Thymoma (patient information): Difference between revisions
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
==Prevention of thymoma== | ==Prevention of thymoma== | ||
For the causes of thymoma are not clear, it is not yet possible to know how to prevent them. | |||
==What to expect (Outook/Prognosis)?== | ==What to expect (Outook/Prognosis)?== | ||
Revision as of 16:01, 26 August 2009
For the WikiDoc page for this topic, click here
| Thymoma (patient information) | |
 | |
|---|---|
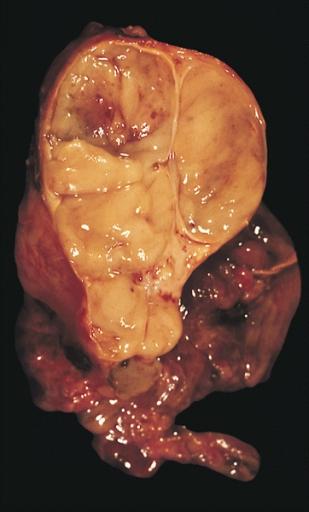
| Thymoma: A bottle-shaped tumor is encapsulated and shows a bulging, rather homogeneous, faintly lobulated ivory-colored cut surface. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology | |
| ICD-10 | C37.9, D60 |
| ICD-9 | 164.0, 212.6 |
| ICD-O: | 8580 |
| DiseasesDB | 13067 |
| MedlinePlus | 001086 |
| eMedicine | med/2752 med/3448 ped/2246 |
| MeSH | D013945 |
Editor-in-Chief: Jinhui Wu
Please Join in Editing This Page and Apply to be an Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [1] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
What is thymoma?
The thymus lies in the upper chest under the breastbone and it is part of the lymph system. There are different types of tumors of the thymus: thymoma and thymic carcinomas. Thymoma usually is benign, and frequently encapsulated. Thymoma doesn't have any early symptoms. With the development of the tumor, frequent symptoms include trouble breathing, cough or chest pain. Treatments include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy or hormone therapy.
How do I know if I have thymoma and what are the symptoms of thymoma?
Early thymoma does not have any symptoms. As the tumor grows larger, people may notice one or more of the following symptoms:
- Cough that doesn't go away
- Trouble breathing
Other health problems may also cause these symptoms. Only a doctor can tell for sure. A person with any of these symptoms should tell the doctor so that the problems can be diagnosed and treated as early as possible.
Who is at risk for thymoma?
Not much is known about why thymoma develop in some people but not in others.
How to know you have thymoma?
- Chest x-ray: An x-ray test is a basic test for thymoma. It may go through the chest and make a picture of areas inside the body.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan and biopsy: CT scans are often used to diagnose thymoma. It can confirm the location of the tumor and show the organs in the mediastinum, as well as lymph nodes. These are helpful for determining whether surgery is a good treatment option. CT scans can also be used to guide biopsy and a biopsy sample is usually removed and looked at under a microscope.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI uses magnetic fields but it is a different type of image than what is produced by computed tomography (CT) and produces detailed images of the body. Like computed tomography (CT), a contrast agent may be injected into a patient’s vein to create a better picture.
When to seek urgent medical care?
Call your health care provider if symptoms of thymoma develop. If you experience either of the following symptoms, seeking urgent medical care as soon as possible:
- Severe shortness of breathing
- Large hemoptysis
Treatment options
Patients with thymoma have many treatment options. The selection depends on the stage of the tumor. The options are surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone treatment, or a combination of these methods. Before treatment starts, ask your health care team about possible side effects and how treatment may change your normal activities. Because cancer treatments often damage healthy cells and tissues, side effects are common. Side effects may not be the same for each person, and they may change from one treatment session to the next.
- Surgery: Surgery is the most common treatment for thymoma. After surgery, other types of treatment can be done in order to increase the chances of a cure.
- Radiation therapy: This therapy does not usually work well for kidney cancer. In some cases, hormone treatments may reduce the growth of the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: The treatment is to use drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing.
- Hormone therapy: This kind of treatment is to remove hormones or block their action and stop cancer cells from growing. Drugs usual used in thymoma is called corticosteroids.
Diseases with similar symptoms
- Dysembryoma
Where to find medical care for thymoma?
Directions to Hospitals Treating thymoma
Prevention of thymoma
For the causes of thymoma are not clear, it is not yet possible to know how to prevent them.
What to expect (Outook/Prognosis)?
The prognosis of thymoma depends on the following:
- The location of the tumor
- The stage of the tumor
- Whether the tumor can be removed completely by surgery
- The patient's general health
- Whether the cancer has just been diagnosed or has recurred
Copyleft Sources
http://www.cancer.org/docroot/cri/content/cri_2_4_1x_what_is_thymus_cancer_42.asp?sitearea=&level=
http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/treatment/thymoma/patient