Thoracic aortic aneurysm pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
* The aortic aneurysms associated with [[Marfan syndrome]] grow at a faster rate and are more prone to rupture. | * The aortic aneurysms associated with [[Marfan syndrome]] grow at a faster rate and are more prone to rupture. | ||
* Most thoracic aneurysms are asymptomatic. However, the enlarging aorta can compress adjacent organs and cause symptoms like [[chest pain]], [[dyspnea]], [[hoarseness]] of voice, [[cough]] and [[dysphagia]]. Also symptoms of [[congestive heart failure]] can occur from severe [[aortic regurgitation]] and congestion of head, neck and upper extremities from [[superior vena cava]] compression. | * Most thoracic aneurysms are asymptomatic. However, the enlarging aorta can compress adjacent organs and cause symptoms like [[chest pain]], [[dyspnea]], [[hoarseness]] of voice, [[cough]] and [[dysphagia]]. Also symptoms of [[congestive heart failure]] can occur from severe [[aortic regurgitation]] and congestion of head, neck and upper extremities from [[superior vena cava]] compression. | ||
===Elastin and collagen=== | |||
* Increased activity of certain enzymes causes degradation of [[elastin]] and [[collagen]] in the arteries. This weakens the aortic wall and causes it to dilate. | |||
===Gross Pathology=== | ===Gross Pathology=== | ||
Revision as of 18:45, 19 October 2012
|
Thoracic aortic aneurysm Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Special Scenarios |
|
Case Studies |
|
Thoracic aortic aneurysm pathophysiology On the Web |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Thoracic aortic aneurysm pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Thoracic aortic aneurysm pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
An aneurysm occurs when a part or entire circumference of the vessel is pathologically dilated. A true aneurysm involves all three layers of the vessel, whereas pseudoaneurysm is characterized by disruption of the intima and media, and the dilated segment of the aorta is lined by adventitia alone.
Pathophysiology
- The clinical manifestations of thoracic aortic aneurysms depends on hemo-dynamic factors as well as factors intrinsic to individual arterial components.
- Cystic medial necrosis is the most common pathology associated with ascending aortic aneurysms, whereas atherosclerosis is most frequently involved in the arch and descending aorta.
- The aortic aneurysms associated with Marfan syndrome grow at a faster rate and are more prone to rupture.
- Most thoracic aneurysms are asymptomatic. However, the enlarging aorta can compress adjacent organs and cause symptoms like chest pain, dyspnea, hoarseness of voice, cough and dysphagia. Also symptoms of congestive heart failure can occur from severe aortic regurgitation and congestion of head, neck and upper extremities from superior vena cava compression.
Elastin and collagen
- Increased activity of certain enzymes causes degradation of elastin and collagen in the arteries. This weakens the aortic wall and causes it to dilate.
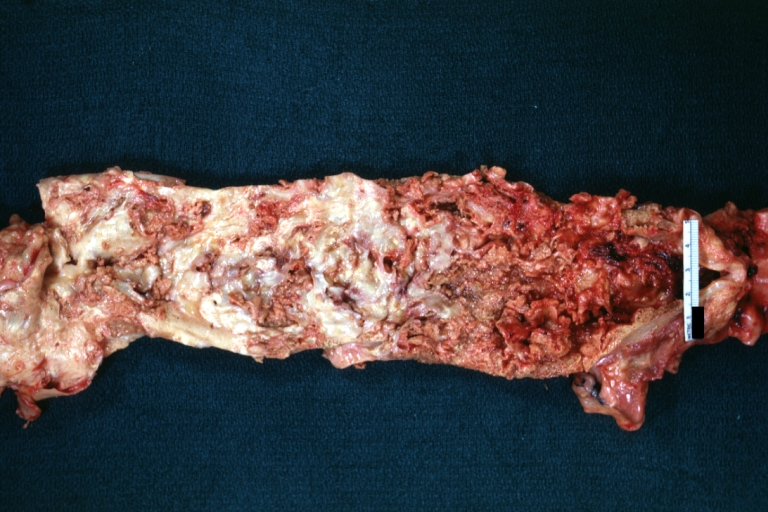
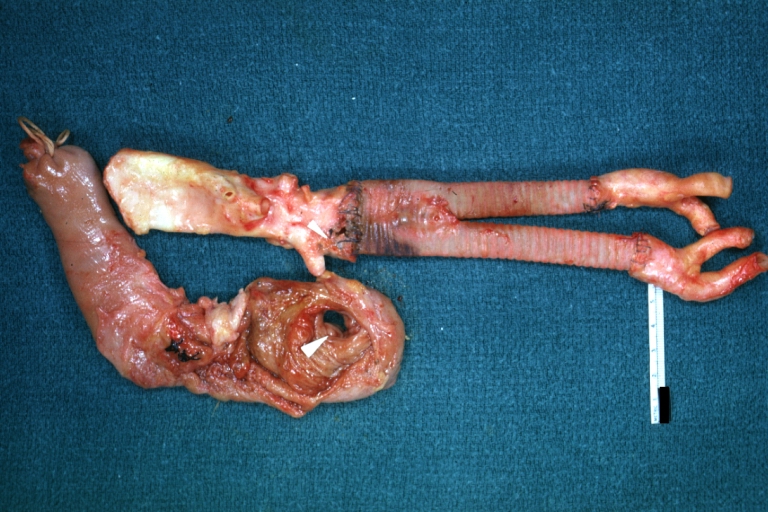
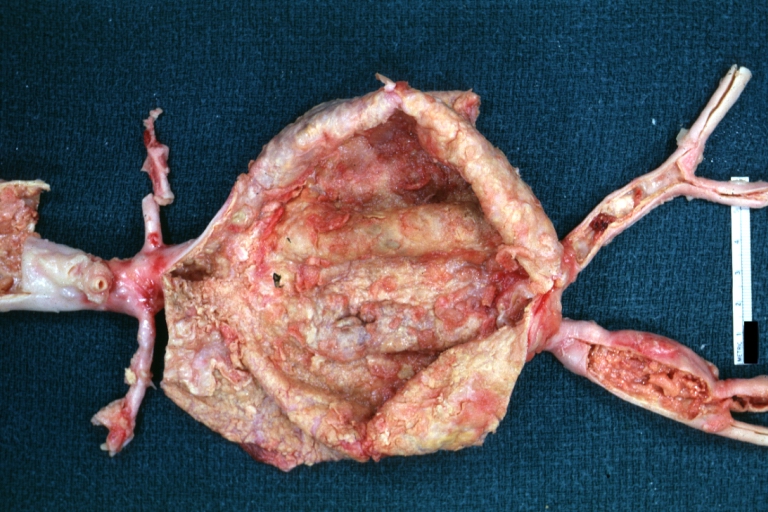
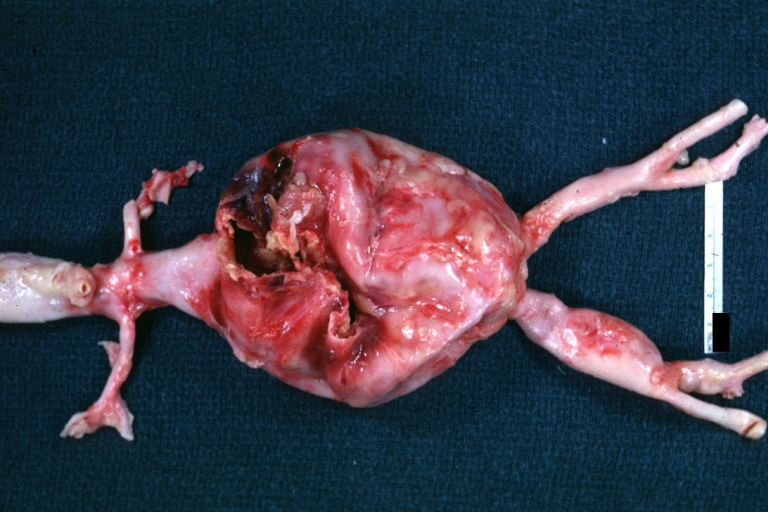
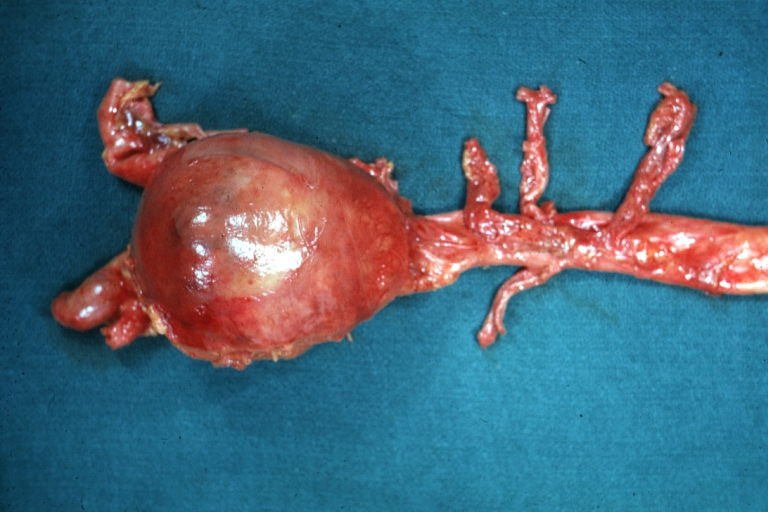
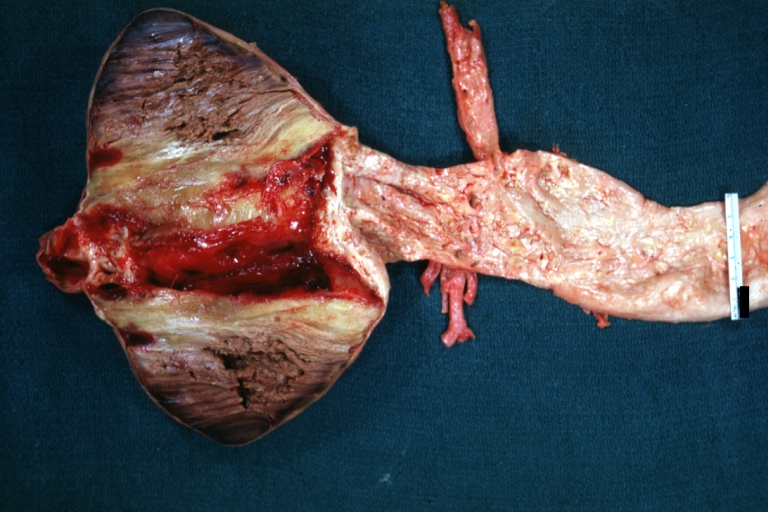
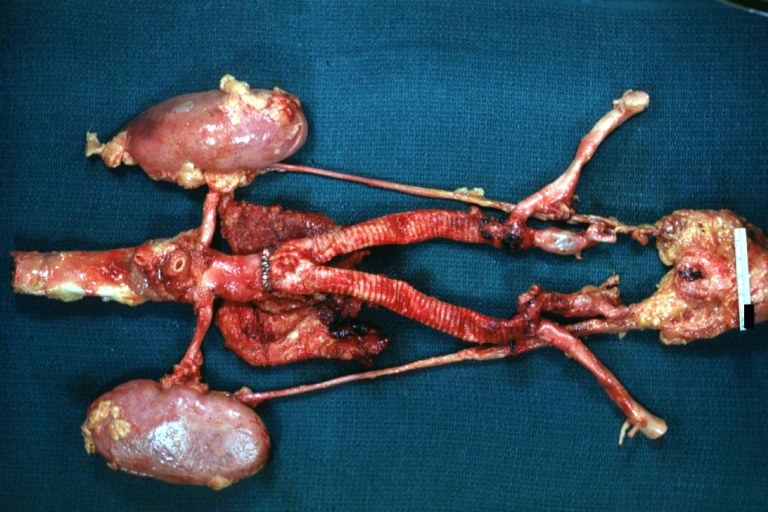
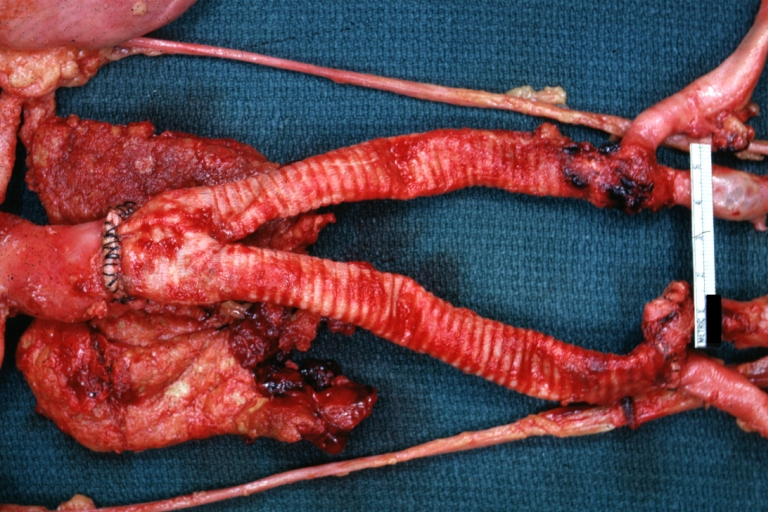
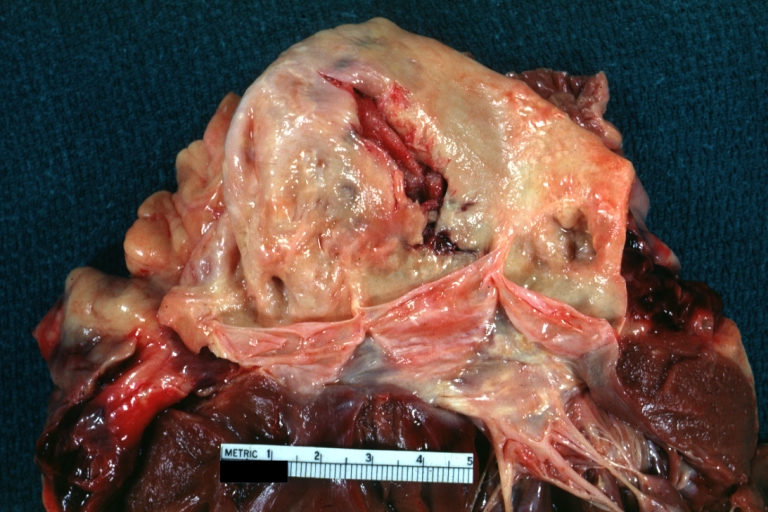
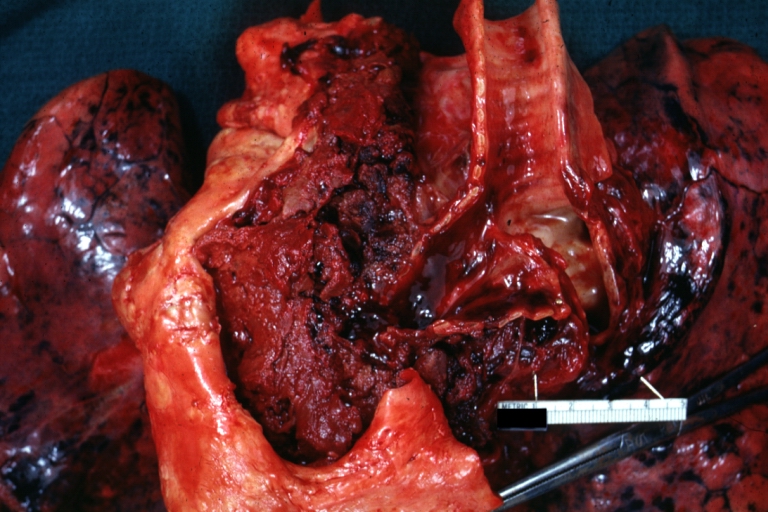
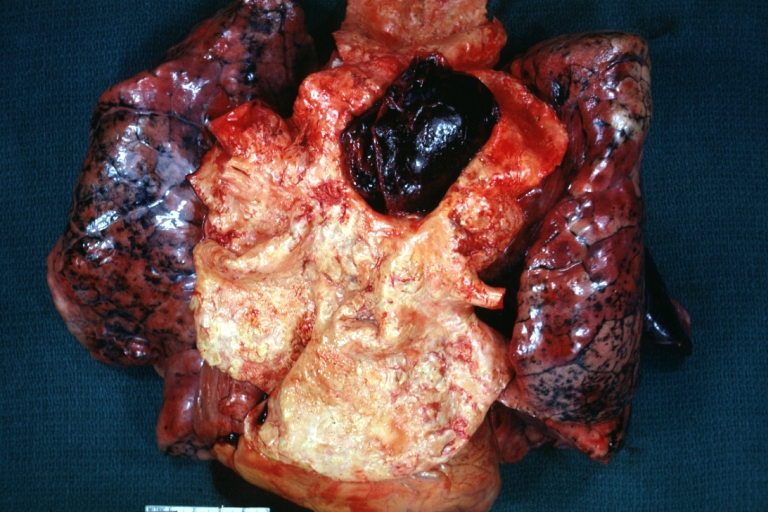
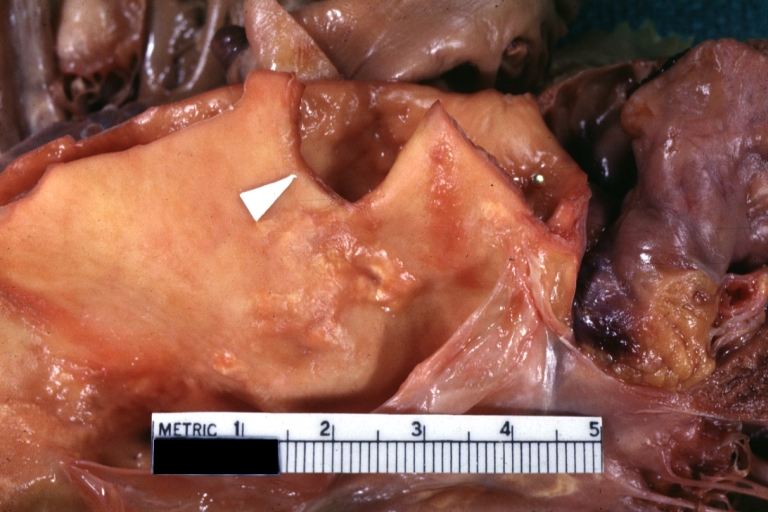
Gross Pathology
-
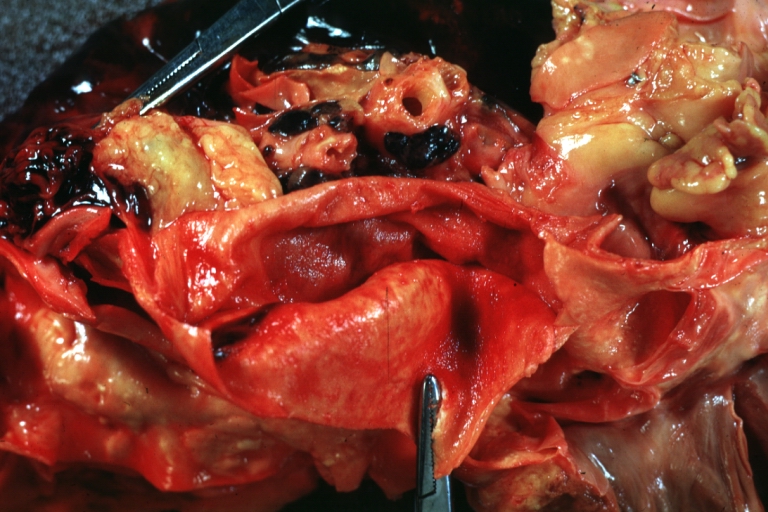
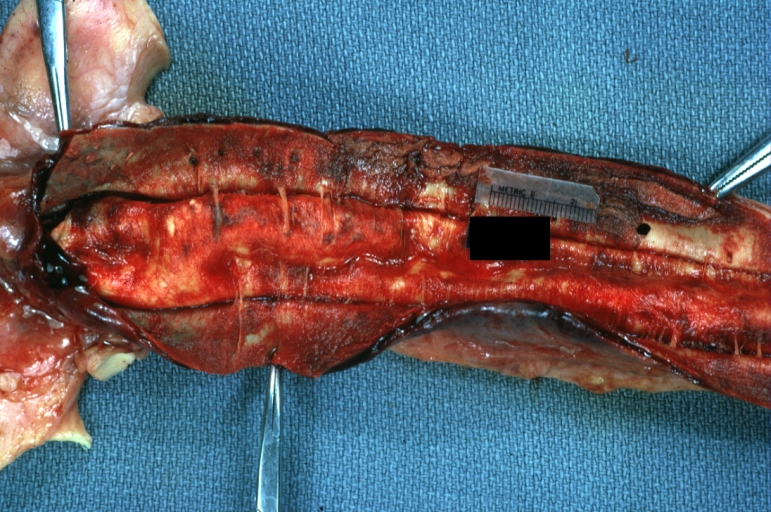
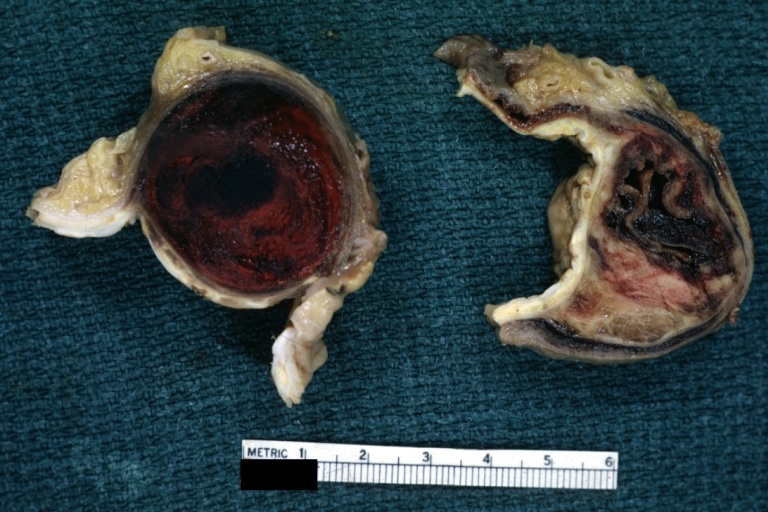
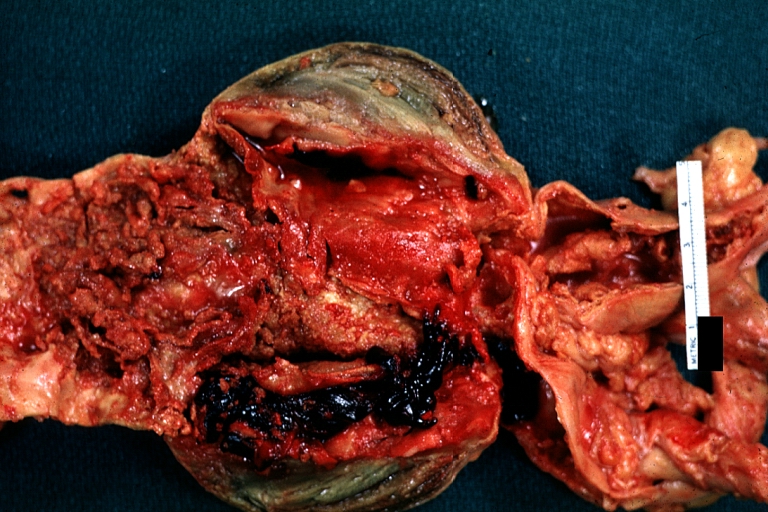
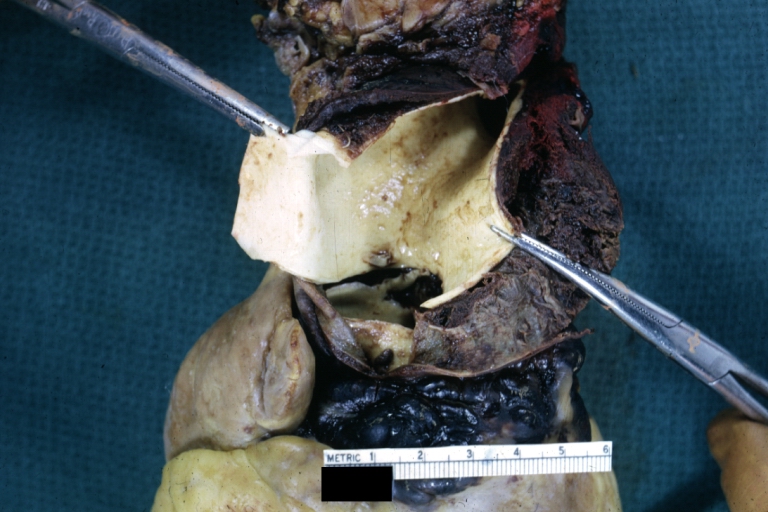
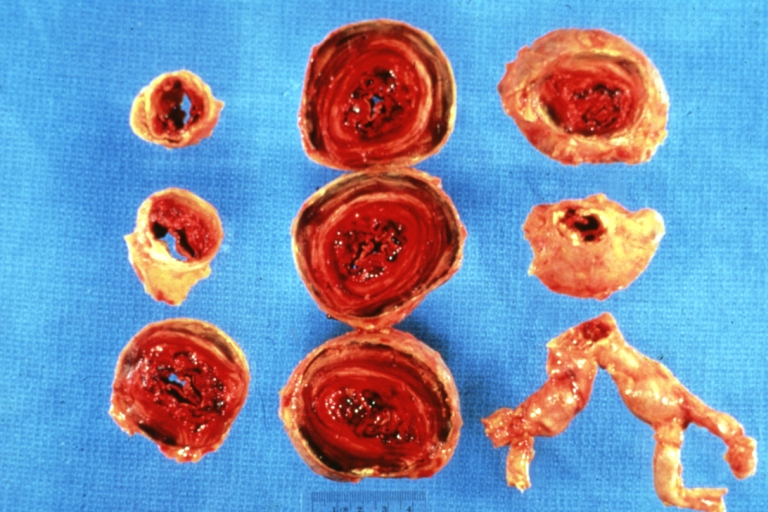
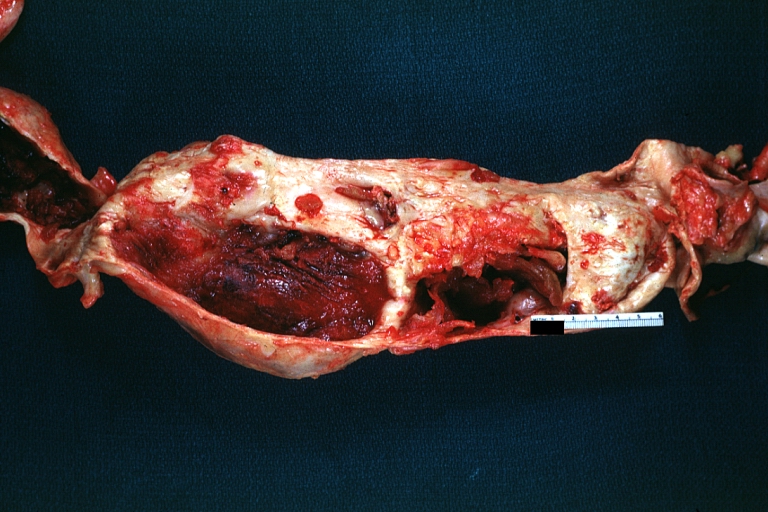
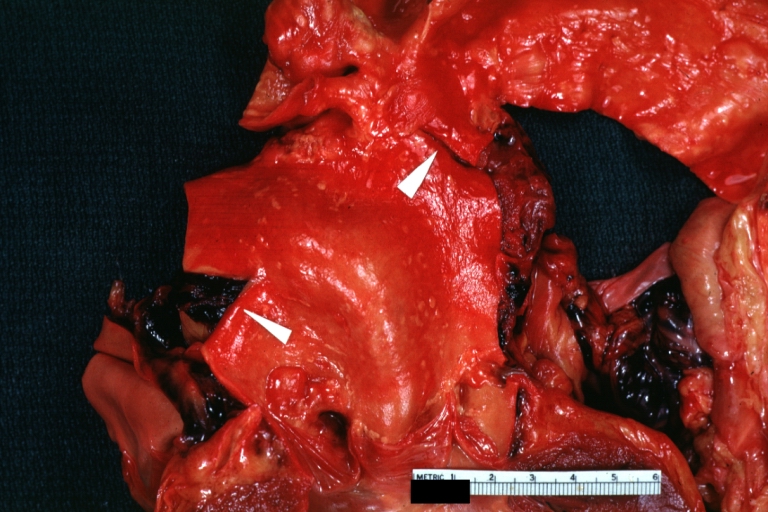
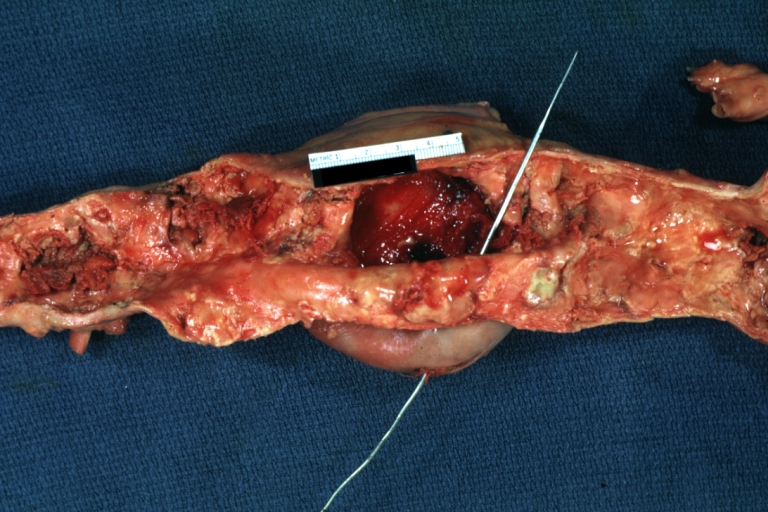
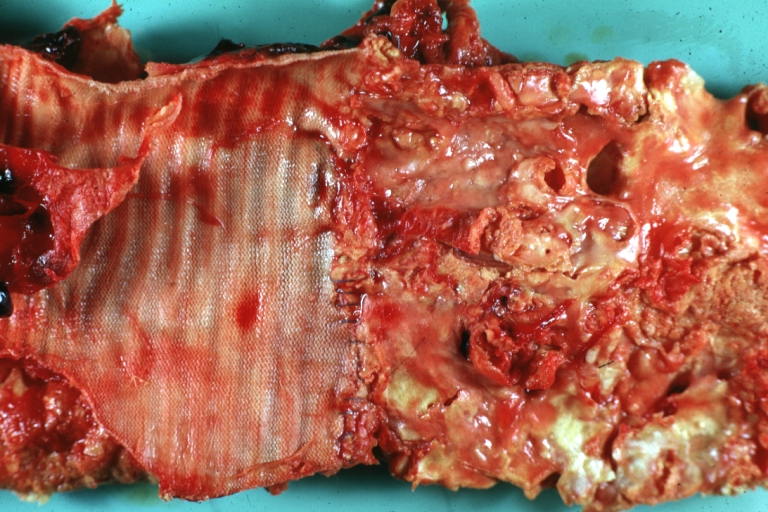
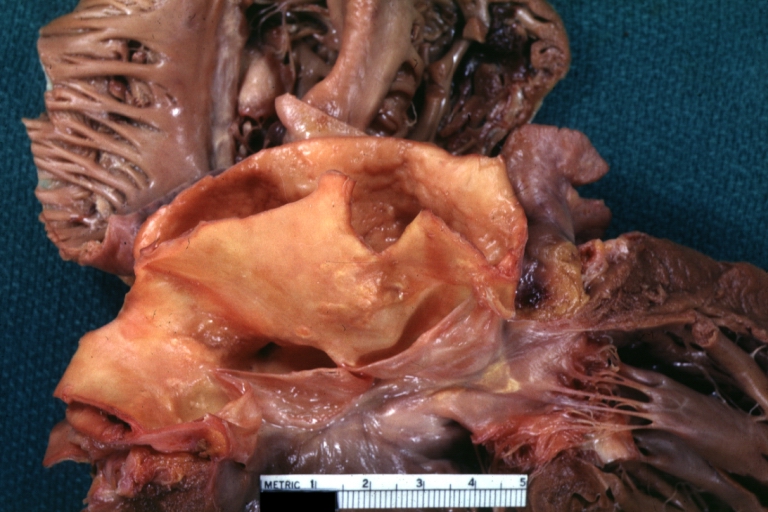
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross very good example dissected channel has been opened
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross external view good appearance from adventitia
-
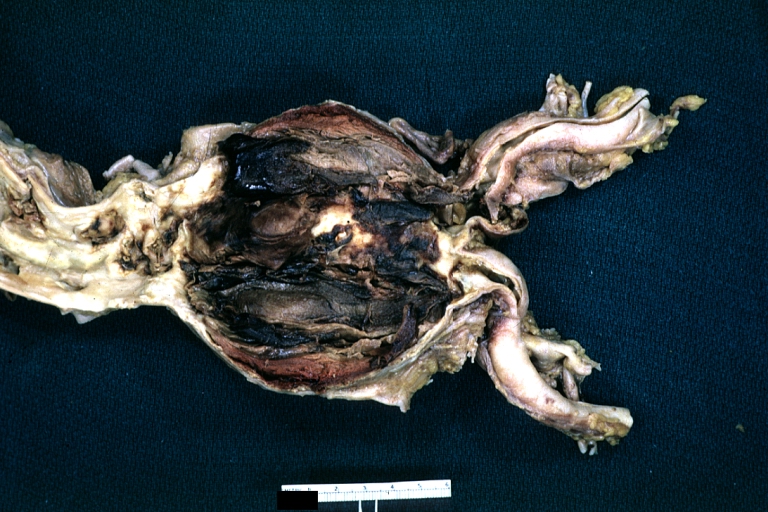
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross opened false channel
-
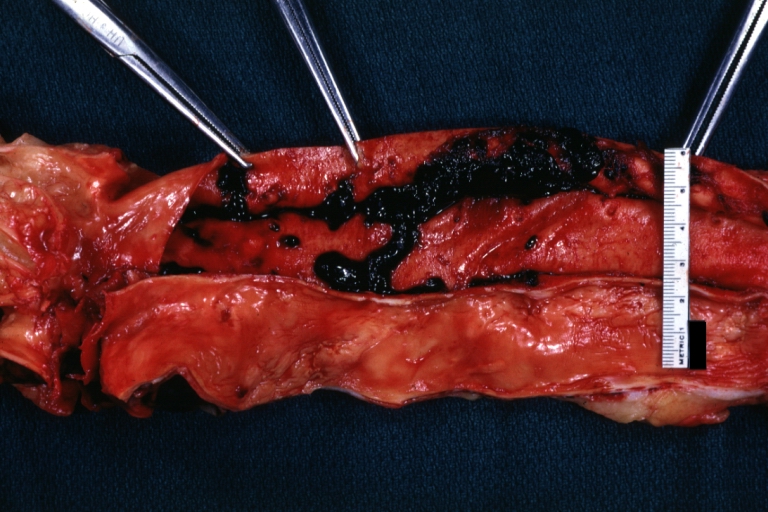
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross good example dissection beginning at third portion aortic arch
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross cross sections showing thrombus in false lumen true lumen has been opened longitudinally
-
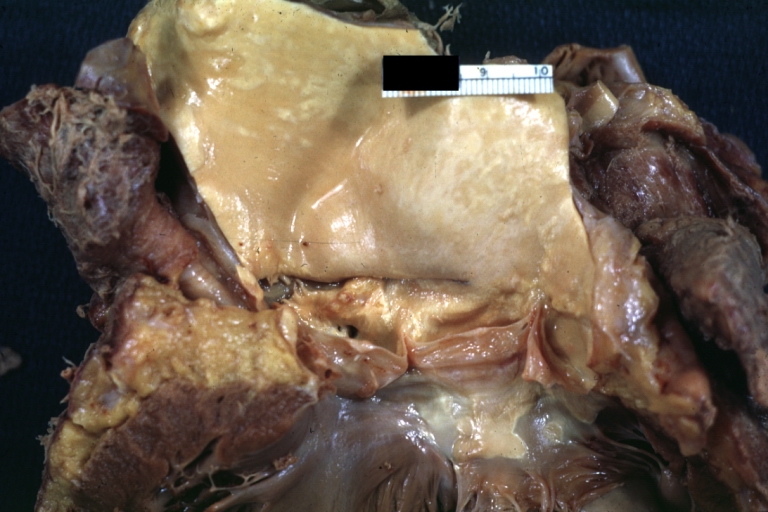
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross shows origin just above aortic valve false channel shown in descending thoracic aorta (very good example)
-
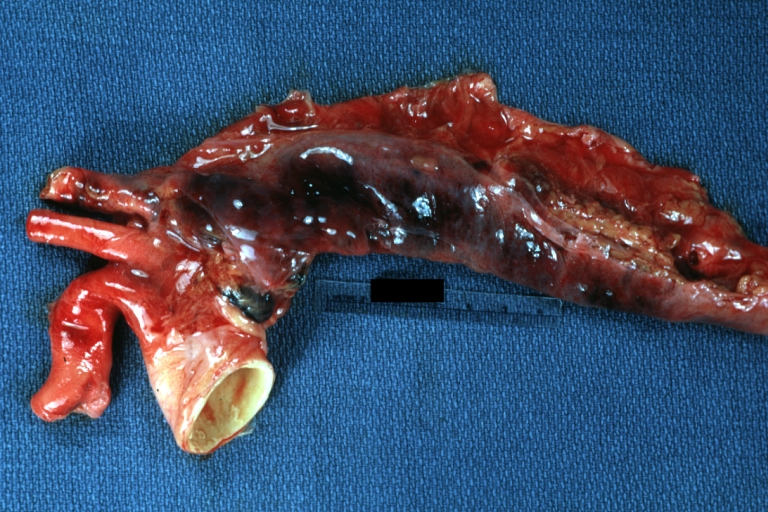
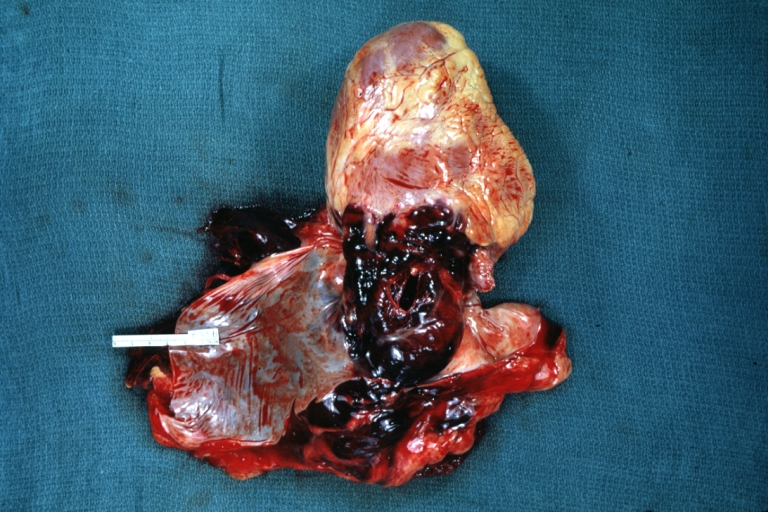
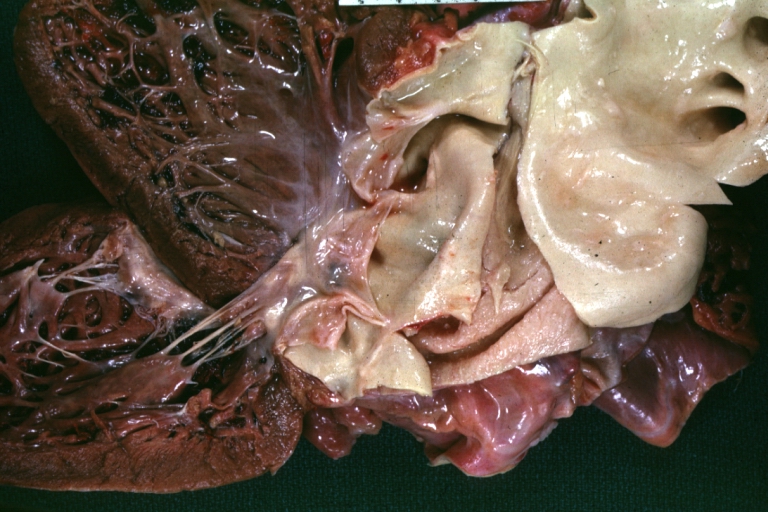
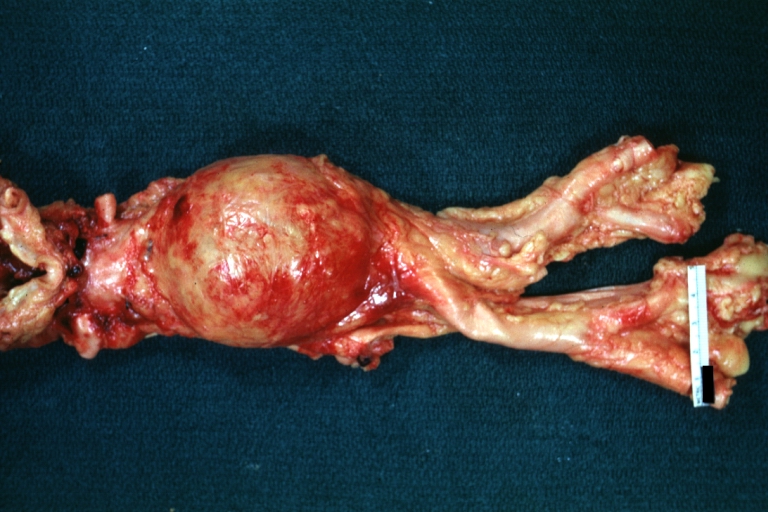
Atherosclerotic Aneurysm: Gross, a good example of typical abdominal aorta aneurysm with mural thrombus
-
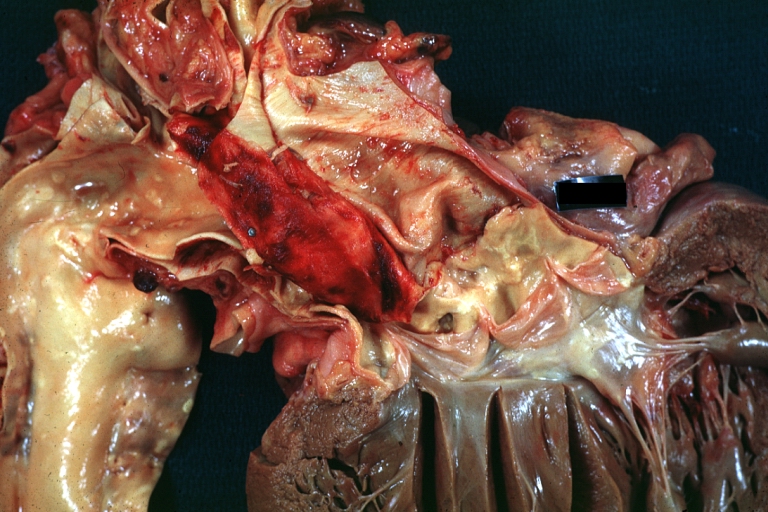
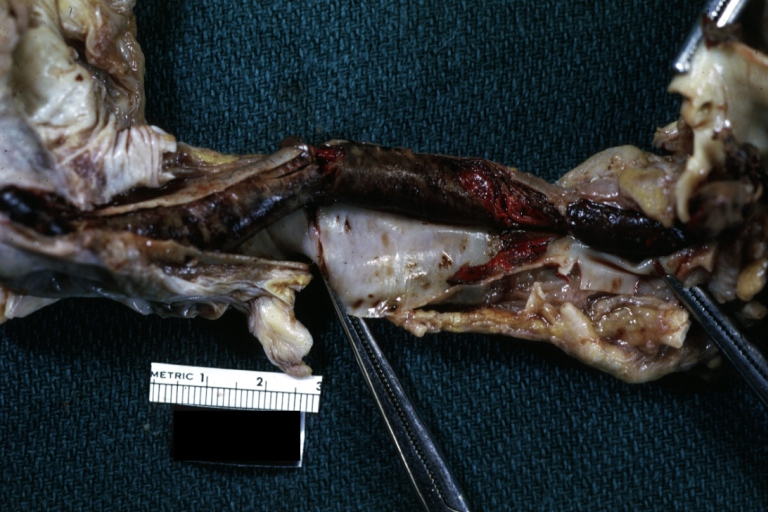
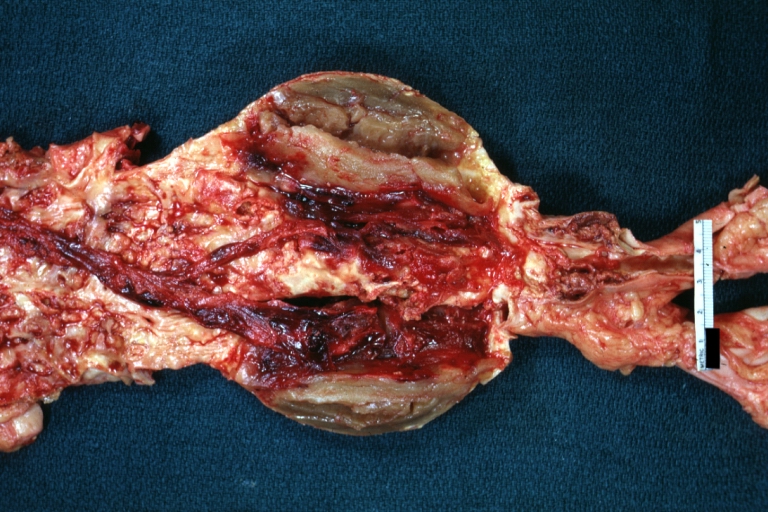
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, a very good example of dissection beginning just above aortic ring
-
Atherosclerotic Aneurysm: Gross, (rather) good example of abdominal aortic aneurysm
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, an excellent example, starting just above the aortic valve with reflection of aorta to show the dissection tract and some thrombus
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross shows dilated aorta with extensive atherosclerosis dissection is seen, a small abdominal aorta atherosclerotic aneurysm is present good for association of dilation with dissection
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross arrow points to start of dissection in first portion aortic arch good but not the best example shows dilation
-
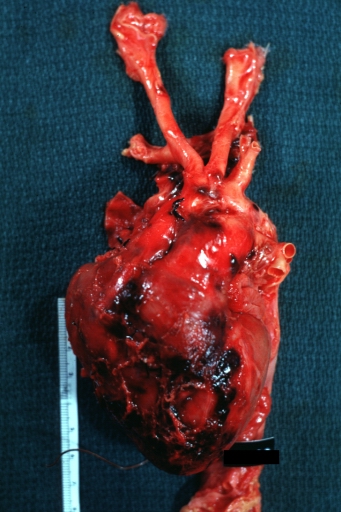
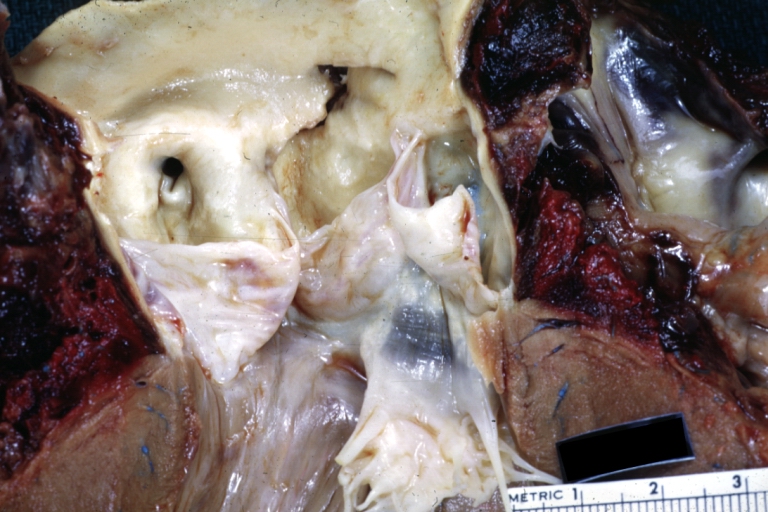
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, very good to show start of dissection above aortic valve and blood in false channel
-
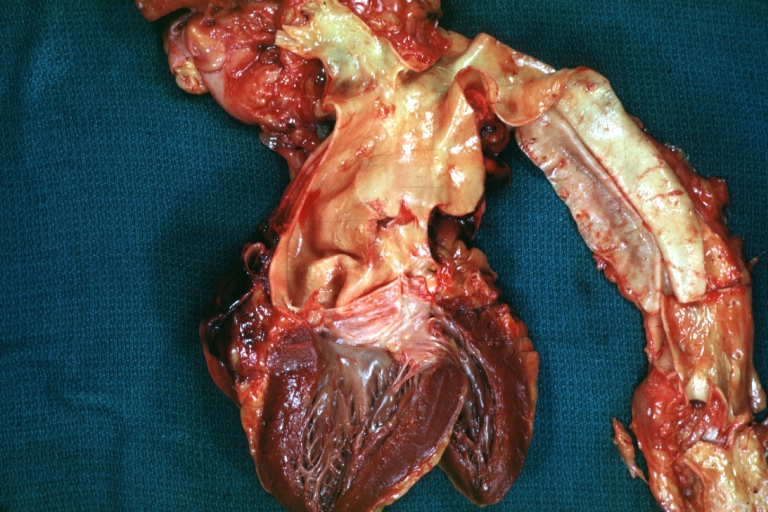
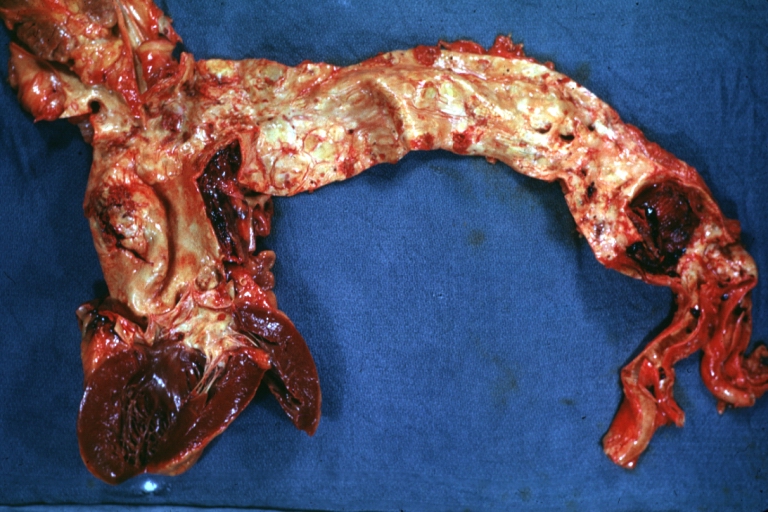
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, heart with root of aorta to show hemorrhage into pericardium (a very good example)
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, of heart and aorta with dissection and large false channel (a good example)
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross cross section of aorta with two channels (a good example)
-
Atherosclerotic Aneurysm: Gross, a nice view of cross section of abdominal aorta aneurysm
-
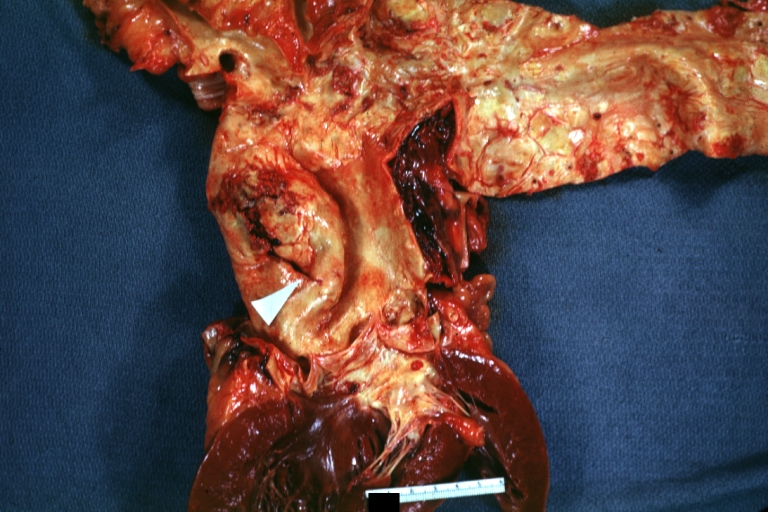
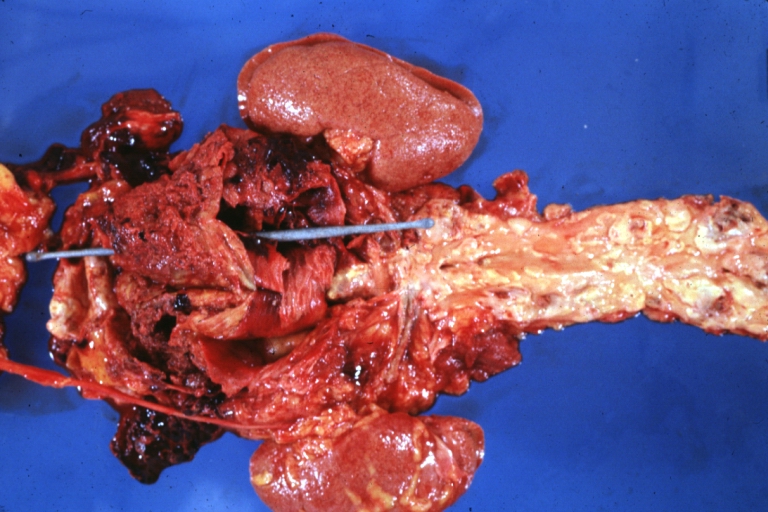
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross good example of typical angular tear above aortic valve
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross good example angular tear above aortic valve
-
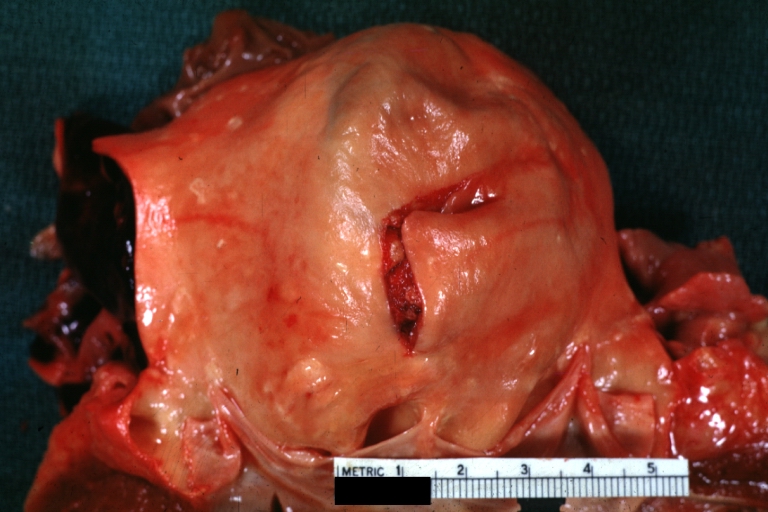
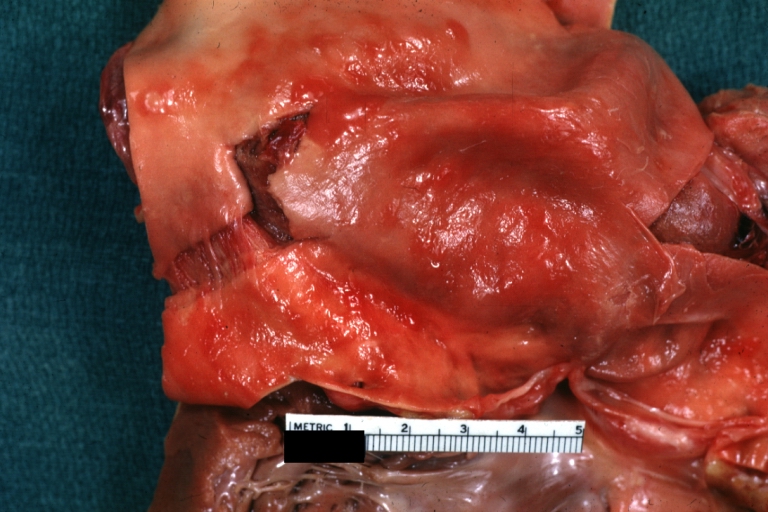
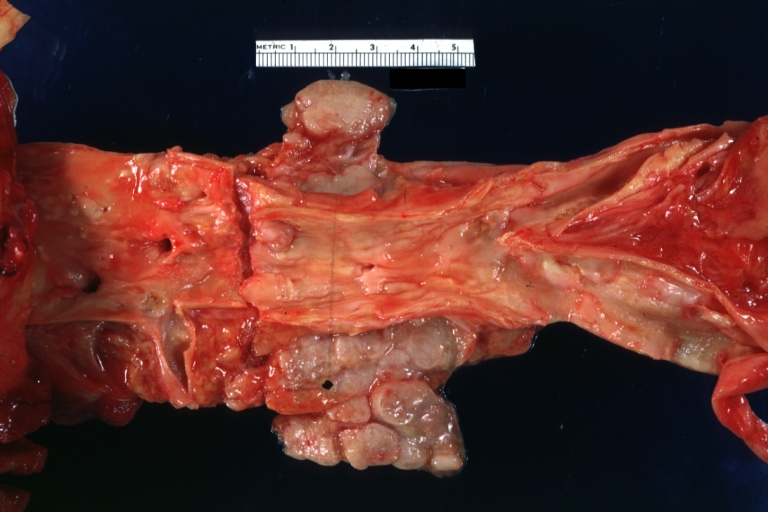
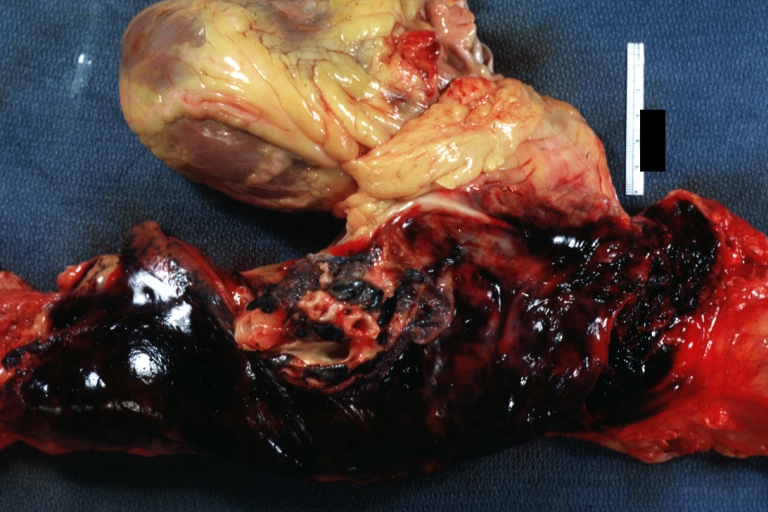
Atherosclerotic Aneurysm: Gross, external natural color very good example of an atherosclerotic thoracic aorta aneurysm with focal rupture
-
Atherosclerotic Aneurysm: Gross, excellent color, opened thoracic segment of aorta with two saccular atherosclerotic ruptured aneurysms
-
Atherosclerotic Aneurysm: Gross, an excellent example, natural color, external view of typical thoracic aortic aneurysms
-
Atherosclerotic Aneurysm: Gross unopened lesion natural color
-
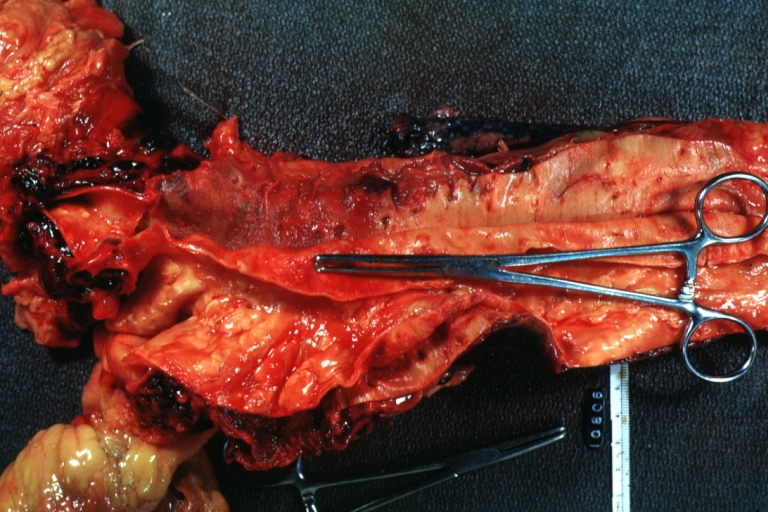
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross dissection first portion of arch fixed specimen (a good example)
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, rather well shown dissection in first portion of the aortic arch
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, rather well shown dissection in first portion of the aortic arch
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, an excellent example of type I lesion
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, external view, an excellent example
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, Type I shows false channel
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, opened to show false channel (good example)
-
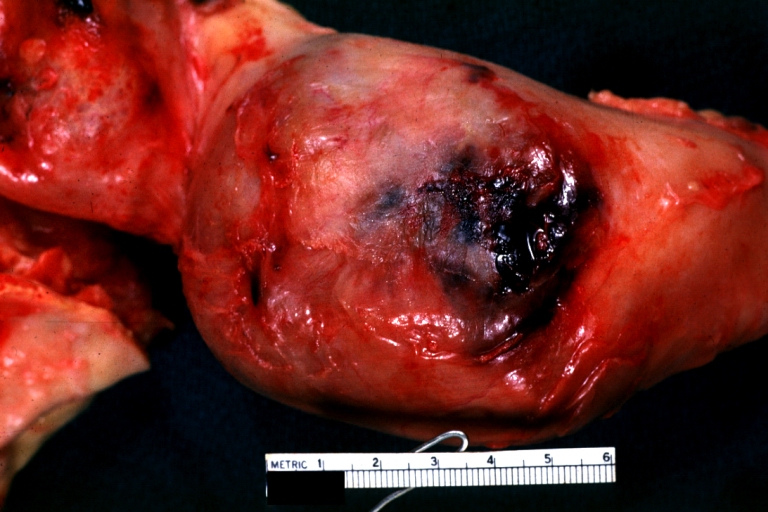
Atherosclerotic Aneurysm: Gross, very good example of ruptured thoracic segment
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, coagulum of blood in false channel
-
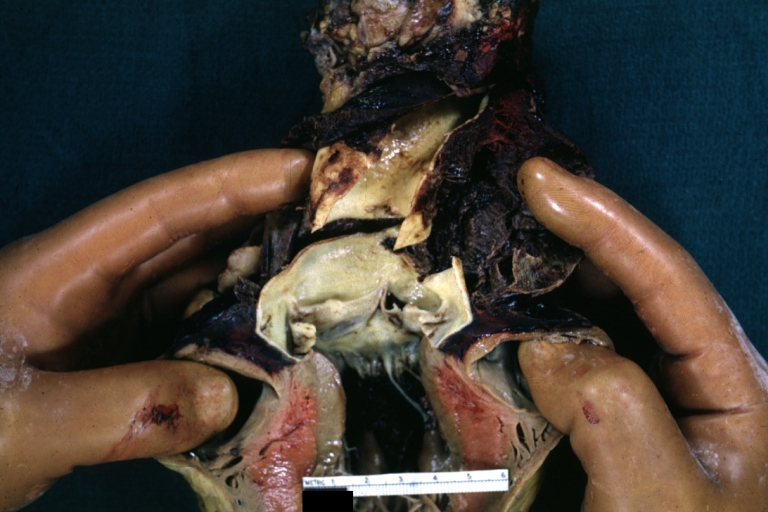
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, aortic valve area dissection (well shown, typical lesion)
-
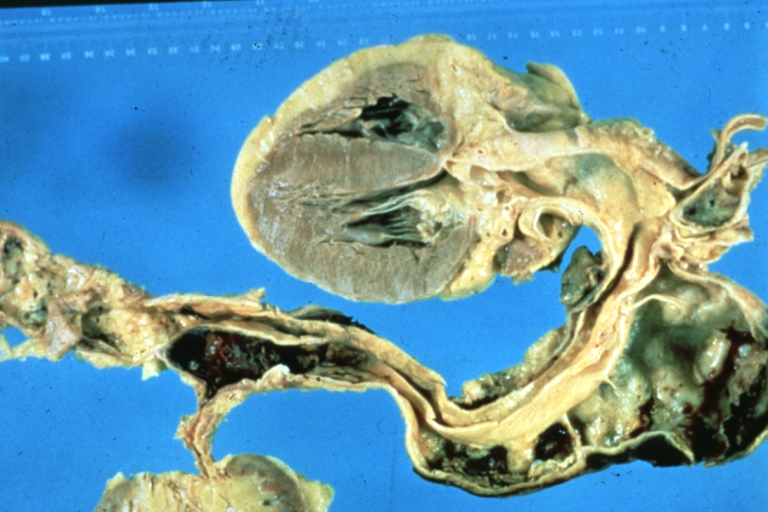
Abdominal Aneurysm Ruptured: Gross (good example) opened kidneys in marked place, atherosclerosis in lower thoracic aorta
-
Abdominal Aneurysm: Gross, (very good example) opened lesion with mural thrombus
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, large tear in first portion of aortic arch, annuloaortic ectasis
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, external view of heart and first portion of aortic arch, annuloaortic ectasia, hemorrhage beneath adventitia is evidence of dissection
-
Atherosclerotic Aneurysm Infected: Gross, infected abdominal aneurysm at superior suture line with rupture into duodenum
-
Atherosclerotic Aneurysm: Gross, cross sections of repaired aneurysm showing Dacron graft and old mural thrombus. A nice example of fibrin layer in graft
-
Ruptured Syphilitic Aneurysm
-
Dissecting Aneurysm in a patient with Marfan's syndrome
-
Traumatic Aneurysm
-
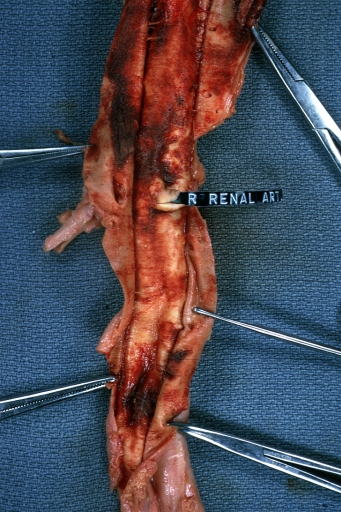
Kidney: Arteriosclerosis: Gross aorta with well shown renal artery containing large plaque and kidney with multiple cortical scars and atrophy also abdominal aorta aneurysm with mural thrombus (excellent example for renovascular hypertension)
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross, fixed tissue, descending thoracic segment dissection opened to show the false channel. The true surface is also visible
-
Aneurysm: Gross, ruptured thoracic aorta aneurysm, in situ lower thoracic portion (probably due to atherosclerosis)
-
Abdominal Aneurysm Graft Repair: Gross, natural color, close-up view, an excellent example of Dacron graft that has been in place for years with pseudointima and atherosclerosis
-
Dacron Graft: Gross, close-up Dacron graft to repair aneurysm. Aorta completely covered with a calcified and ulcerated plaque with small mural thrombi (an excellent depiction of proximal suture line)
-
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross natural color descending aorta opened into false channel
-
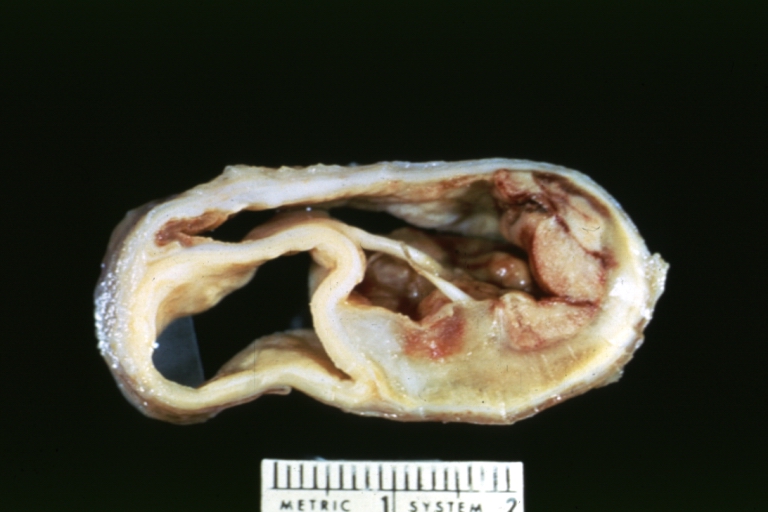
Abdominal Aneurysm: Gross, natural color, unopened specimen with about a six centimeter aneurysm between renals and bifurcation (a very good example of opened aneurysm)
-
Abdominal Aneurysm: Gross, natural color, an opened aneurysm showing quite well laminated thrombus
-
Atherosclerosis with Mural Thrombi: Gross, natural color, a nice photo of descending thoracic aorta with extensive ulcerated plaques and mural thrombi in distal portion. The case also has an abdominal aneurysm
-
Pseudoaneurysm Ruptured Into Duodenum: Gross natural color aorta and duodenum with arrow pointing to rupture point of aortobifemoral bypass pseudoaneurysm rupture and another in duodenum a very good demonstration of this very well known complication of aortic prostheses
-
Abdominal Aneurysm: Gross, natural color, large aneurysm opened showing sessile calcified plaques with no mural thrombus. Lesion extends from renal arteries to the bifurcation (the same lesion seen externally with focus of rupture)
-
Abdominal Aneurysm Ruptured: Gross, natural color, external view with large area of apparent rupture. Aorta is opened to show this aneurysm)
-
Abdominal Aneurysm: Gross, natural color, unopened large and quite typical aneurysm extending from below renal arteries to bifurcation
-
Abdominal Aneurysm: Gross, natural color, opened aneurysm with well shown and typical laminated thrombus (external view)
-
Aortobifemoral Prosthesis: Gross, natural color, nice dissection showing Dacron prosthesis replacing abdominal segment of aorta with portion of atherosclerotic aneurysm with renal arteries and kidneys
-
Aortobifemoral Prosthesis: Gross natural color close-up view of nicely dissected prosthesis extending from below renals to common iliac arteries portion of atherosclerotic aneurysm behind prosthesis
-
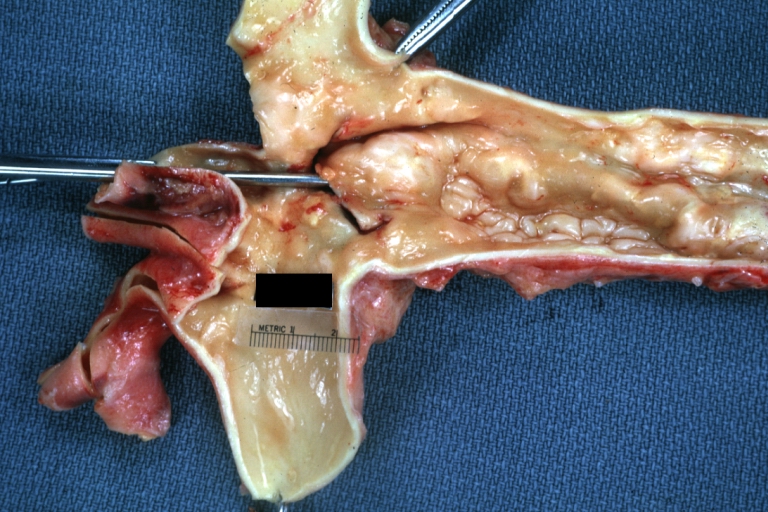
Dissecting Aneurysm: Gross natural color close-up view of aortic valve and proximal aortic arch with ruptured intima rather good illustration of this lesion
-
Syphilitic Aneurysm: Gross natural color rather a close-up view and outstanding photo of aneurysm ruptured into the left main stem bronchus
-
Syphilitic Aneurysm: Gross natural color typical tree barking in aorta aneurysm opening is seen in which is a thrombus aneurysm ruptured into left main stem bronchus (shown very well)
-
Dissecting Aneurysm Chronic: Gross natural color first portion of aortic arch with intimal rent well shown with healed margins and view into false channel that shows a surface looking like atherosclerosis which is known to develop in a chronic dissection
-
Dissecting Aneurysm Chronic: Gross, natural color, closer view of the previous one (a very good example)