WBR0843: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
YazanDaaboul (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m (refreshing WBR questions) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor={{YD}} (Reviewed by {{YD}}) | |QuestionAuthor= {{YD}} (Reviewed by {{YD}}) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
|SubCategory=Dermatology | |SubCategory=Dermatology | ||
|Prompt=A 28-year-old man presents to the dermatology clinic with a lesion on his | |Prompt=A 28-year-old man presents to the dermatology clinic with a lesion on his left forearm. Upon further questioning, he informs the physician that he sustained 2 burns in his left forearm 1 year ago; and the current lesions developed at the sites of the previous burn wounds. On physical examination, the physician notes 2 raised pink lesions along the left forearm as shown in the image below. Which of the following is an appropriate therapeutic option for this patient's condition? | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:WBR0843question.jpg|500px]] | ||
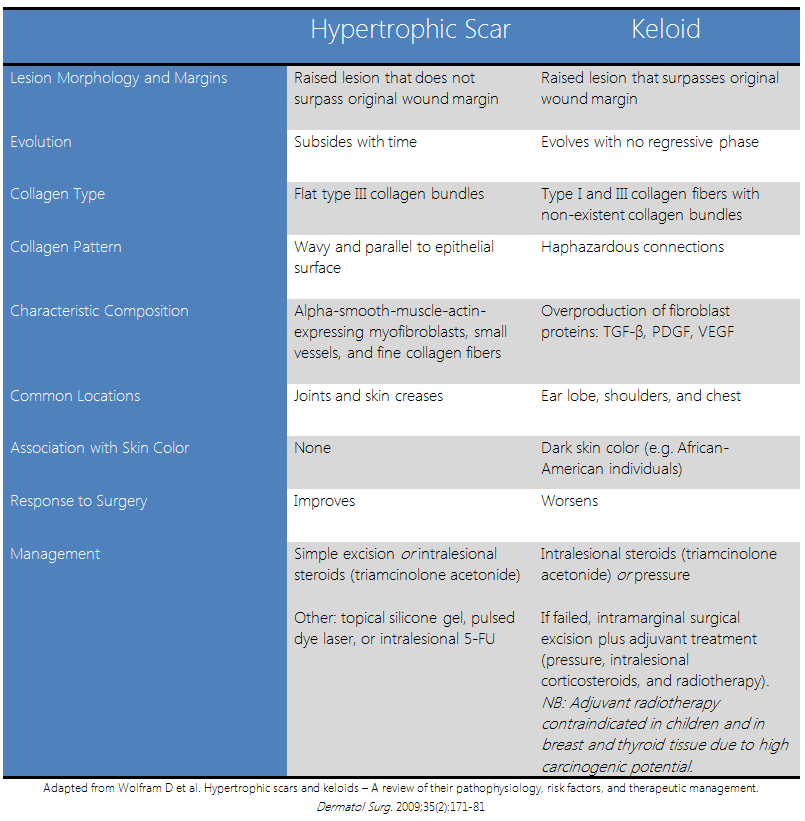
|Explanation=The patient is presenting with a | |Explanation=The patient is presenting with a hypertrophic scar. While intralesional corticosteroids are treatment options for both hypertrophic scars and keloids, simple excision alone is often considered a first line therapeutic option for patients with hypertrophic scar, but not keloids. The following table compares hypertrophic scars with keloids and demonstrates the optimal therapeutic options for both lesions. | ||
|AnswerA= | [[Image:Hypertrophic Scar vs. Keloid Comparison Table (Lesion morphology, margins, evolution, collagen, locations, composition, management).png|800px]] | ||
|AnswerAExp= | |AnswerA=Simple excision | ||
|AnswerAExp=Simple excision alone is often considered a first line therapeutic option for patients with hypertrophic scar, but not keloids. | |||
|AnswerB=Systemic corticosteroids | |AnswerB=Systemic corticosteroids | ||
|AnswerBExp=Systemic corticosteroids are not helpful for the treatment of | |AnswerBExp=Systemic corticosteroids are not helpful for the treatment of hypertrophic scars or keloids. | ||
|AnswerC=Topical corticosteroids | |AnswerC=Topical corticosteroids | ||
|AnswerCExp=Topical corticosteroids are not helpful for the treatment of | |AnswerCExp=Topical corticosteroids are not helpful for the treatment of hypertrophic scars or keloids. | ||
|AnswerD= | |AnswerD=Neoadjuvant radiotherapy | ||
|AnswerDExp= | |AnswerDExp=Hypertrophic scars do not usually require radiotherapy. For keloids, neither neoadjuvant (before surgery) radiotherapy nor radiotherapy alone is a good therapeutic option. Instead, adjuvant radiotherapy (following intramarginal excision) is often useful. | ||
|AnswerE=Systemic chemotherapy | |AnswerE=Systemic chemotherapy | ||
|AnswerEExp=Intralesional chemotherapy | |AnswerEExp=Intralesional chemotherapy may be effective for the treatment of hypertrophic scars or keloids. In contrast, systemic chemotherapy is not a therapeutic option for hypertrophic scars or keloids | ||
|EducationalObjectives= | |EducationalObjectives=Simple excision alone is often considered a first line therapeutic option for patients with hypertrophic scar, but not keloids. | ||
|References=Juckett G, Hartmann-Adams H. Management of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Am Fam Physicians. 2009;80(3):253-260. | |References=Wolfram D, Tzankov A, Pülzl P, et al. Hypertrophic scars and keloids - a review of their pathophysiology, risk factors, and therapeutic management. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(2):171-81. | ||
Juckett G, Hartmann-Adams H. Management of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Am Fam Physicians. 2009;80(3):253-260.<br> | |||
Image: "Hypertrophic scar -4 months after incident- 2013-04-05 00-46.jpg" by user:Cgomez447, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. http://commons.wikimedia.org/ retrieved 1-Jan-2015.<br> | |||
First Aid 2014 page 225 | |||
|RightAnswer=A | |RightAnswer=A | ||
|WBRKeyword=Keloid, Scar, Intralesional corticosteroids, | |WBRKeyword=Hypertrophic scar, Keloid, Scar, Intralesional corticosteroids, Corticosteroids, Steroids, Treatment, Burn | ||
|Approved=No | |Approved=No | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:51, 28 October 2020
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Yazan Daaboul, M.D. (Reviewed by Yazan Daaboul, M.D.)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Pathology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Dermatology |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 28-year-old man presents to the dermatology clinic with a lesion on his left forearm. Upon further questioning, he informs the physician that he sustained 2 burns in his left forearm 1 year ago; and the current lesions developed at the sites of the previous burn wounds. On physical examination, the physician notes 2 raised pink lesions along the left forearm as shown in the image below. Which of the following is an appropriate therapeutic option for this patient's condition? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Simple excision |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::Simple excision alone is often considered a first line therapeutic option for patients with hypertrophic scar, but not keloids. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Systemic corticosteroids |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::Systemic corticosteroids are not helpful for the treatment of hypertrophic scars or keloids. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Topical corticosteroids |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::Topical corticosteroids are not helpful for the treatment of hypertrophic scars or keloids. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Neoadjuvant radiotherapy |
| Answer D Explanation | [[AnswerDExp::Hypertrophic scars do not usually require radiotherapy. For keloids, neither neoadjuvant (before surgery) radiotherapy nor radiotherapy alone is a good therapeutic option. Instead, adjuvant radiotherapy (following intramarginal excision) is often useful.]] |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Systemic chemotherapy |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::Intralesional chemotherapy may be effective for the treatment of hypertrophic scars or keloids. In contrast, systemic chemotherapy is not a therapeutic option for hypertrophic scars or keloids |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::A |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::The patient is presenting with a hypertrophic scar. While intralesional corticosteroids are treatment options for both hypertrophic scars and keloids, simple excision alone is often considered a first line therapeutic option for patients with hypertrophic scar, but not keloids. The following table compares hypertrophic scars with keloids and demonstrates the optimal therapeutic options for both lesions.
|
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Hypertrophic scar, WBRKeyword::Keloid, WBRKeyword::Scar, WBRKeyword::Intralesional corticosteroids, WBRKeyword::Corticosteroids, WBRKeyword::Steroids, WBRKeyword::Treatment, WBRKeyword::Burn |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |