Valgus deformity
| Valgus deformity | |
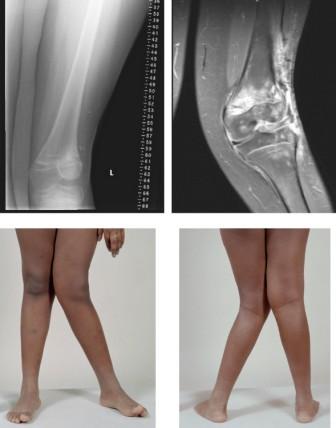 | |
|---|---|
| Valgus Deformity MRI and photograph | |
| ICD-10 | M21.0 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
In orthopedics, a valgus deformity is a term for the outward angulation of the distal segment of a bone or joint. The opposite of valgus is called varus.
The terms varus and valgus always refer to the direction that the distal segment of the joint points.
For a discussion of the etymology of these words, see the entry under varus.
Examples
- Hip: coxa valga (from Latin coxa = hip) — the shaft of the femur is bent outward in respect to the neck of the femur, causing bowleggedness.
- Knee: genu valgum (from Latin genu = knee) — the tibia is turned outward in relation to the femur, resulting in a knock-kneed appearance.
- Ankle: talipes valgus (from Latin talus = ankle and Greek pes = foot) — outward turning of the heel, resulting in clubfoot with the person walking on the inner part of the foot.
- Toe: hallux valgus (Latin hallux = big toe) — outward deviation of the big toe toward the second toe.
- Elbows: cubitus valgus (Latin cubitus = elbow) — turned-out elbows
See also
Template:Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue