WBR0414: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m (refreshing WBR questions) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor={{ | |QuestionAuthor= {{YD}} (Reviewed by {{YD}}) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology | |MainCategory=Pharmacology | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology | |MainCategory=Pharmacology | ||
|SubCategory=Renal | |SubCategory=Renal | ||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology | |||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology | |MainCategory=Pharmacology | ||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology | |MainCategory=Pharmacology | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
|MainCategory=Pharmacology | |MainCategory=Pharmacology | ||
|SubCategory=Renal | |SubCategory=Renal | ||
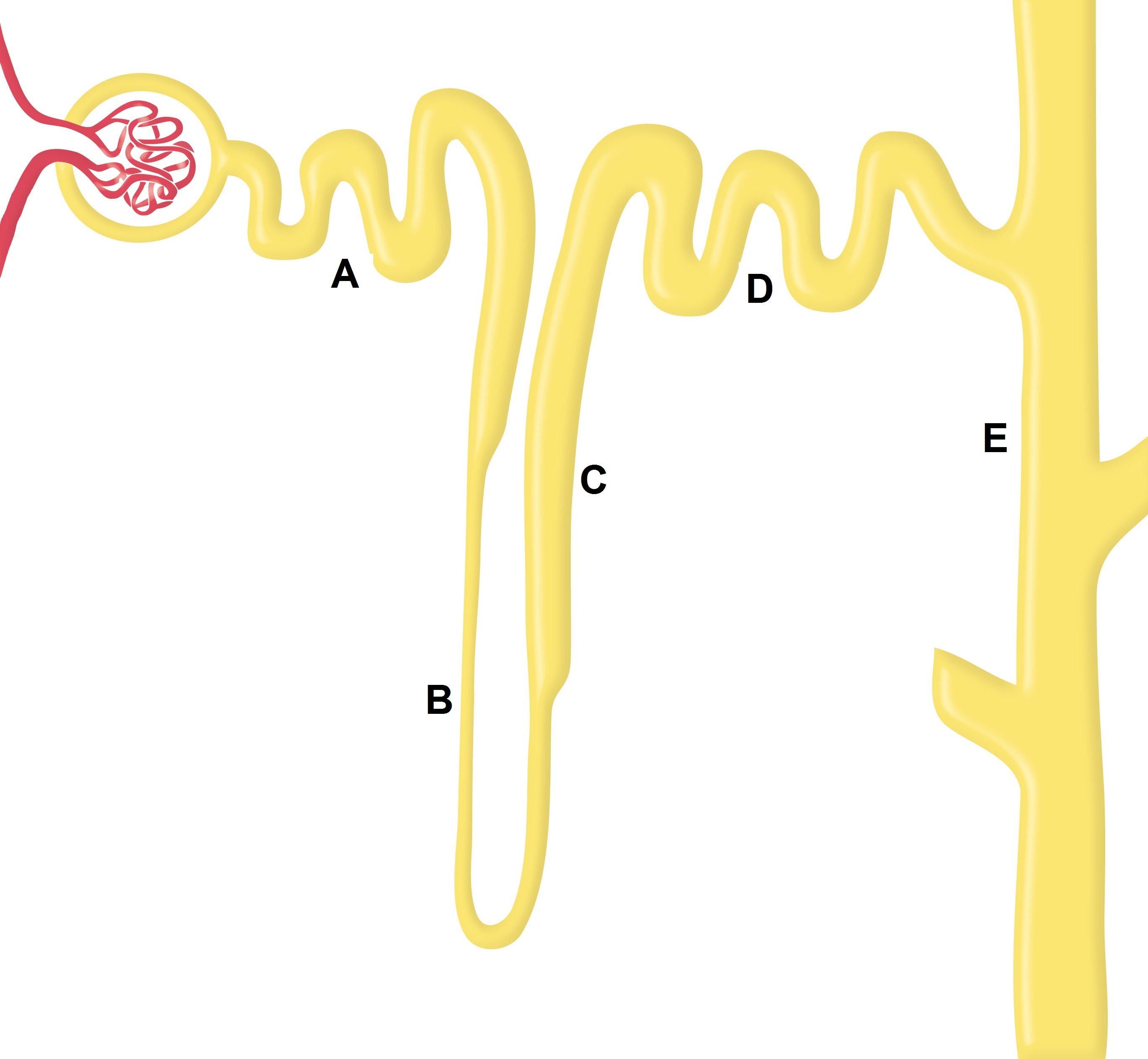
|Prompt=A 76 year old | |Prompt=A 76-year-old man presents to the physician’s office with complaints of dyspnea at rest and fatigue for the past 2 weeks. The patient has been recently diagnosed with congestive heart failure. Physical examination in the office is remarkable for jugular venous distension and bilateral lower extremity pitting edema. Pulmonary auscultation is significant for crackles at the lung bases bilaterally. The physician prescribes a diuretic to relieve the patient's symptoms. Several weeks later, the patient’s routine work-up demonstrates elevated concentrations of serum calcium and uric acid. Based on the image below, the diuretic prescribed to this patient acts at the level of which segment of the nephron? | ||
[[Image:NephronWBR.jpg|600px]] | |||
Thiazide diuretics inhibit NaCl reabsorption | |Explanation=[[Thiazide diuretics]] inhibit NaCl reabsorption at the level of the distal tubule. [[Thiazide]]s are commonly prescribed to patients with advanced heart failure for relief of symptoms associated with fluid overload. The most common adverse drug reactions associated with thiazide intake are hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hyperuricemia, and hypercalcemia. | ||
|AnswerA=A | |AnswerA=A | ||
|AnswerAExp=The proximal tubule is the site of action of osmotic diuretics, | |AnswerAExp=The proximal convoluted tubule is the site of action of osmotic diuretics, such as mannitol, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, such as acetazolamide. | ||
|AnswerB=B | |AnswerB=B | ||
|AnswerBExp= | |AnswerBExp=The thin descending [[loop of Henle]] is not a specific site of action of any diuretic. | ||
|AnswerC=C | |AnswerC=C | ||
|AnswerCExp=Thick ascending loop of Henle is the site of action of loop diuretics. | |AnswerCExp=Thick ascending loop of Henle is the site of action of loop diuretics. | ||
|AnswerD=D | |AnswerD=D | ||
|AnswerDExp=Thiazide diuretics inhibit NaCl reabsorption at the level of the distal tubule | |AnswerDExp=[[Thiazide]] diuretics inhibit NaCl reabsorption at the level of the distal tubule. | ||
|AnswerE=E | |AnswerE=E | ||
|AnswerEExp=The collecting duct is the main site of action of aldosterone receptor antagonists, | |AnswerEExp=The collecting duct is the main site of action of [[aldosterone receptor antagonists]], such as [[spironolactone]]. | ||
|EducationalObjectives=[[Thiazide diuretics]] inhibit NaCl reabsorption at the level of the distal tubule. | |||
|References=First Aid 2014 page 425 | |||
|RightAnswer=D | |RightAnswer=D | ||
|Approved= | |WBRKeyword=Thiazide, Nephron, NaCl channel, Congestive heart failure, Fluid overload, Pharmacologic therapy, Hypercalcemia, Hyperuricemia | ||
|Approved=Yes | |||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 00:29, 28 October 2020
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Yazan Daaboul, M.D. (Reviewed by Yazan Daaboul, M.D.)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Pharmacology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Renal |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 76-year-old man presents to the physician’s office with complaints of dyspnea at rest and fatigue for the past 2 weeks. The patient has been recently diagnosed with congestive heart failure. Physical examination in the office is remarkable for jugular venous distension and bilateral lower extremity pitting edema. Pulmonary auscultation is significant for crackles at the lung bases bilaterally. The physician prescribes a diuretic to relieve the patient's symptoms. Several weeks later, the patient’s routine work-up demonstrates elevated concentrations of serum calcium and uric acid. Based on the image below, the diuretic prescribed to this patient acts at the level of which segment of the nephron? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::A |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::The proximal convoluted tubule is the site of action of osmotic diuretics, such as mannitol, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, such as acetazolamide. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::B |
| Answer B Explanation | [[AnswerBExp::The thin descending loop of Henle is not a specific site of action of any diuretic.]] |
| Answer C | AnswerC::C |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::Thick ascending loop of Henle is the site of action of loop diuretics. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::D |
| Answer D Explanation | [[AnswerDExp::Thiazide diuretics inhibit NaCl reabsorption at the level of the distal tubule.]] |
| Answer E | AnswerE::E |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::The collecting duct is the main site of action of aldosterone receptor antagonists, such as spironolactone.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::D |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::Thiazide diuretics inhibit NaCl reabsorption at the level of the distal tubule. Thiazides are commonly prescribed to patients with advanced heart failure for relief of symptoms associated with fluid overload. The most common adverse drug reactions associated with thiazide intake are hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hyperuricemia, and hypercalcemia. Educational Objective: Thiazide diuretics inhibit NaCl reabsorption at the level of the distal tubule. |
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Thiazide, WBRKeyword::Nephron, WBRKeyword::NaCl channel, WBRKeyword::Congestive heart failure, WBRKeyword::Fluid overload, WBRKeyword::Pharmacologic therapy, WBRKeyword::Hypercalcemia, WBRKeyword::Hyperuricemia |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |