm Res |volume=7 |issue= |pages=113–20 |date=2014 |pmid=25075198 |pmc=4106026 |doi=10.2147/JIR.S65979 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | colspan="3" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Tenesmus
| |
| *
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | +
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Discontinuous lesions
| |
| * Strictures
| |
| * Linear ulcerations<ref name="pmid25075198">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fakhoury M, Negrulj R, Mooranian A, Al-Salami H |title=Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments |journal=J Inflamm Res |volume=7 |issue= |pages=113–20 |date=2014 |pmid=25075198 |pmc=4106026 |doi=10.2147/JIR.S65979 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Transmural pattern of inflammation<ref name="pmid25075198">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fakhoury M, Negrulj R, Mooranian A, Al-Salami H |title=Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and treatments |journal=J Inflamm Res |volume=7 |issue= |pages=113–20 |date=2014 |pmid=25075198 |pmc=4106026 |doi=10.2147/JIR.S65979 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| * Mucosal damage
| |
| * Focal infiltration of leukocytes into the epithelium
| |
| * Granulomas
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Endoscopy and a mucosal biopsy<ref name="pmid16902215">{{cite journal |vauthors=Collins P, Rhodes J |title=Ulcerative colitis: diagnosis and management |journal=BMJ |volume=333 |issue=7563 |pages=340–3 |date=August 2006 |pmid=16902215 |pmc=1539087 |doi=10.1136/bmj.333.7563.340 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Irritable bowel syndrome
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |[[Constipation]] and [[diarrhea]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |+
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | colspan="3" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Straining during [[defecation]]
| |
| * [[Urgency]]
| |
| * Sensation of incomplete evacuation
| |
| * [[Mucus]] passage
| |
| * [[Bloating]]
| |
| * Weight loss
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |-
| |
| | colspan="2" style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | -
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |Nor recommended
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |-
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| * Diagnosis of exclusion with fulfilment of [[Irritable bowel syndrome diagnostic criteria|Rome criteria]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Appendicitis]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| |- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;"
| |
| !Diseases
| |
| !Symptom 1
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" |Symptom 2
| |
| !Symptom 3
| |
| !Physical exam 1
| |
| ! colspan="1" rowspan="1" |Physical exam 2
| |
| !Physical exam 3
| |
| !Lab 1
| |
| !Lab 2
| |
| !Lab 3
| |
| !Imaging 1
| |
| !Imaging 2
| |
| !Imaging 3
| |
| !Histopathology
| |
| |'''Gold standard'''
| |
| !Additional findings
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Strangulated hernia]]
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Prostate Cancer
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |Bowel endometriosis
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| | style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |
| |
| |} | | |} |
| | |
| | {| |
| | |
| | |
| | # [[Superior vena cava obstruction]] |
| | # [[Partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection]] |
| | # [[Esophageal achalasia]] |
| | # [[Esophageal cancer]] |
| | # [[Esophageal rupture]] |
| | # [[Hiatus hernia]] |
| | # [[Hilar lymphadenopathy]] |
| | # [[Pneumomediastinum]] |
| | # [[Sarcoidosis]] |
| | # [[Lymphoma]] |
| | # [[Neurilemmoma]] |
| | # [[Non-Hodgkin lymphoma]] |
| | # [[Teratoma]] |
| | # [[Thymoma]] |
| | |
| | # [[Thyroid cancer]] |
| | # [[Goitre]] |
| | # [[Mediastinal germ cell tumor]], |
| | # [[Mediastinal tumor]], |
| | # [[Mediastinitis]] |
| | |
| | # [[Churg-Strauss syndrome]] |
| | # [[Bronchogenic cyst]], |
| | # [[Dermoid cyst]] |
| | # [[Anthrax]]: |
| | # [[Tularemia]] |
| | |
| | |
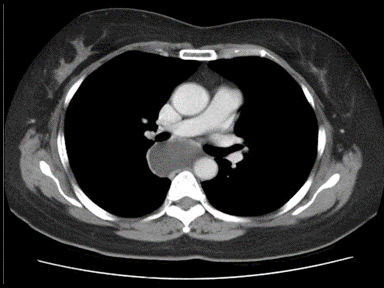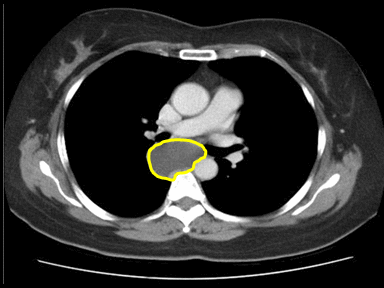
| | [[File:Mediastinal lymohangioma GIF.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan shows cystic mass which was located on the posterior to the lower esophagus later diagnosed as thoracic duct lymphangioma. [https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2014.47.4.423 Source:Case courtesy of Jin San Bok et al, Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital]]] |
| | |
| | |
| | [[File:Posterior-mediastinal-schwannoma.gif|x200px|thumb| CT scan showing a soft tissue density lesion within the left posterior mediastinum, in a paravertebral location. The lesion is closely related to the left neural exit foramen, but there is no definite extension into the spinal canal. The lesion does extend into the intercostal space. |
| | Case courtesy of Dr Paul Leong |
| | (Picture courtesy:[https://radiopaedia.org/cases/26625 Radiopedia])]] |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | {{SI}} |
| | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Trusha}}, {{AM}} |
| | |
| | {{SK}} Mediastinal enlargement; mass in the mediastinum |
| | |
| | ==Overview== |
| | |
| | The [[mediastinum]] is a non-delineated group of structures in the thorax (chest), surrounded by loose connective tissue. Since it is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity, and it contains a lot of important structures, it is the site of involvement of various tumors. |
| | |
| | ==Causes== |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | ==Initial Evaluation== |
| | {{familytree/start}} |
| | {{Family tree |border=2|boxstyle=background: WhiteSmoke;| | | | | A01 | | | | |A01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 25em; padding: 1em;">'''Mediastinal Mass'''</div>}} |
| | {{familytree | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | }} |
| | {{familytree | | | | | B01 | | | |B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; padding: 1em; "> '''Workups''' |
| | ---- |
| | ❑ CT chest with contrast <br> ❑ Serum beta-HCG, AFP, if appropriate <br> ❑ CBC, platelets <br> ❑ PET-CT scan (optional) <br> ❑ Pulmonary function tests if clinically indicated <br> ❑ MRI chest if clinically indicated |
| | </div>}} |
| | {{familytree | |,|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|.| | | | | | | }} |
| | {{familytree | C01 | | | | | | C02 | | | |C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em;"> '''Thymic Tumor Likely''' </div> |C02= <div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em;"> '''Thymic Tumor Unlikely''' </div>}} |
| | {{familytree | |!| | | | | | | |!| | | | | }} |
| | |
| | {{familytree | D01 | | | | | | D02 | | | |D01=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em; text-size: 85%;">Consider [[Thymoma surgery|surgery]]</div>|D02=<div style="float: left; text-align: center; height: 1.25em; width: 15em; padding: 1em; text-size: 85%;">Disease-specific management</div>}} |
| | |
| | {{familytree/start}} |
| | |
|
| |
|
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| {{Reflist|2}} | | {{Reflist|2}} |