Orbicularis oculi muscle
The orbicularis oculi is a muscle in the face that closes the eyelids. It arises from the nasal part of the frontal bone, from the frontal process of the maxilla in front of the lacrimal groove, and from the anterior surface and borders of a short fibrous band, the medial palpebral ligament.
From this origin, the fibers are directed lateralward, forming a broad and thin layer, which occupies the eyelids or palpebræ, surrounds the circumference of the orbit, and spreads over the temple, and downward on the cheek.
The palpebral portion of the muscle is thin and pale; it arises from the bifurcation of the medial palpebral ligament, forms a series of concentric curves, and is inserted into the lateral palpebral raphé.
The orbital portion is thicker and of a reddish color; its fibers form a complete ellipse without interruption at the lateral palpebral commissure; the upper fibers of this portion blend with the Frontalis and Corrugator.
The lacrimal part (Tensor tarsi) is a small, thin muscle, about 6 mm. in breadth and 12 mm. in length, situated behind the medial palpebral ligament and lacrimal sac.
It arises from the posterior crest and adjacent part of the orbital surface of the lacrimal bone, and passing behind the lacrimal sac, divides into two slips, upper and lower, which are inserted into the superior and inferior tarsi medial to the puncta lacrimalia; occasionally it is very indistinct.
Actions
The muscle acts to close the eye and is the only muscle capable of doing so. Loss of function for any reason results in an inability to close the eye, necessitating eye drops at the minimum to removal of the eye in extreme cases.
The Orbicularis oculi is the sphincter muscle of the eyelids.
The palpebral portion acts involuntarily, closing the lids gently, as in sleep or in blinking; the orbital portion is subject to the will.
When the entire muscle is brought into action, the skin of the forehead, temple, and cheek is drawn toward the medial angle of the orbit, and the eyelids are firmly closed, as in photophobia.
The skin thus drawn upon is thrown into folds, especially radiating from the lateral angle of the eyelids; these folds become permanent in old age, and form the so-called “crow's feet.”
The Levator palpebræ superioris is the direct antagonist of this muscle; it raises the upper eyelid and exposes the front of the bulb of the eye.
Each time the eyelids are closed through the action of the Orbicularis, the medial palpebral ligament is tightened, the wall of the lacrimal sac is thus drawn lateralward and forward, so that a vacuum is made in it and the tears are sucked along the lacrimal canals into it.
The lacrimal part of the Orbicularis oculi draws the eyelids and the ends of the lacrimal canals medialward and compresses them against the surface of the globe of the eye, thus placing them in the most favorable situation for receiving the tears; it also compresses the lacrimal sac.
Additional images
-
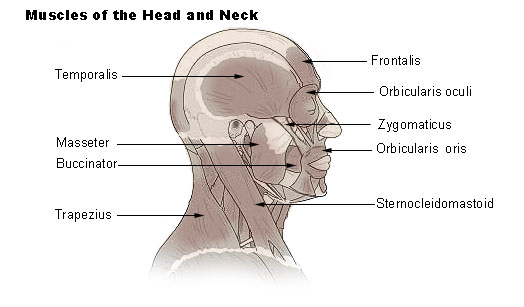
Muscles of head and neck
-
Frontal bone. Outer surface.
-
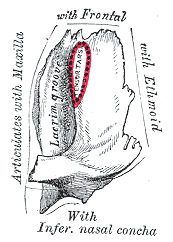
Left lacrimal bone. Orbital surface. Enlarged
-
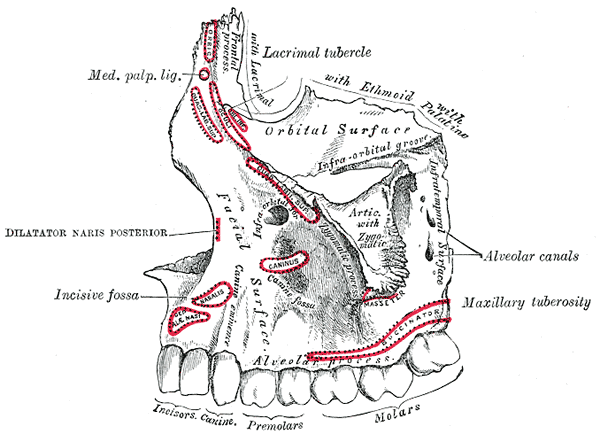
Left maxilla. Outer surface.
-
The arteries of the face and scalp.
-
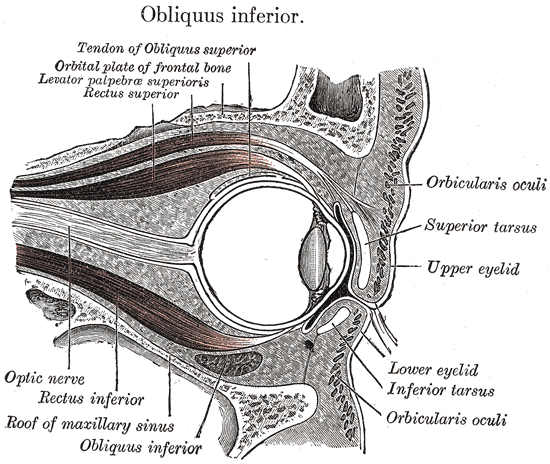
Sagittal section of right orbital cavity.
-
Sagittal section through the upper eyelid.
External links
Template:Gray's Template:Muscles of head
de:Musculus orbicularis oculi it:Muscolo orbicolare dell'occhio hu:Szem körüli izom