WBR0047: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
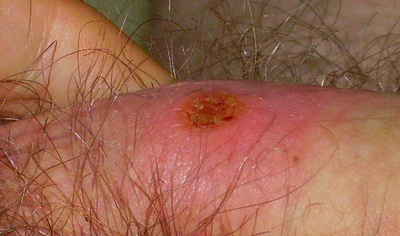
|Explanation=The patient has primary syphillus which is characterized by the appearance of a painless chancre (an ulcer-like lesion). Syphillis is caused by infection with the spirochete Treponema Pallidum and can be identified by darkfield microscopy or flourescent antibody staining. The fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption ([[FTA-Abs]]) assay uses Typonemal antigens fixed to a glass slide to detect whether antibodies specific to the organism are present in the serum from a human sample. The FTA-Abs assay is more specific than the Rapid Plasmin Reagin (RPR) or VDRL tests for Syphillus. None of the other answer choices could be used to visualize Treponema. | |Explanation=The patient has primary syphillus which is characterized by the appearance of a painless chancre (an ulcer-like lesion). Syphillis is caused by infection with the spirochete Treponema Pallidum and can be identified by darkfield microscopy or flourescent antibody staining. The fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption ([[FTA-Abs]]) assay uses Typonemal antigens fixed to a glass slide to detect whether antibodies specific to the organism are present in the serum from a human sample. The FTA-Abs assay is more specific than the Rapid Plasmin Reagin (RPR) or VDRL tests for Syphillus. None of the other answer choices could be used to visualize Treponema. | ||
'''References:''' | |||
'''References:''' | |||
|AnswerA=Giemas stain | |AnswerA=Giemas stain | ||
|AnswerAExp= | |AnswerAExp=Giemsa stain is used to identify Borellia, Plasmodium and Chlamydia. | ||
|AnswerB=Carbol-fuschin | |AnswerB=Carbol-fuschin | ||
|AnswerBExp= | |AnswerBExp=Carbol-fuschin (also known as Ziehl-Neelsen stain) is used to identify acid fast organisms. Syphillis is not an acid-fast organism. | ||
|AnswerC=Silver stain | |AnswerC=Silver stain | ||
|AnswerCExp= | |AnswerCExp=Silver stain is used to identify Fungi such as [[pneumocystis carinii]]. Pneumocystis carinii classically causes pneumonia in individuals with advanced HIV infection. | ||
|AnswerD=Fluorescent antibody | |AnswerD=Fluorescent antibody | ||
|AnswerDExp= | |AnswerDExp=Treponema Pallidum can be identified using a Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption (FTA-Abs) assay. This assay is more specific than the Rapid Plasmin Reagin (RPR) or VDRL tests for Syphillus. | ||
|AnswerE=India Ink | |AnswerE=India Ink | ||
|AnswerEExp= | |AnswerEExp=India ink is used to visualize Cryptococcus Neoformans. Cryptococcus neoformans is classically associated with meningitis in HIV-positive individuals. | ||
|EducationalObjectives=Primary syphillis is caused by Treponema pallidum which can be identified by fluorescent antibody staining. | |||
|References=First Aid 2014 page 122 (stains) | |||
First Aid 2014 page 141 (Syphilis) | |||
First Aid 2012 page 165. | |||
|RightAnswer=D | |RightAnswer=D | ||
|WBRKeyword=Microbiology, Syphilis, Bacteria, Laboratory, Sex, STD, STI, Sexually transmitted | |WBRKeyword=Microbiology, Syphilis, Bacteria, Laboratory, Sex, STD, STI, Sexually transmitted | ||
|Approved=Yes | |Approved=Yes | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 20:23, 15 March 2014
| Author | PageAuthor::William J Gibson |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Microbiology, MainCategory::Pathology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::General Principles, SubCategory::Infectious Disease |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 25 year old male presents to his primary care physician for the a painless lesion on his penis (pictured below). He reports unprotected vaginal intercourse with a sex worker while on a trip to approximately one month ago. Physical exam is negative for inguinal adenopathy, or vesicular lesions on other areas of the body. The most likely causal organism can be identified by which of the following stains? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Giemas stain |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::Giemsa stain is used to identify Borellia, Plasmodium and Chlamydia. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Carbol-fuschin |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::Carbol-fuschin (also known as Ziehl-Neelsen stain) is used to identify acid fast organisms. Syphillis is not an acid-fast organism. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Silver stain |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::Silver stain is used to identify Fungi such as pneumocystis carinii. Pneumocystis carinii classically causes pneumonia in individuals with advanced HIV infection.]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Fluorescent antibody |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::Treponema Pallidum can be identified using a Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption (FTA-Abs) assay. This assay is more specific than the Rapid Plasmin Reagin (RPR) or VDRL tests for Syphillus. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::India Ink |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::India ink is used to visualize Cryptococcus Neoformans. Cryptococcus neoformans is classically associated with meningitis in HIV-positive individuals. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::D |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::The patient has primary syphillus which is characterized by the appearance of a painless chancre (an ulcer-like lesion). Syphillis is caused by infection with the spirochete Treponema Pallidum and can be identified by darkfield microscopy or flourescent antibody staining. The fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption (FTA-Abs) assay uses Typonemal antigens fixed to a glass slide to detect whether antibodies specific to the organism are present in the serum from a human sample. The FTA-Abs assay is more specific than the Rapid Plasmin Reagin (RPR) or VDRL tests for Syphillus. None of the other answer choices could be used to visualize Treponema.
References: |
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Microbiology, WBRKeyword::Syphilis, WBRKeyword::Bacteria, WBRKeyword::Laboratory, WBRKeyword::Sex, WBRKeyword::STD, WBRKeyword::STI, WBRKeyword::Sexually transmitted |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |