Von Willebrand disease pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
Prince Djan (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Prince Djan (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
In healthy individuals, VWF circulates as high-molecular-weight multimers carrying factor VIII. Some persons have mildly reduced VWF levels, which may contribute to a bleeding phenotype but are not necessarily caused by defects in the VWF gene. Persons with low VWF levels and a bleeding tendency are classified as having low VWF, rather than von Willebrand’s disease (VWD). There is a partial deficiency of functionally normal VWF in type 1 VWD and a complete deficiency in type 3 disease. This deficiency can result from a reduction in protein synthesis, which is often caused by null alleles (large gene deletions, stop codons, frame-shift mutations, or splice-site mutations) but may also be due to mutations in the promotor regions. Homozygosity or compound heterozygosity for these defects results in type 3 VWD. Some heterozygous carriers have mild symptoms and receive a diagnosis of type 1 disease. However, most cases of type 1 VWD are caused by heterozygous missense mutations that exert a dominant-negative effect because the mutant subunits are incorporated into the multimer together with the normal subunits, resulting in a abnormality of the entire multimer. | In healthy individuals, VWF circulates as high-molecular-weight multimers carrying factor VIII. Some persons have mildly reduced [[VWF]] levels, which may contribute to a bleeding phenotype but are not necessarily caused by defects in the VWF gene. Persons with low VWF levels and a bleeding tendency are classified as having low VWF, rather than [[von Willebrand’s disease]] (VWD). There is a partial deficiency of functionally normal [[VWF]] in type 1 [[VWD]] and a complete deficiency in type 3 disease. This deficiency can result from a reduction in protein synthesis, which is often caused by null alleles (large gene deletions, stop codons, [[frame-shift mutations]], or [[splice-site mutations]]) but may also be due to [[mutations]] in the [[promotor]] regions. Homozygosity or compound heterozygosity for these defects results in type 3 VWD. Some heterozygous carriers have mild symptoms and receive a diagnosis of type 1 disease. However, most cases of type 1 [[VWD]] are caused by heterozygous [[missense]] mutations that exert a dominant-negative effect because the mutant subunits are incorporated into the multimer together with the normal subunits, resulting in a abnormality of the entire multimer. | ||
Deficiency of vWF shows primarily in organs with extensive small vessels, such as the skin, the [[gastrointestinal tract]] and the [[uterus]]. | Deficiency of [[vWF]] shows primarily in organs with extensive small vessels, such as the skin, the [[gastrointestinal tract]] and the [[uterus]]. | ||
In more severe cases of type 1 vWD, genetic changes are common within the vWF gene and are highly [[Penetrance|penetrant]]. In milder cases of type 1 vWD there may be a complex spectrum of molecular [[pathology]] in addition to [[Polymorphism (biology)|polymorphism]]s of the vWF gene alone.<ref>{{cite journal | author = James P, Notley C, Hegadorn C, Leggo J, Tuttle A, Tinlin S, Brown C, Andrews C, Labelle A, Chirinian Y, O'Brien L, Othman M, Rivard G, Rapson D, Hough C, Lillicrap D | title = The mutational spectrum of type 1 von Willebrand disease: Results from a Canadian cohort study | journal = Blood | volume = 109 | issue = 1 | pages = 145–54 | year = 2007 | pmid = 17190853 | doi = 10.1182/blood-2006-05-021105}}</ref> The individual's [[ABO blood group system|ABO blood group]] can influence presentation and pathology of vWD. Those individuals with blood group O have a lower mean level than individuals with other blood groups. Unless ABO group–specific vWF:antigen reference ranges are used, normal group O individuals can be diagnosed as type I vWD, and some individuals of blood group AB with a genetic defect of vWF may have the diagnosis overlooked because vWF levels are elevated due to blood group.<ref>{{cite journal | last = Gill | first = JC | coauthors = Endres-Brooks J, Bauer PJ, Marks WJ, Montgomery RR | title = The effect of ABO blood group on the diagnosis of von Willebrand disease | journal = Blood | volume = 69 | issue = 6 | pages = 1691–5 | publisher = | date = 1987 | url = http://www.bloodjournal.org/cgi/content/abstract/69/6/1691 | doi = | pmid = 3495304 | accessdate = }}</ref> | In more severe cases of type 1 [[vWD]], genetic changes are common within the [[vWF]] gene and are highly [[Penetrance|penetrant]]. In milder cases of type 1 [[vWD]] there may be a complex spectrum of molecular [[pathology]] in addition to [[Polymorphism (biology)|polymorphism]]s of the vWF gene alone.<ref>{{cite journal | author = James P, Notley C, Hegadorn C, Leggo J, Tuttle A, Tinlin S, Brown C, Andrews C, Labelle A, Chirinian Y, O'Brien L, Othman M, Rivard G, Rapson D, Hough C, Lillicrap D | title = The mutational spectrum of type 1 von Willebrand disease: Results from a Canadian cohort study | journal = Blood | volume = 109 | issue = 1 | pages = 145–54 | year = 2007 | pmid = 17190853 | doi = 10.1182/blood-2006-05-021105}}</ref> The individual's [[ABO blood group system|ABO blood group]] can influence presentation and pathology of vWD. Those individuals with blood group O have a lower mean level than individuals with other blood groups. Unless ABO group–specific vWF:antigen reference ranges are used, normal group O individuals can be diagnosed as type I vWD, and some individuals of blood group AB with a genetic defect of vWF may have the diagnosis overlooked because vWF levels are elevated due to blood group.<ref>{{cite journal | last = Gill | first = JC | coauthors = Endres-Brooks J, Bauer PJ, Marks WJ, Montgomery RR | title = The effect of ABO blood group on the diagnosis of von Willebrand disease | journal = Blood | volume = 69 | issue = 6 | pages = 1691–5 | publisher = | date = 1987 | url = http://www.bloodjournal.org/cgi/content/abstract/69/6/1691 | doi = | pmid = 3495304 | accessdate = }}</ref> | ||
===Genetics=== | ===Genetics=== | ||
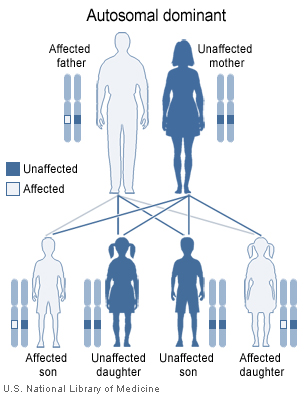
Von Willebrand disease types 1 and 2 (except type 2N which is inherited recessively) are inherited as autosomal dominant traits and type 3 is inherited as autosomal recessive. The diagram below illustrates autosomal dominant inheritance. | [[Von Willebrand disease]] types 1 and 2 (except type 2N which is inherited recessively) are inherited as [[autosomal dominant]] traits and type 3 is inherited as [[autosomal recessive]]. The diagram below illustrates [[autosomal dominant]] inheritance. | ||
{| align="center" | {| align="center" | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
* It has 52 exons spanning 178kbp. * | * It has 52 exons spanning 178kbp. * | ||
*VWD Types 1 and 2 are inherited as [[autosomal dominant]] traits and type 3 is inherited as [[autosomal recessive]]. Occasionally type 2 also inherits recessively. | *VWD Types 1 and 2 are inherited as [[autosomal dominant]] traits and type 3 is inherited as [[autosomal recessive]]. Occasionally type 2 also inherits recessively. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 18:50, 29 November 2016
|
Von Willebrand disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Von Willebrand disease pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Von Willebrand disease pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Von Willebrand disease pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Pathophysiology
In healthy individuals, VWF circulates as high-molecular-weight multimers carrying factor VIII. Some persons have mildly reduced VWF levels, which may contribute to a bleeding phenotype but are not necessarily caused by defects in the VWF gene. Persons with low VWF levels and a bleeding tendency are classified as having low VWF, rather than von Willebrand’s disease (VWD). There is a partial deficiency of functionally normal VWF in type 1 VWD and a complete deficiency in type 3 disease. This deficiency can result from a reduction in protein synthesis, which is often caused by null alleles (large gene deletions, stop codons, frame-shift mutations, or splice-site mutations) but may also be due to mutations in the promotor regions. Homozygosity or compound heterozygosity for these defects results in type 3 VWD. Some heterozygous carriers have mild symptoms and receive a diagnosis of type 1 disease. However, most cases of type 1 VWD are caused by heterozygous missense mutations that exert a dominant-negative effect because the mutant subunits are incorporated into the multimer together with the normal subunits, resulting in a abnormality of the entire multimer.
Deficiency of vWF shows primarily in organs with extensive small vessels, such as the skin, the gastrointestinal tract and the uterus.
In more severe cases of type 1 vWD, genetic changes are common within the vWF gene and are highly penetrant. In milder cases of type 1 vWD there may be a complex spectrum of molecular pathology in addition to polymorphisms of the vWF gene alone.[1] The individual's ABO blood group can influence presentation and pathology of vWD. Those individuals with blood group O have a lower mean level than individuals with other blood groups. Unless ABO group–specific vWF:antigen reference ranges are used, normal group O individuals can be diagnosed as type I vWD, and some individuals of blood group AB with a genetic defect of vWF may have the diagnosis overlooked because vWF levels are elevated due to blood group.[2]
Genetics
Von Willebrand disease types 1 and 2 (except type 2N which is inherited recessively) are inherited as autosomal dominant traits and type 3 is inherited as autosomal recessive. The diagram below illustrates autosomal dominant inheritance.
 |
- The vWF gene is located on chromosome twelve (12p13.2).
- It has 52 exons spanning 178kbp. *
- VWD Types 1 and 2 are inherited as autosomal dominant traits and type 3 is inherited as autosomal recessive. Occasionally type 2 also inherits recessively.
References
- ↑ James P, Notley C, Hegadorn C, Leggo J, Tuttle A, Tinlin S, Brown C, Andrews C, Labelle A, Chirinian Y, O'Brien L, Othman M, Rivard G, Rapson D, Hough C, Lillicrap D (2007). "The mutational spectrum of type 1 von Willebrand disease: Results from a Canadian cohort study". Blood. 109 (1): 145–54. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-05-021105. PMID 17190853.
- ↑ Gill, JC (1987). "The effect of ABO blood group on the diagnosis of von Willebrand disease". Blood. 69 (6): 1691–5. PMID 3495304. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help)