Superior thyroid artery
| Cardiology Network |
 Discuss Superior thyroid artery further in the WikiDoc Cardiology Network |
| Adult Congenital |
|---|
| Biomarkers |
| Cardiac Rehabilitation |
| Congestive Heart Failure |
| CT Angiography |
| Echocardiography |
| Electrophysiology |
| Cardiology General |
| Genetics |
| Health Economics |
| Hypertension |
| Interventional Cardiology |
| MRI |
| Nuclear Cardiology |
| Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| Prevention |
| Public Policy |
| Pulmonary Embolism |
| Stable Angina |
| Valvular Heart Disease |
| Vascular Medicine |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Course
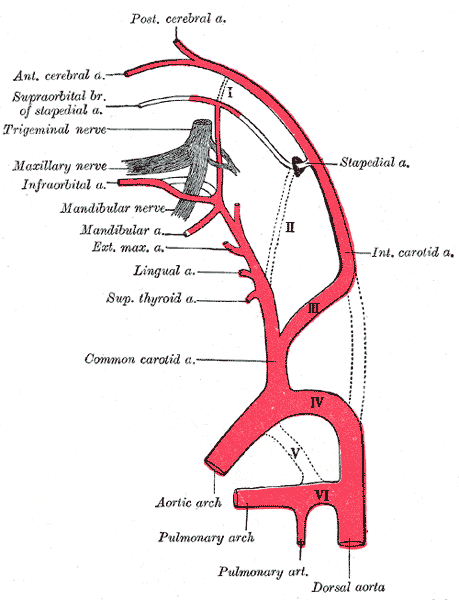
The superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery just below the level of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and ends in the thyroid gland.
Relations
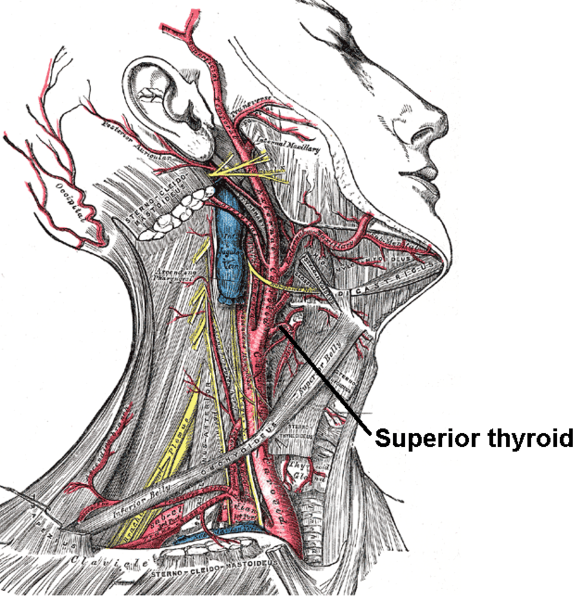
From its origin under the anterior border of the Sternocleidomastoideus it runs upward and forward for a short distance in the carotid triangle, where it is covered by the skin, Platysma, and fascia; it then arches downward beneath the Omohyoideus, Sternohyoideus, and Sternothyreoideus.
To its medial side are the Constrictor pharyngis inferior and the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve.
Branches
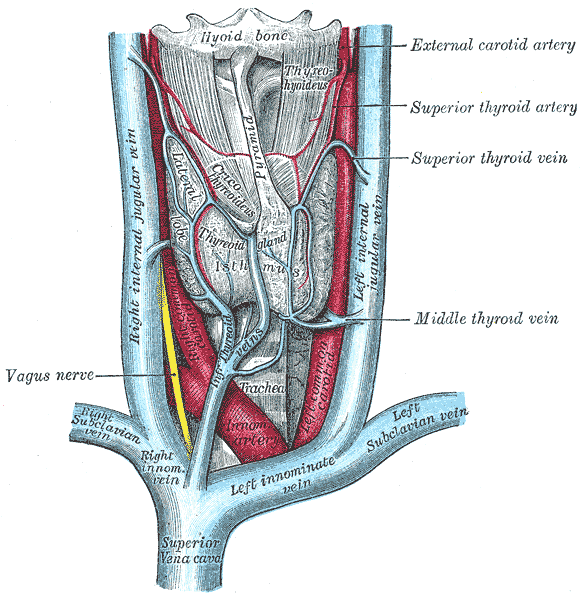
It distributes twigs to the adjacent muscles, and numerous branches to the thyroid gland, anastomosing with its fellow of the opposite side, and with the inferior thyroid arteries.
The branches to the gland are generally two in number; one, the larger, supplies principally the anterior surface; on the isthmus of the gland it anastomoses with the corresponding artery of the opposite side: a second branch descends on the posterior surface of the gland and anastomoses with the inferior thyroid artery.
Besides the arteries distributed to the muscles and to the thyroid gland, the branches of the superior thyroid are:[1]
- Hyoid (infrahyoid) artery
- Sternocleidomastoid artery
- Superior laryngeal artery
- Cricothyroid artery
Hyoid (infrahyoid) branch
The Hyoid Branch (ramus hyoideus; infrahyoid branch) is small and runs along the lower border of the hyoid bone beneath the Thyreohyoideus and anastomoses with the vessel of the opposite side.
Sternocleidomastoid branch
The Sternocleidomastoid branch (ramus sternocleidomastoideus; sternomastoid branch) runs downward and lateralward across the sheath of the common carotid artery, and supplies the Sternocleidomastoideus and neighboring muscles and integument; it frequently arises as a separate branch from the external carotid.
Superior laryngeal artery
The superior laryngeal artery, larger than either of the preceding, accompanies the internal laryngeal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve, beneath the Thyreohyoideus
Cricothyroid branch
The Cricothyroid Branch (ramus cricothyreoideus) is small and runs transversely across the cricothyroid membrane, communicating with the artery of the opposite side.
See also
Additional images
-
Diagram showing the origins of the main branches of the carotid arteries.
-
The internal carotid and vertebral arteries. Right side. (Superior thyroid visible at center.)
-
The thyroid gland and its relations.
-
Side of neck, showing chief surface markings.