Trimethobenzamide (injection): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
Geriatric Patients | Geriatric Patients | ||
Dose adjustments such as reducing the total dose administered at each dosing or increasing the dosing interval should be considered in elderly patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤ 70 mL/min/1.73m2). Final dose adjustment should be based upon integration of clinical efficacy and safety considerations. | Dose adjustments such as reducing the total dose administered at each dosing or increasing the dosing interval should be considered in elderly patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤ 70 mL/min/1.73m2). Final dose adjustment should be based upon integration of clinical efficacy and safety considerations. | ||
Patients with Renal Impairment | Patients with Renal Impairment | ||
In subjects with renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤ 70 mL/min/1.73m2), dose adjustment such as reducing the total dose administered at each dosing or increasing the dosing interval should be considered. | In subjects with renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤ 70 mL/min/1.73m2), dose adjustment such as reducing the total dose administered at each dosing or increasing the dosing interval should be considered. | ||
INJECTABLE, 100 mg/mL (Not for use in pediatric patients) | INJECTABLE, 100 mg/mL (Not for use in pediatric patients) | ||
Revision as of 19:02, 7 May 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Turky Alkathery, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Trimethobenzamide (injection) is an antiemetic that is FDA approved for the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting and for nausea associated with gastroenteritis. Common adverse reactions include hypotension, anticholinergic adverse reaction and somnolence.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride is indicated for the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting and for nausea associated with gastroenteritis.
Dosage
Dosage should be adjusted according to the indication for therapy, severity of symptoms and the response of the patient.
Geriatric Patients Dose adjustments such as reducing the total dose administered at each dosing or increasing the dosing interval should be considered in elderly patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤ 70 mL/min/1.73m2). Final dose adjustment should be based upon integration of clinical efficacy and safety considerations.
Patients with Renal Impairment In subjects with renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤ 70 mL/min/1.73m2), dose adjustment such as reducing the total dose administered at each dosing or increasing the dosing interval should be considered.
INJECTABLE, 100 mg/mL (Not for use in pediatric patients)
Usual Adult Dosage 2 mL (200 mg) t.i.d. or q.i.d. intramuscularly. NOTE: The injectable form is intended for intramuscular administration only; it is not recommended for intravenous use.
Intramuscular administration may cause pain, stinging, burning, redness and swelling at the site of injection. Such effects may be minimized by deep injection into the upper outer quadrant of the gluteal region, and by avoiding the escape of solution along the route.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
The injectable form of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride is contraindicated in pediatric patients and in patients with known hypersensitivity to trimethobenzamide.
Warnings
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride may produce drowsiness. Patients should not operate motor vehicles or other dangerous machinery until their individual responses have been determined.
Precautions
During the course of acute febrile illness, encephalitides, gastroenteritis, dehydration and electrolyte imbalance, especially in children and the elderly or debilitated, CNS reactions such as opisthotonos, convulsions, coma and extrapyramidal symptoms have been reported with and without use of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride or other antiemetic agents. In such disorders caution should be exercised in administering trimethobenzamide hydrochloride, particularly to patients who have recently received other CNS-acting agents (phenothiazines, barbiturates, belladonna derivatives). Primary emphasis should be directed toward the restoration of body fluids and electrolyte balance, the relief of fever and relief of the causative disease process. Overhydration should be avoided since it may result in cerebral edema.
The antiemetic effects of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride may render diagnosis more difficult in such conditions as appendicitis and obscure signs of toxicity due to overdosage of other drugs.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There have been reports of hypersensitivity reactions and Parkinson-like symptoms. There have been instances of hypotension reported following parenteral administration to surgical patients. There have been reports of blood dyscrasias, blurring of vision, coma, convulsions, depression of mood, diarrhea, disorientation, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, jaundice, muscle cramps and opisthotonos. If these occur, the administration of the drug should be discontinued. Allergic-type skin reactions have been observed; therefore, the drug should be discontinued at the first sign of sensitization. While these symptoms will usually disappear spontaneously, symptomatic treatment may be indicated in some cases.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride was studied in reproduction experiments in rats and rabbits and no teratogenicity was suggested. The only effects observed were an increased percentage of embryonic resorptions or stillborn pups in rats administered 20 mg and 100 mg/kg and increased resorptions in rabbits receiving 100 mg/kg. In each study these adverse effects were attributed to one or two dams. The relevance to humans is not known. Since there is no adequate experience in pregnant or lactating women who have received this drug, safety in pregnancy or in nursing mothers has not been established.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Trimethobenzamide (injection) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
Clinical studies of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Although there are studies reported in the literature that include elderly patients >65 years old with younger patients, it is not known if there are differences in efficacy or safety parameters for elderly and non-elderly patients treated with trimethobenzamide. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
A substantial route of elimination of unchanged trimethobenzamide is via the kidney. Dosage adjustment should be considered in patients with reduced renal function including some elderly patients.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Trimethobenzamide (injection) in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Trimethobenzamide (injection) and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
| |
Trimethobenzamide (injection)
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
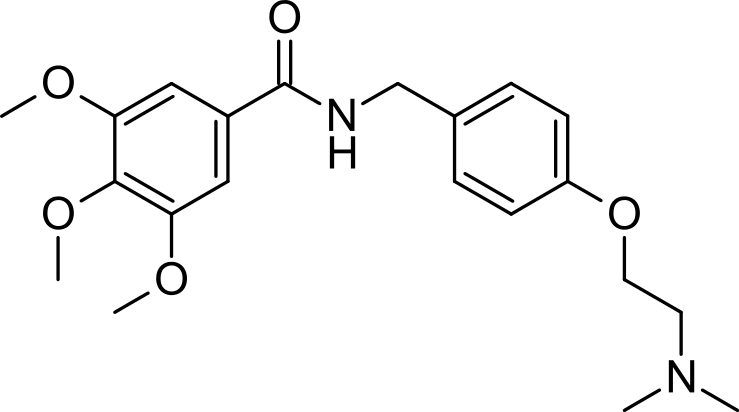
| N-{[4-(2-dimethylaminoethoxy)phenyl]methyl}- 3,4,5-trimethoxy-benzamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | R06 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 388.458 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60-100% |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | 7 to 9 hours (mean) |
| Excretion | urine (30-50%), faeces |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
C(US) |
| Legal status |
[[Prescription drug|Template:Unicode-only]](US) |
| Routes | Oral, rectal, intramuscular |
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride as determined in animals is obscure, but may involve the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ), an area in the medulla oblongata through which emetic impulses are conveyed to the vomiting center; direct impulses to the vomiting center apparently are not similarly inhibited. In dogs pretreated with trimethobenzamide HCl, the emetic response to apomorphine is inhibited, while little or no protection is afforded against emesis induced by intragastric copper sulfate.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of trimethobenzamide have been studied in healthy adult subjects. Following administration of 200 mg (100 mg/mL) trimethobenzamide hydrochloride IM injection, the time to reach maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) was about half an hour, about 15 minutes longer for trimethobenzamide hydrochloride 300 mg oral capsule than an IM injection. A single dose of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride 300 mg oral capsule provided a plasma concentration profile of trimethobenzamide similar to trimethobenzamide hydrochloride 200 mg IM. The relative bioavailability of the capsule formulation compared to the solution is 100%. The mean elimination half-life of trimethobenzamide is 7 to 9 hours. Between 30 – 50% of a single dose in humans is excreted unchanged in the urine within 48 – 72 hours. The metabolic disposition of trimethobenzamide in humans is not known. Specifically, it is not known if active metabolites are generated in humans.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
Single Dose Vials, 2 mL, trays of 25 NDC 42023-143-25 100 mg/mL in 2 mL Single Dose Vials Multi-Dose Vials, 20 mL NDC 42023-142-01 100 mg/mL in 20 mL Multi-Dose Vials
Storage
Store between 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). (See USP Controlled Room Temperature.)
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Trimethobenzamide (injection) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Trimethobenzamide (injection) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Concomitant use of alcohol with trimethobenzamide hydrochloride may result in an adverse drug interaction.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Trimethobenzamide (injection) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.