WBR0186
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Ogheneochuko Ajari, MB.BS, MS [1] (Reviewed by Serge Korjian)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Microbiology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Infectious Disease |
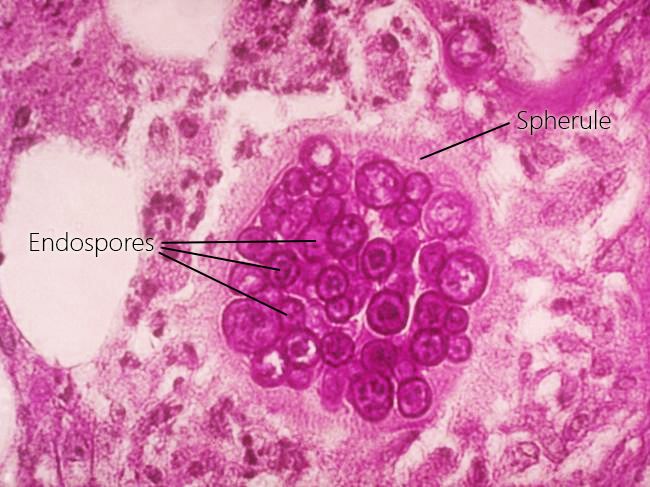
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 40-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office for several weeks of cough and intermittent fever. Initial work-up reveals a heterogeneous right lower lobe mass, hilar lymphadenopathy and a left sided pleural effusion on chest x-ray. Bronchoscopy with transbronchial biopsy reveals necrotic lung tissue with spherules containing hundreds of uninucleated endospores. Which of the following is the most likely etiologic agent?]] |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Histoplasma capsulatum |
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::Histoplasma capsulatum is a dimorphic fungus that forms hyphae with microconidia and tuberculate macroconidia. It does not form spherules with endospores. The tissue forms are small intracellular yeasts with narrow neck on bud with no capsules.]] |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Blastomyces dermatitidis |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::Blastomyces dermatitidis forms hyphae with nondescript conidia. The tissue form is a broad-based budding yeast. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Coccidioides immitis |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::Coccidioides immitis is a dimorphic fungus with the hyphae breaking into arthroconidia. It forms spherules with endospores. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Aspergillus fumigatus |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::Aspergillus fumigatus is a monomorphic filamentous fungus, dichotomously branching septate hyphae at 45 degrees angle. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Cryptococcus neoformans |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::Cryptococcus neoformans is an encapsulated monomorphic yeast. It does not form spherules with endospores. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::C |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::Coccidioidomycosis is a fungal infection caused by the dimorphic fungus Coccidioides immitis. Coccidioidomycosis is most prevalent in the southwestern United States, particularly in Arizona, California, Nevada, and New Mexico. In the soil, the organism exists as a mold with septate hyphae. When inhaled, spores evolve into round structures called spherules that grow and undergo internal division to form smaller structures called endospores. Large spherules can rupture to release packets of endospores, resulting in new foci of infection within the same host.
|
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |