Lipohemarthosis
|
WikiDoc Resources for Lipohemarthosis |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Lipohemarthosis Most cited articles on Lipohemarthosis |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Lipohemarthosis |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Lipohemarthosis at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Lipohemarthosis Clinical Trials on Lipohemarthosis at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Lipohemarthosis NICE Guidance on Lipohemarthosis
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Lipohemarthosis Discussion groups on Lipohemarthosis Patient Handouts on Lipohemarthosis Directions to Hospitals Treating Lipohemarthosis Risk calculators and risk factors for Lipohemarthosis
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Lipohemarthosis |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
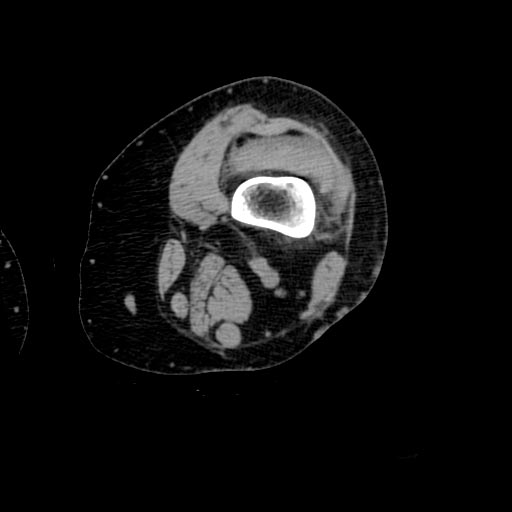
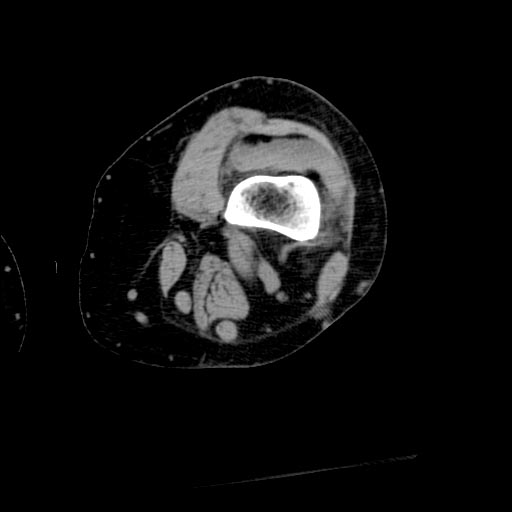
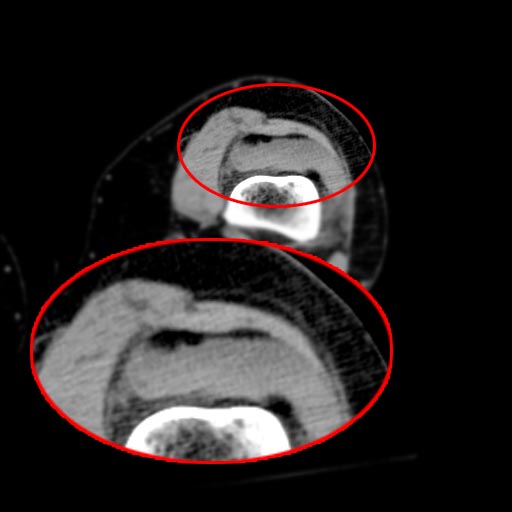
Lipohemarthrosis results from the extrusion of fat and blood from bone marrow into the joint space after an intraarticular fracture. Lipohemarthrosis is most common in knee fractures, especially tibial plateau fractures.
Diagnosis
The imaging findings are
- Because fat floats on the associated blood, a fat-fluid level is present and may be shown on radiographs when the image is taken with a horizontal beam.
- Both CT and MRI can provide a more specific assessment than conventional radiography of the composition of joint effusions.
Patient #1: Lateral tibial plateau fracture
Patient #2: MRI image demonstrates an ankle lipohemarthrosis