Cefepime dosage and administration
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Abdurahman Khalil, M.D. [2]
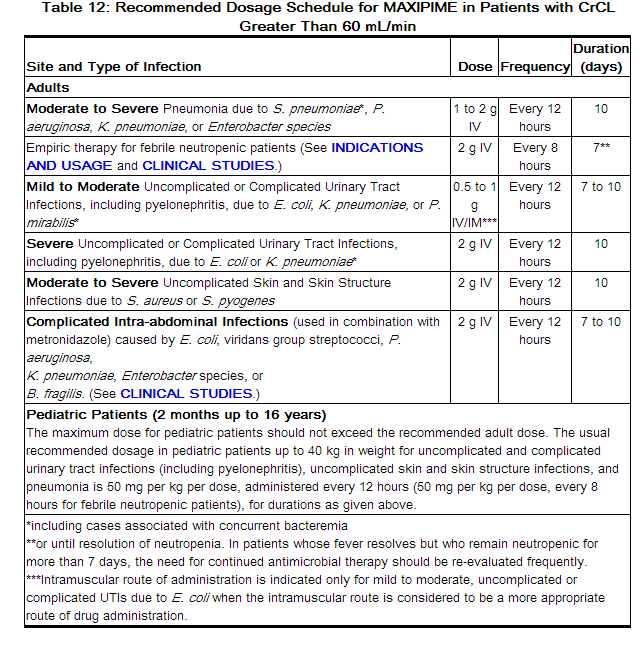
The recommended adult and pediatric dosages and routes of administration are outlined in the following table. MAXIPIME should be administered intravenously over approximately 30 minutes.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No adjustment is necessary for patients with hepatic impairment.
Patients with Renal Impairment
In patients with creatinine clearance less than or equal to 60 mL/min, the dose of MAXIPIME should be adjusted to compensate for the slower rate of renal elimination. The recommended initial dose of MAXIPIME should be the same as in patients with normal renal function except in patients undergoing hemodialysis. The recommended doses of MAXIPIME in patients with renal impairment are presented in Table 13.
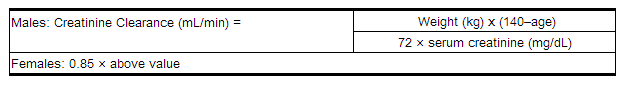
When only serum creatinine is available, the following formula (Cockcroft and Gault equation)3 may be used to estimate creatinine clearance. The serum creatinine should represent a steady state of renal function:
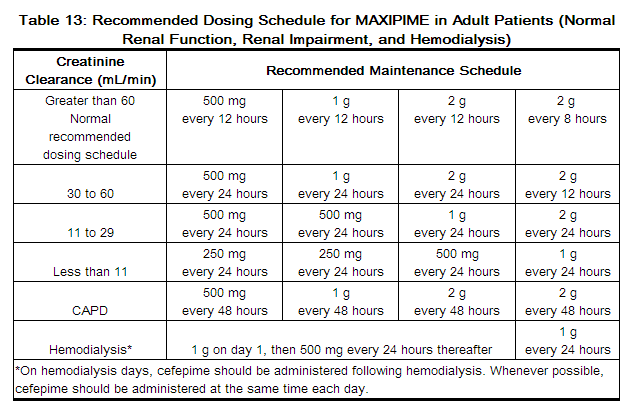
In patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, MAXIPIME may be administered at normally recommended doses at a dosage interval of every 48 hours (see Table 13).
In patients undergoing hemodialysis, approximately 68% of the total amount of cefepime present in the body at the start of dialysis will be removed during a 3-hour dialysis period. The dosage of MAXIPIME for hemodialysis patients is 1 g on Day 1 followed by 500 mg every 24 hours for the treatment of all infections except febrile neutropenia, which is 1 g every 24 hours.
MAXIPIME should be administered at the same time each day and following the completion of hemodialysis on hemodialysis days (see Table 13).
Data in pediatric patients with impaired renal function are not available; however, since cefepime pharmacokinetics are similar in adults and pediatric patients (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY), changes in the dosing regimen proportional to those in adults (see Tables 12 and 13) are recommended for pediatric patients.
Administration
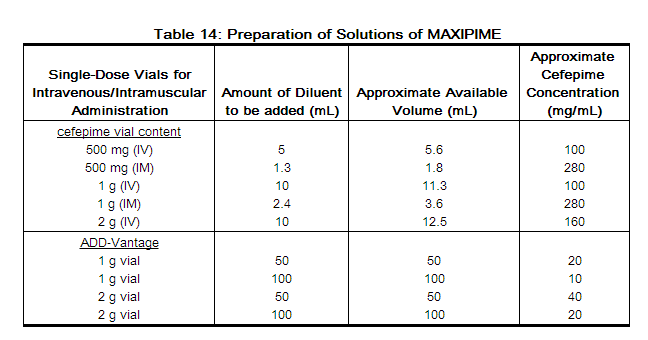
For Intravenous Infusion, Dilute with a suitable parenteral vehicle prior to intravenous infusion. Constitute the 500 mg, 1 g, or 2 g vial, and add an appropriate quantity of the resulting solution to an intravenous container with one of the compatible intravenous fluids listed in the Compatibility and Stability subsection. THE RESULTING SOLUTION SHOULD BE ADMINISTERED OVER APPROXIMATELY 30 MINUTES.
Intermittent intravenous infusion with a Y-type administration set can be accomplished with compatible solutions. However, during infusion of a solution containing cefepime, it is desirable to discontinue the other solution.
ADD-Vantage™ vials are to be constituted only with 50 mL or 100 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection in ADD-Vantage flexible diluent containers. (See ADD-Vantage Vial Instructions for Use.)
Intramuscular Administration: For intramuscular administration, MAXIPIME (cefepime hydrochloride) should be constituted with one of the following diluents: Sterile Water for Injection, 0.9% Sodium Chloride, 5% Dextrose Injection, 0.5% or 1 % Lidocaine Hydrochloride, or Sterile Bacteriostatic Water for Injection with Parabens or Benzyl Alcohol (refer to Table 14).
Preparation of MAXIPIME solutions is summarized in Table 14.