Typhlitis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 162: | Line 162: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
Revision as of 14:58, 6 March 2015
|
WikiDoc Resources for Typhlitis |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Typhlitis |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Typhlitis at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Typhlitis at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Typhlitis
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Typhlitis Discussion groups on Typhlitis Directions to Hospitals Treating Typhlitis Risk calculators and risk factors for Typhlitis
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Typhlitis |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Synonyms and keywords: Neutropenic colitis; neutropenic enterocolitis
Overview
Typhlitis occurs in neutropenic patients undergoing treatment for a malignancy, most frequently patients with acute leukemia who are receiving chemotherapy. It has also been reported in patients with aplastic anemia, lymphoma, or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and after kidney transplantation. Typhlitis is characterized by edema and inflammation of the cecum, the ascending colon, and sometimes the terminal ileum. The inflammation can be so severe that transmural necrosis, perforation, and death can result. The mechanism of the condition is not known, but it is probably due to a combination of ischemia, infection (especially with cytomegalovirus), mucosal hemorrhage, and perhaps neoplastic infiltration. Treatment consists of bowel rest, total parenteral nutrition, antibiotics, and aggressive fluid and electrolyte replacement.
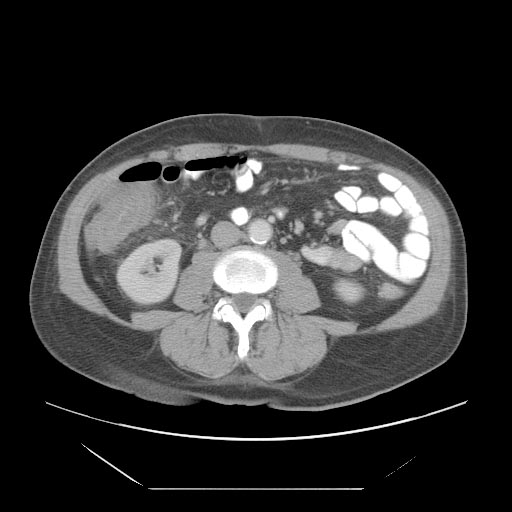
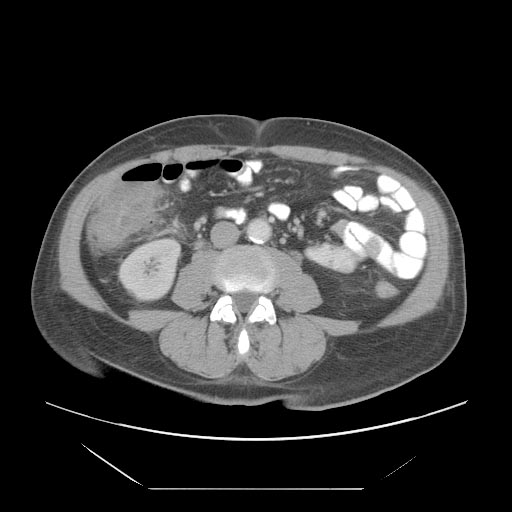
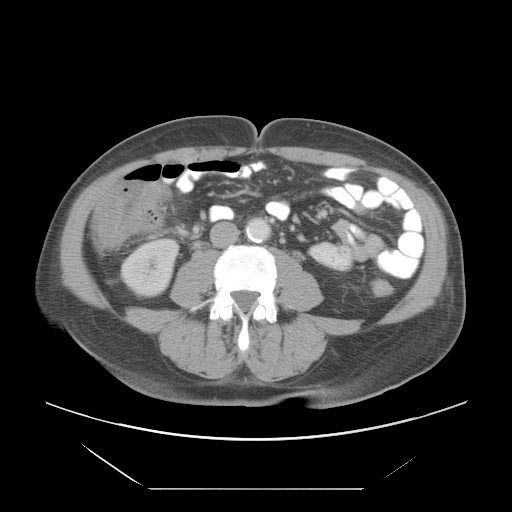
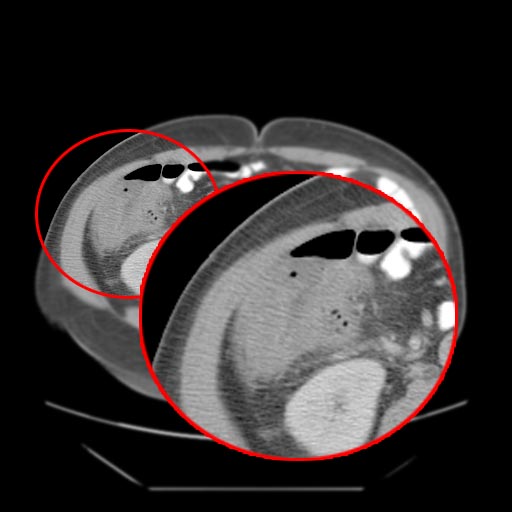
CT
- Cecal distention and circumferential thickening of the cecal wall
- Inflammatory stranding of the adjacent mesenteric fat is a common finding.
- Detection of complications such as pneumatosis, pneumoperitoneum, and pericolic fluid collections is important because they indicate a need for urgent surgical management.
Causes
Life Threatening Causes
Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated.
Common Causes
Causes by Organ System
| Cardiovascular | No underlying causes |
| Chemical/Poisoning | No underlying causes |
| Dental | No underlying causes |
| Dermatologic | No underlying causes |
| Drug Side Effect | Doxorubicin Hydrochloride, Sulfasalazine |
| Ear Nose Throat | No underlying causes |
| Endocrine | No underlying causes |
| Environmental | No underlying causes |
| Gastroenterologic | No underlying causes |
| Genetic | No underlying causes |
| Hematologic | No underlying causes |
| Iatrogenic | No underlying causes |
| Infectious Disease | No underlying causes |
| Musculoskeletal/Orthopedic | No underlying causes |
| Neurologic | No underlying causes |
| Nutritional/Metabolic | No underlying causes |
| Obstetric/Gynecologic | No underlying causes |
| Oncologic | No underlying causes |
| Ophthalmologic | No underlying causes |
| Overdose/Toxicity | No underlying causes |
| Psychiatric | No underlying causes |
| Pulmonary | No underlying causes |
| Renal/Electrolyte | No underlying causes |
| Rheumatology/Immunology/Allergy | No underlying causes |
| Sexual | No underlying causes |
| Trauma | No underlying causes |
| Urologic | No underlying causes |
| Miscellaneous | No underlying causes |