Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome
Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome is a rare disorder of brain development that causes moderate to severe mental retardation and problems with movement. This condition, which occurs exclusively in males, disrupts development from before birth.
Most children with Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome have weak muscle tone (hypotonia) and underdevelopment of many muscles (muscle hypoplasia). As they get older, they usually develop joint deformities called contractures, which restrict the movement of certain joints. Abnormal muscle stiffness (spasticity), muscle weakness, and involuntary movements of the arms and legs also limit mobility. As a result, many people with Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome are unable to walk independently and become wheelchair-bound by adulthood.
Mutations in the SLC16A2 gene cause Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome. The SLC16A2 gene, also known as MCT8, provides instructions for making a protein that plays a critical role in the development of the nervous system. This protein transports a particular hormone into nerve cells in the developing brain. This hormone, called triiodothyronine or T3, is produced by the thyroid. T3 appears to be critical for the normal formation and growth of nerve cells, as well as the development of junctions between nerve cells (synapses) where cell-to-cell communication occurs. T3 and other forms of thyroid hormone also help regulate the development of other organs and control the rate of chemical reactions in the body.
Gene mutations alter the structure and function of the SLC16A2 protein. As a result, this protein is unable to transport T3 into nerve cells effectively. A lack of this critical hormone in certain parts of the brain disrupts normal brain development, resulting in mental retardation and problems with movement. Because T3 is not taken up by nerve cells, excess amounts of this hormone continue to circulate in the bloodstream. Increased T3 levels in the blood may be toxic to some organs and contribute to the signs and symptoms of Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome.
This condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern. A condition is considered X-linked if the mutated gene that causes the disorder is located on the X chromosome, one of the two sex chromosomes. In males (who have only one X chromosome), one altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition. In females (who have two X chromosomes), a mutation must be present in both copies of the gene to cause the disorder. Males are affected by X-linked recessive disorders much more frequently than females. A striking characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons.
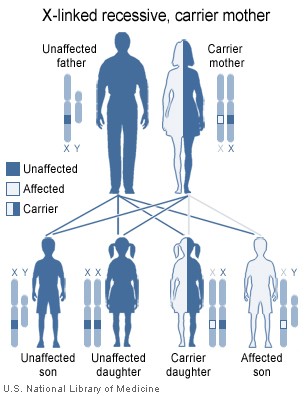
In X-linked recessive inheritance, a female with one altered copy of the gene in each cell is called a carrier. She can pass on the mutated gene, but usually does not experience signs and symptoms of the disorder. Carriers of SLC16A2 mutations have normal intelligence and do not experience problems with movement. Some carriers have been diagnosed with thyroid disease, a condition which is relatively common in the general population. It is unclear whether thyroid disease is related to SLC16A2 mutations in these cases.
References
- National Library of Medicine. Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome