Abnormal posturing
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Abnormal posturing | |
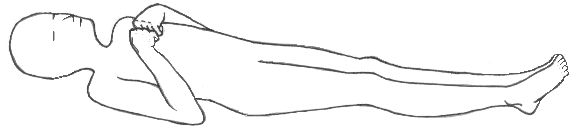 | |
|---|---|
| Decorticate posturing, with elbows, wrists and fingers flexed, and legs extended and rotated inward. |
|
Abnormal posturing Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Abnormal posturing On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Abnormal posturing |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Synonyms and keywords: Decorticate posturing; decorticate response; decorticate rigidity; flexor posturing; mummy baby; decerebrate posturing; decerebrate response; decerebrate rigidity; extensor posturing
Overview
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Risk Factors
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | EKG | CT | MRI | Other Imaging Findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies
Case Studies
Template:Nervous and musculoskeletal system symptoms and signs