Sideroblastic anemia diagnostic study of choice: Difference between revisions
Nazia Fuad (talk | contribs) |
Shyam Patel (talk | contribs) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Sideroblastic anemia}} | {{Sideroblastic anemia}} | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} | {{CMG}} {{shyam}}; {{AE}} {{N.F}} | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
[[Bone marrow]] aspiration and [[biopsy]] is the gold standard test for the diagnosis of sideroblastic anemia. Light [[microscopy]], [[Prussian blue]] staining and [[electron microscopy]] are performed on [[bone marrow]] [[biopsy]] samples. The [[bone marrow]] aspirate will show [[erythroid hyperplasia]] and pale red blood cell precursors. Prussian blue staining of [[bone marrow]] aspirate reveals [[iron]]-positive granules surrounding the [[nucleus]] of the [[erythroblast]] in ring form. | |||
== Diagnostic Study of Choice == | == Diagnostic Study of Choice == | ||
* Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy is the gold standard test for the diagnosis of sideroblastic anemia. | * [[Bone marrow]] aspiration and [[biopsy]] is the gold standard test for the diagnosis of sideroblastic anemia.<ref name="pmid25064706">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bottomley SS, Fleming MD |title=Sideroblastic anemia: diagnosis and management |journal=Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. |volume=28 |issue=4 |pages=653–70, v |date=August 2014 |pmid=25064706 |doi=10.1016/j.hoc.2014.04.008 |url=}}</ref> | ||
* Light microscopy, | * Light microscopy, Prussian blue staining and electron microscopy are performed on [[bone marrow]] [[biopsy]] samples. | ||
=== Diagnostic results === | === Diagnostic results === | ||
The following finding on performing the bone marrow biopsy is confirmatory for sideroblastic anemia. | The following finding on performing the [[bone marrow]] [[biopsy]] is confirmatory for sideroblastic anemia. | ||
===== Bone marrow aspirate smear ===== | ===== Bone marrow aspirate smear ===== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
* Normoblastic erythroid hyperplasia | * Normoblastic erythroid hyperplasia | ||
* RBC precursors with pale cytoplasm | * RBC precursors with pale [[cytoplasm]] | ||
* Dysplastc changes ( in MDS disorders) | * [[Dysplasia|Dysplastc]] changes (in MDS disorders) | ||
==== Prussian blue staining ==== | ==== Prussian blue staining ==== | ||
Prussian blue staining of [[bone marrow]] aspirate reveals: | |||
* Red cell precursors with numerous iron- positive granules surrounding the nucleus | * [[Red cell precursors]] with numerous [[iron]]-positive granules surrounding the [[nucleus]]. | ||
* In most | * In most cases these [[iron]] deposits form a complete ring around the [[nucleus]]. | ||
==== Electron microscopy ==== | ==== Electron microscopy ==== | ||
* The electron microscopy of an | * The electron microscopy of an [[erythroblast]] shows [[iron]] laden [[mitochondria]]<ref name="pmid10233378">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bessho F, Ohnishi H, Tabuchi K, Kobayashi M, Hayashi Y |title=Significance of electron-dense deposits in the mitochondrial matrix of erythroid precursors in aplastic anaemia and myelodysplastic syndrome |journal=Br. J. Haematol. |volume=105 |issue=1 |pages=149–54 |date=April 1999 |pmid=10233378 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
[ | |||
* Insoluble [[iron]] complexes are clustered around [[Mitochondrion|mitochondria]] nucleus | |||
' | =====Sequence of Diagnostic Studies===== | ||
** [[CBC]] | |||
** [[Reticulocyte count]] | |||
** [[Peripheral blood smear]] | |||
** [[Iron studies]] ([[serum iron]], [[serum ferritin]], [[and transferrin saturation]]) | |||
** [[Bone marrow]] examination | |||
** [[Genetic testing]] | |||
*** [[Genetic testing]] is well considered in all patients with [[congenital]] sideroblastic anemias | |||
*** A [[gene]] (or genes) is selected for analysis that is consistent with the patient's [[phenotype]] | |||
*** Genetic testing is the most determining way to establish the exact diagnosis and to identify the [[mutation]] | |||
*** [[Genetic testing]] is done by DNA sequence analysis | |||
*** The [[leukocytes]] are taken from peripheral blood | |||
*** This testing is useful for management, [[genetic counseling]] and testing of first-degree relatives | |||
Sideroblastic anemia may be diagnosed at any time if one or more of the following criteria are met: | |||
* Microcytic hypochromic anemia | |||
* Ring sideroblasts | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:23, 19 December 2018
|
Sideroblastic anemia Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Sideroblastic anemia diagnostic study of choice On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Sideroblastic anemia diagnostic study of choice |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Sideroblastic anemia diagnostic study of choice |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Shyam Patel [2]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Nazia Fuad M.D.
Overview
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy is the gold standard test for the diagnosis of sideroblastic anemia. Light microscopy, Prussian blue staining and electron microscopy are performed on bone marrow biopsy samples. The bone marrow aspirate will show erythroid hyperplasia and pale red blood cell precursors. Prussian blue staining of bone marrow aspirate reveals iron-positive granules surrounding the nucleus of the erythroblast in ring form.
Diagnostic Study of Choice
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy is the gold standard test for the diagnosis of sideroblastic anemia.[1]
- Light microscopy, Prussian blue staining and electron microscopy are performed on bone marrow biopsy samples.
Diagnostic results
The following finding on performing the bone marrow biopsy is confirmatory for sideroblastic anemia.
Bone marrow aspirate smear
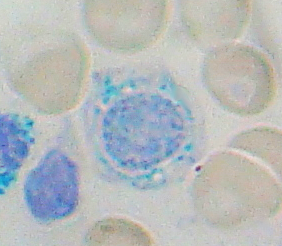 |
- Normoblastic erythroid hyperplasia
- RBC precursors with pale cytoplasm
- Dysplastc changes (in MDS disorders)
Prussian blue staining
Prussian blue staining of bone marrow aspirate reveals:
- Red cell precursors with numerous iron-positive granules surrounding the nucleus.
- In most cases these iron deposits form a complete ring around the nucleus.
Electron microscopy
- The electron microscopy of an erythroblast shows iron laden mitochondria[2]
- Insoluble iron complexes are clustered around mitochondria nucleus
Sequence of Diagnostic Studies
- CBC
- Reticulocyte count
- Peripheral blood smear
- Iron studies (serum iron, serum ferritin, and transferrin saturation)
- Bone marrow examination
- Genetic testing
- Genetic testing is well considered in all patients with congenital sideroblastic anemias
- A gene (or genes) is selected for analysis that is consistent with the patient's phenotype
- Genetic testing is the most determining way to establish the exact diagnosis and to identify the mutation
- Genetic testing is done by DNA sequence analysis
- The leukocytes are taken from peripheral blood
- This testing is useful for management, genetic counseling and testing of first-degree relatives
Sideroblastic anemia may be diagnosed at any time if one or more of the following criteria are met:
- Microcytic hypochromic anemia
- Ring sideroblasts
References
- ↑ Bottomley SS, Fleming MD (August 2014). "Sideroblastic anemia: diagnosis and management". Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 28 (4): 653–70, v. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2014.04.008. PMID 25064706.
- ↑ Bessho F, Ohnishi H, Tabuchi K, Kobayashi M, Hayashi Y (April 1999). "Significance of electron-dense deposits in the mitochondrial matrix of erythroid precursors in aplastic anaemia and myelodysplastic syndrome". Br. J. Haematol. 105 (1): 149–54. PMID 10233378.