Wolffian duct
|
WikiDoc Resources for Wolffian duct |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Wolffian duct Most cited articles on Wolffian duct |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Wolffian duct |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Wolffian duct at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Wolffian duct Clinical Trials on Wolffian duct at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Wolffian duct NICE Guidance on Wolffian duct
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Wolffian duct Discussion groups on Wolffian duct Patient Handouts on Wolffian duct Directions to Hospitals Treating Wolffian duct Risk calculators and risk factors for Wolffian duct
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Wolffian duct |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
The Wolffian duct (also known as archinephric duct, Leydig's duct, mesonephric duct, or nephric duct) is a paired organ found in mammals including humans during embryogenesis.
It connects the primitive kidney Wolffian body (or mesonephros) to the cloaca and serves as the anlage for certain male reproductive organs.
Development
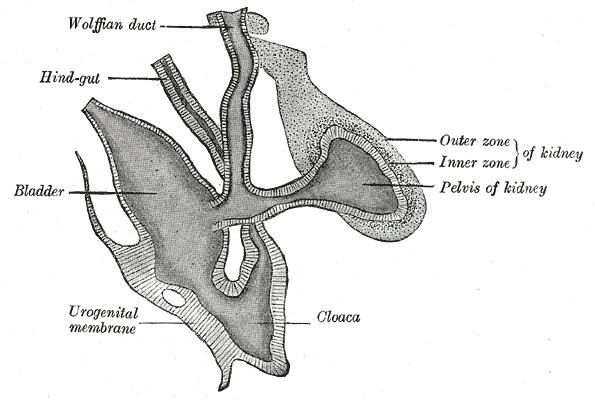
In both the male and the female the Wolffian duct develops in to the trigone of urinary bladder, a part of the bladder wall. However, further development differentiates between the sexes in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.
Male development
In a male, it develops into a system of connected organs between the testis and the prostate, namely the rete testis, the efferent ducts, the epididymis, the vas deferens, the seminal vesicle, and the prostate.
For this it is critical that the ducts are exposed to testosterone during embryogenesis. Testosterone binds to and activates androgen receptor, affecting intracellular signals and modifying the expression of numerous genes.[1]
In the mature male, the function of this system is to store and mature sperm, and provide accessory semen fluid.
Female development
In the female, in the absence of testosterone support, the Wolffian ducts regresses,and inclusions may persist . As a residual the epoophoron and Skene's glands may be present. Also, lateral to the wall of the vagina a Gartner's duct or cyst could develop as a remnant.
History
It is named after Caspar Friedrich Wolff who described the mesonephros and its ducts in his dissertation in 1759. [2]
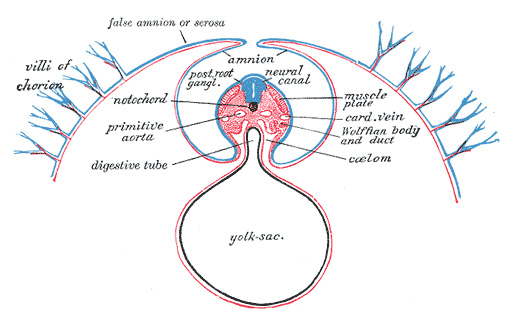
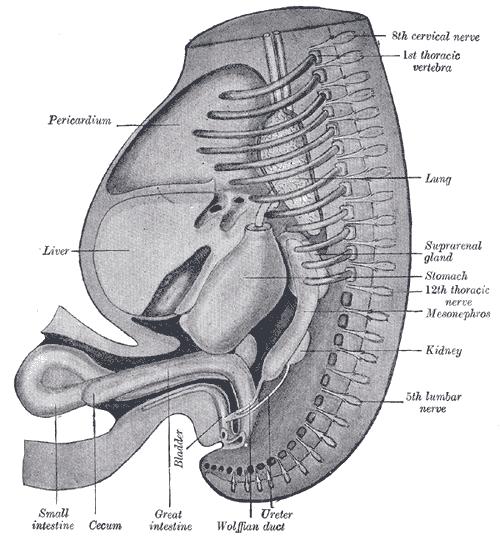
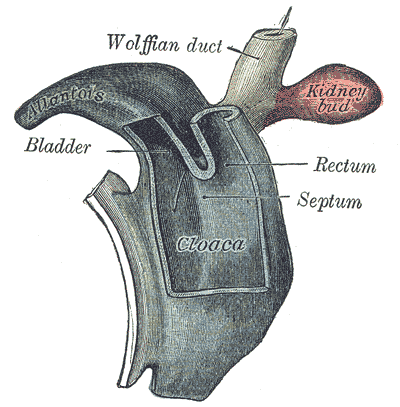
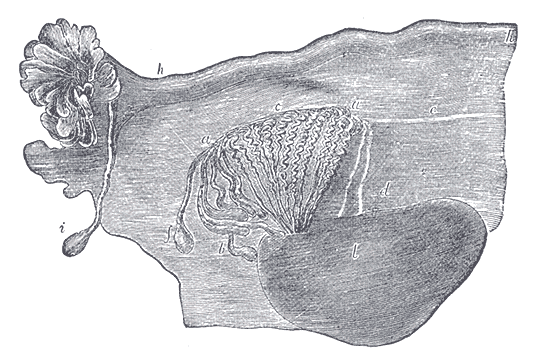
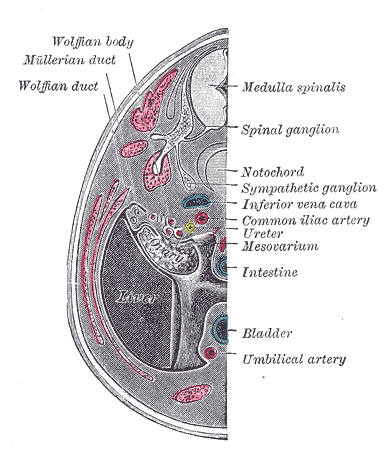
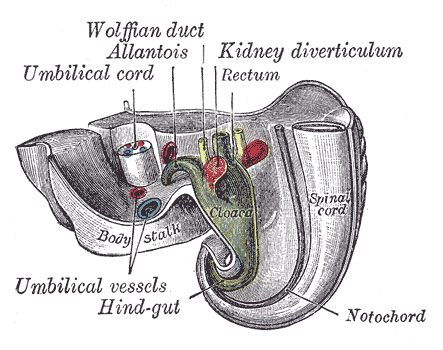
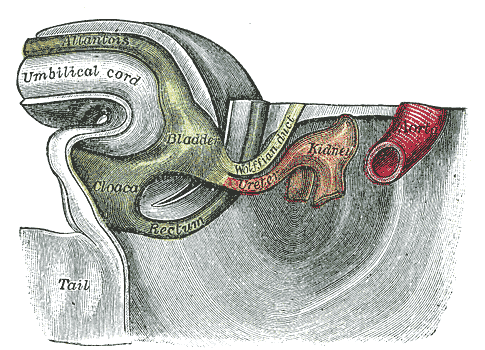
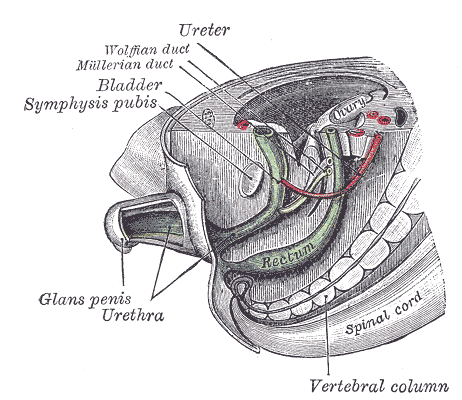
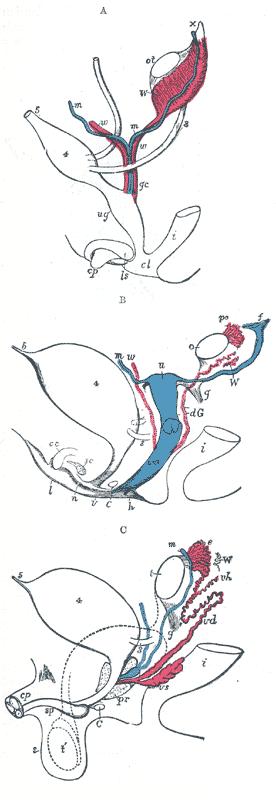
Additional images
-
Diagram of a transverse section, showing the mode of formation of the amnion in the chick.
-
Reconstruction of a human embryo of 17 mm.
-
Cloaca of human embryo from twenty-five to twenty-seven days old.
-
Broad ligament of adult, showing epoöphoron.
-
Transverse section of human embryo eight and a half to nine weeks old.
-
Tail end of human embryo twenty-five to twenty-nine days old.
-
Tail end of human embryo thirty-two to thirty-three days old.
-
Tail end of human embryo; from eight and a half to nine weeks old.
-
Primitive kidney and bladder, from a reconstruction.
See also
- Fetal genitalia
- List of homologues of the human reproductive system
- Masculinization
- Sexual differentiation
- Müllerian duct
References
- ↑ Hannema SE, Print CG, Charnock-Jones DS, Coleman N, Hughes IA (2006). "Changes in gene expression during Wolffian duct development". Horm. Res. 65 (4): 200–9. doi:10.1159/000092408. PMID 16567946.
- ↑ Template:WhoNamedIt