Lovaza
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Lovaza is a combination of ethyl esters of omega 3 fatty acids, principally EPA and DHA that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of hypertriglyceridemia. Common adverse reactions include eructation, dyspepsia, and taste perversion.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Hypertriglyceridemia
- LOVAZA® (omega-3-acid ethyl esters) is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce triglyceride (TG) levels in adult patients with severe (≥500 mg/dL) hypertriglyceridemia (HTG).
- Dosing Information
- Assess triglyceride levels carefully before initiating therapy. Identify other causes (e.g., diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, medications) of high triglyceride levels and manage as appropriate.
- Patients should be placed on an appropriate lipid-lowering diet before receiving LOVAZA, and should continue this diet during treatment with LOVAZA. In clinical studies, LOVAZA was administered with meals.
- The daily dose of LOVAZA is 4 grams per day. The daily dose may be taken as a single 4-gram dose (4 capsules) or as two 2-gram doses (2 capsules given twice daily).
- Patients should be advised to swallow LOVAZA capsules whole. Do not break open, crush, dissolve, or chew LOVAZA.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Lovaza in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Coronary arteriosclerosis - Hypertriglyceridemia
- Dosing Information
- Omega-3 PUFA 2 g twice daily.
Familial combined hyperlipidemia
- Dosing Information
- Omega-3-acid ethyl esters (4 g/day).
Heart failure
- Dosing Information
- Long-term treatment with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) 1 g daily.
Hyperlipidemia - Hypertriglyceridemia, Triglyceride levels less than 500 mg/dL
- Dosing Information
- Omega-3-acid ethyl esters (P-OM3) 4 g/day.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Lovaza in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Lovaza in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Lovaza in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- LOVAZA is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reaction) to LOVAZA or any of its components.
Warnings
Precautions
- Monitoring: Laboratory Tests
- In patients with hepatic impairment, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels should be monitored periodically during therapy with LOVAZA. In some patients, increases in ALT levels without a concurrent increase in AST levels were observed.
- In some patients, LOVAZA increases LDL-C levels. LDL-C levels should be monitored periodically during therapy with LOVAZA.
- Laboratory studies should be performed periodically to measure the patient’s TG levels during therapy with LOVAZA.
- Fish Allergy
- LOVAZA contains ethyl esters of omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) obtained from the oil of several fish sources. It is not known whether patients with allergies to fish and/or shellfish, are at increased risk of an allergic reaction to LOVAZA. LOVAZA should be used with caution in patients with known hypersensitivity to fish and/or shellfish.
- Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation (AF) or Flutter
- In a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 663 subjects with symptomatic paroxysmal AF (n = 542) or persistent AF (n = 121), recurrent AF or flutter was observed in subjects randomized to LOVAZA who received 8 grams/day for 7 days and 4 grams/day thereafter for 23 weeks at a higher rate relative to placebo. Subjects in this trial had median baseline triglycerides of 127 mg/dL, had no substantial structural heart disease, were taking no anti-arrhythmic therapy (rate control permitted), and were in normal sinus rhythm at baseline.
- At 24 weeks, in the paroxysmal AF stratum, there were 129 (47%) first recurrent symptomatic AF or flutter events on placebo and 141 (53%) on LOVAZA [primary endpoint, HR 1.19; 95% CI: 0.93, 1.35]. In the persistent AF stratum, there were 19 (35%) events on placebo and 34 (52%) events on LOVAZA [HR 1.63; 95% CI: 0.91, 2.18]. For both strata combined, the HR was 1.25; 95% CI: 1.00, 1.40. Although the clinical significance of these results is uncertain, there is a possible association between LOVAZA and more frequent recurrences of symptomatic atrial fibrillation or flutter in patients with paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation, particularly within the first 2 to 3 months of initiating therapy.
- LOVAZA is not indicated for the treatment of AF or flutter.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
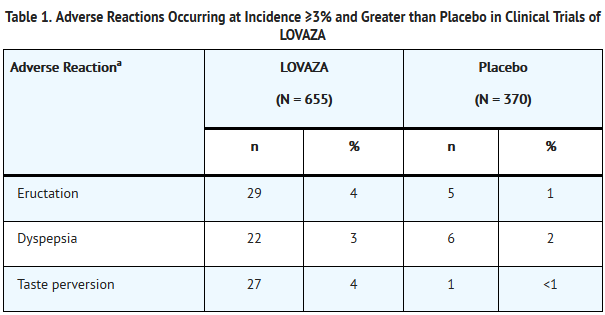
- Adverse reactions reported in at least 3% and at a greater rate than placebo for subjects treated with LOVAZA based on pooled data across 23 clinical trials are listed in Table 1.
- Additional adverse reactions from clinical trials are listed below:
Digestive System
Constipation, gastrointestinal disorder and vomiting.
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders
Increased ALT and increased AST.
Skin
Postmarketing Experience
- In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials, the events described below have been identified during post-approval use of LOVAZA. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or to always establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- The following events have been reported: anaphylactic reaction, hemorrhagic diathesis.
Drug Interactions
- Anticoagulants or Other Drugs Affecting Coagulation
- Some trials with omega-3-acids demonstrated prolongation of bleeding time. The prolongation of bleeding time reported in these trials has not exceeded normal limits and did not produce clinically significant bleeding episodes. Clinical trials have not been done to thoroughly examine the effect of LOVAZA and concomitant anticoagulants. Patients receiving treatment with LOVAZA and an anticoagulant or other drug affecting coagulation (e.g., anti-platelet agents) should be monitored periodically.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C
- There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. It is unknown whether LOVAZA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. LOVAZA should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the patient justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Animal Data
- Omega-3-acid ethyl esters have been shown to have an embryocidal effect in pregnant rats when given in doses resulting in exposures 7 times the recommended human dose of 4 grams/day based on a body surface area comparison.
- In female rats given oral gavage doses of 100, 600, and 2,000 mg/kg/day beginning 2 weeks prior to mating and continuing through gestation and lactation, no adverse effects were observed in the high-dose group (5 times human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 grams/day based on body surface area comparison).
- In pregnant rats given oral gavage doses of 1,000, 3,000, and 6,000 mg/kg/day from gestation day 6 through 15, no adverse effects were observed (14 times human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 grams/day based on a body surface area comparison).
- In pregnant rats given oral gavage doses of 100, 600, and 2,000 mg/kg/day from gestation day 14 through lactation day 21, no adverse effects were seen at 2,000 mg/kg/day (5 times the human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 grams/day based on a body surface area comparison). However, decreased live births (20% reduction) and decreased survival to postnatal day 4 (40% reduction) were observed in a dose-ranging study using higher doses of 3,000 mg/kg/day (7 times the human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 grams/day based on a body surface area comparison).
- In pregnant rabbits given oral gavage doses of 375, 750, and 1,500 mg/kg/day from gestation day 7 through 19, no findings were observed in the fetuses in groups given 375 mg/kg/day (2 times human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 grams/day based on a body surface area comparison). However, at higher doses, evidence of maternal toxicity was observed (4 times human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 grams/day based on a body surface area comparison).
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Lovaza in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Lovaza during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Studies with omega-3-acid ethyl esters have demonstrated excretion in human milk. The effect of this excretion on the infant of a nursing mother is unknown; caution should be exercised when LOVAZA is administered to a nursing mother. An animal study in lactating rats given oral gavage 14C-ethyl EPA demonstrated that drug levels were 6 to 14 times higher in milk than in plasma.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatic Use
- A limited number of subjects older than 65 years were enrolled in the clinical trials of LOVAZA. Safety and efficacy findings in subjects older than 60 years did not appear to differ from those of subjects younger than 60 years.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lovaza with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lovaza with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lovaza in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lovaza in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lovaza in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Lovaza in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Lovaza in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Lovaza in the drug label.
Overdosage
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Lovaza in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Lovaza Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- The mechanism of action of LOVAZA is not completely understood. Potential mechanisms of action include inhibition of acyl-CoA:1,2-diacylglycerol acyltransferase, increased mitochondrial and peroxisomal β-oxidation in the liver, decreased lipogenesis in the liver, and increased plasma lipoprotein lipase activity. LOVAZA may reduce the synthesis of triglycerides in the liver because EPA and DHA are poor substrates for the enzymes responsible for TG synthesis, and EPA and DHA inhibit esterification of other fatty acids.
Structure
- LOVAZA, a lipid-regulating agent, is supplied as a liquid-filled gel capsule for oral administration. Each 1-gram capsule of LOVAZA contains at least 900 mg of the ethyl esters of omega-3 fatty acids sourced from fish oils. These are predominantly a combination of ethyl esters of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA - approximately 465 mg) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA - approximately 375 mg).
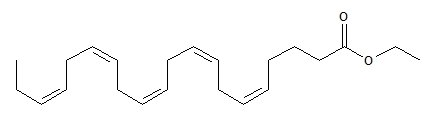
- The empirical formula of EPA ethyl ester is C22H34O2, and the molecular weight of EPA ethyl ester is 330.51. The structural formula of EPA ethyl ester is:
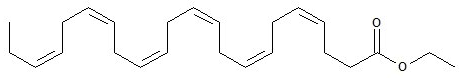
- The empirical formula of DHA ethyl ester is C24H36O2, and the molecular weight of DHA ethyl ester is 356.55. The structural formula of DHA ethyl ester is:
- LOVAZA capsules also contain the following inactive ingredients: 4 mg α-tocopherol (in a carrier of soybean oil), and gelatin, glycerol, and purified water (components of the capsule shell).
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Lovaza in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- In healthy volunteers and in subjects with hypertriglyceridemia, EPA and DHA were absorbed when administered as ethyl esters orally. Omega-3-acids administered as ethyl esters (LOVAZA) induced significant, dose-dependent increases in serum phospholipid EPA content, though increases in DHA content were less marked and not dose-dependent when administered as ethyl esters.
- Specific Populations:
- Age:
- Uptake of EPA and DHA into serum phospholipids in subjects treated with LOVAZA was independent of age (<49 years versus ≥49 years).
- Gender:
- Females tended to have more uptake of EPA into serum phospholipids than males. The clinical significance of this is unknown.
- Pediatric:
- Pharmacokinetics of LOVAZA have not been studied.
- Renal or Hepatic Impairment:
- LOVAZA has not been studied in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
- Drug-Drug Interactions:
- Simvastatin:
- In a 14-day trial of 24 healthy adult subjects, daily coadministration of simvastatin 80 mg with LOVAZA 4 grams did not affect the extent (AUC) or rate (Cmax) of exposure to simvastatin or the major active metabolite, beta-hydroxy simvastatin at steady state.
- Atorvastatin:
- In a 14-day trial of 50 healthy adult subjects, daily coadministration of atorvastatin 80 mg with LOVAZA 4 grams did not affect AUC or Cmax of exposure to atorvastatin, 2-hydroxyatorvastatin, or 4-hydroxyatorvastatin at steady state.
- Rosuvastatin:
- In a 14-day trial of 48 healthy adult subjects, daily coadministration of rosuvastatin 40 mg with LOVAZA 4 grams did not affect AUC or Cmax of exposure to rosuvastatin at steady state.
- In vitro studies using human liver microsomes indicated that clinically significant cytochrome P450-mediated inhibition by EPA/DHA combinations are not expected in humans.
Nonclinical Toxicology
- In a rat carcinogenicity study with oral gavage doses of 100, 600, and 2,000 mg/kg/day, males were treated with omega-3-acid ethyl esters for 101 weeks and females for 89 weeks without an increased incidence of tumors (up to 5 times human systemic exposures following an oral dose of 4 grams/day based on a body surface area comparison). Standard lifetime carcinogenicity bioassays were not conducted in mice.
- Omega-3-acid ethyl esters were not mutagenic or clastogenic with or without metabolic activation in the bacterial mutagenesis (Ames) test with Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli or in the chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster V79 lung cells or human lymphocytes. Omega-3-acid ethyl esters were negative in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
- In a rat fertility study with oral gavage doses of 100, 600, and 2,000 mg/kg/day, males were treated for 10 weeks prior to mating and females were treated for 2 weeks prior to and throughout mating, gestation, and lactation. No adverse effect on fertility was observed at 2,000 mg/kg/day (5 times human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 grams/day based on a body surface area comparison).
Clinical Studies
Severe Hypertriglyceridemia
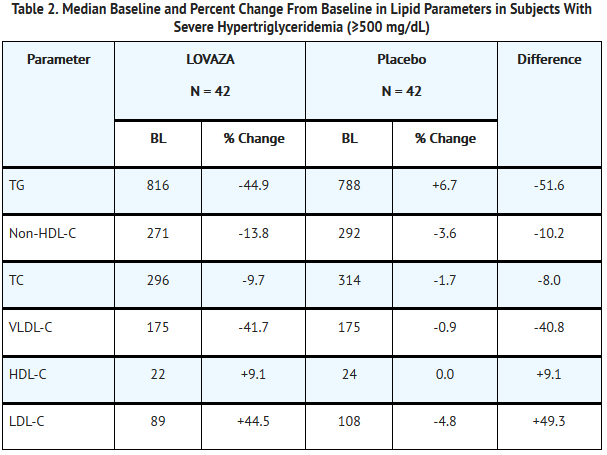
- The effects of LOVAZA 4 grams per day were assessed in 2 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group trials of 84 adult subjects (42 on LOVAZA, 42 on placebo) with very high triglyceride levels. Subjects whose baseline triglyceride levels were between 500 and 2,000 mg/dL were enrolled in these 2 trials of 6 and 16 weeks’ duration. The median triglyceride and LDL-C levels in these subjects were 792 mg/dL and 100 mg/dL, respectively. Median HDL-C level was 23.0 mg/dL.
- The changes in the major lipoprotein lipid parameters for the groups receiving LOVAZA or placebo are shown in Table 2.
- BL = Baseline (mg/dL); % Change = Median Percent Change from Baseline; Difference = LOVAZA Median % Change – Placebo Median % Change.
- LOVAZA 4 grams per day reduced median TG, VLDL-C, and non-HDL-C levels and increased median HDL-C from baseline relative to placebo. Treatment with LOVAZA to reduce very high TG levels may result in elevations in LDL-C and non-HDL-C in some individuals. Patients should be monitored to ensure that the LDL-C level does not increase excessively.
- The effect of LOVAZA on the risk of pancreatitis has not been determined.
- The effect of LOVAZA on cardiovascular mortality and morbidity has not been determined.
How Supplied
- LOVAZA (omega-3-acid ethyl esters) capsules are supplied as 1-gram, transparent, soft-gelatin capsules filled with light-yellow oil and bearing the designation LOVAZA.
- Bottles of 120: NDC 0173-0783-02.
- Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). Do not freeze. Keep out of reach of children.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Lovaza Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Lovaza |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Lovaza |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- LOVAZA should be used with caution in patients with known sensitivity or allergy to fish and/or shellfish.
- Advise patients that use of lipid-regulating agents does not reduce the importance of adhering to diet.
- Advise patients not to alter LOVAZA capsules in any way and to ingest intact capsules only.
- Instruct patients to take LOVAZA as prescribed. If a dose is missed, advise patients to take it as soon as they remember. However, if they miss one day of LOVAZA, they should not double the dose when they take it.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Lovaza interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- LOVAZA®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- Lovaza® — LORazepam®[2]
- Omacor® — Amicar®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "LOVAZA omega-3-acid ethyl esters capsule, liquid filled".
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Lovaza |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Lovaza |Label Name=Lovaza04.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Lovaza |Label Name=Lovaza05.png
}}