Ticarcillin
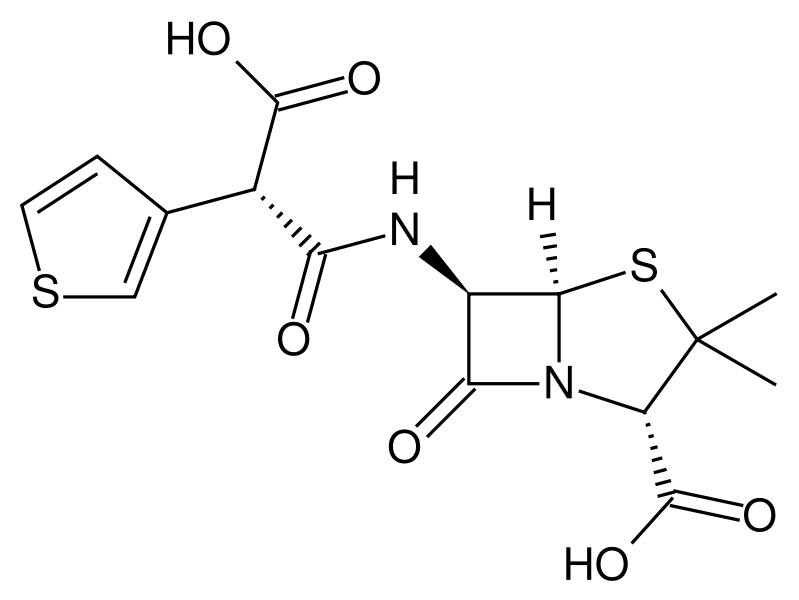 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 45% |
| Elimination half-life | 1.1 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H16N2O6S2 |
| Molar mass | 384.429 g/mol |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Ticarcillin |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Ticarcillin Most cited articles on Ticarcillin |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Ticarcillin |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Ticarcillin at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Ticarcillin at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Ticarcillin
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Ticarcillin Discussion groups on Ticarcillin Patient Handouts on Ticarcillin Directions to Hospitals Treating Ticarcillin Risk calculators and risk factors for Ticarcillin
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Ticarcillin |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Ticarcillin is a carboxypenicillin. It is almost invariably sold and used in combination with clavulanate as Timentin®. Because it is a penicillin, it also falls within the larger class of beta-lactam antibiotics. Its main clinical use is as an injectable antibiotic for the treatment of gram negative bacteria, in particular, Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Chemically, ticarcillin is C15H16N2O6S2 (CAS number 34787-01-4). It is provided as a white or pale yellow powder. It is highly soluble in water, but should only be dissolved immediately before use to prevent degradation.
Mechanism of Action
Ticarcillin's antibiotic properties arise from its ability to prevent cross-linking of peptidoglycan during cell wall synthesis when the bacteria tries to divide, causing death.
Ticarcillin is similar to penicilin in that it contains a β-lactam ring. This can lead to resistance in bacteria containing β-lactamase, which cleaves the ring and inactivates it. It is often paired with a β-lactamase inhibitor such as clavulanic acid. Because of ticarcillins similarties to penicillin, including the β-lactam ring, it can cause similar allergic reactions in patients sensitive to penicillin.
Other Uses
In molecular biology, ticarcillin is used to as an alternative to ampicillin to test the uptake of marker genes into bacteria. It prevents the appearance of satellite colonies that occur when ampicillin breaks down in the media. It is also used in plant molecular biology to kill agrobacterium, which is used to deliver genes to plant cells.
Dosing and Posology
Ticarcillin is not absorbed orally, and therefore must be given by intravenous or intramuscular injection. The usual adult dose of Timentin is 3.5g four times a day.
Trade Names and Preparations
- Ticarcillin: Ticar® (Formerly marketed by Beecham, then SmithKline Beecham until 1999, when it merged with Glaxo to form GlaxoSmithKline; no longer available in the UK. US distribution ceased in 2004. Ticar was replaced by Timentin.)
- Ticarcillin/clavulanate: Timentin® (UK and US, marketed by Beecham, then GlaxoSmithKline).
- Pages with script errors
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Beta-lactam antibiotics
- Pharmacology
- Antibiotics