Subdural empyema: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
m (Changes made per Mahshid's request) |
||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Infobox disease| | {{Infobox disease | ||
| Name = Subdural Empyema | |||
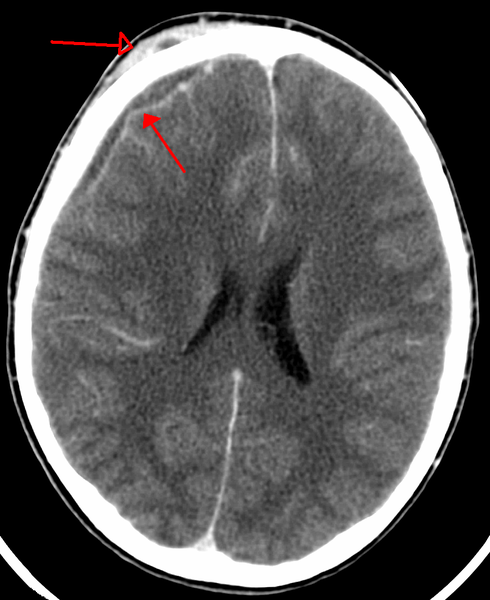
| Image = Subduralempyemaandskinabscess.png | |||
| Caption = Subdural empyema with skin abscess as seen on CT | |||
}} | }} | ||
'''For patient information, click [[Subdural empyema (patient information)|here]].''' | |||
{{Subdural empyema}} | |||
Subdural empyema | {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{JS}}; {{AG}} | ||
{{SK}} Circumscript meningitis; Pachymeningitis interna; Purulent pachymeningitis; Subdural abscess; SDE | |||
== | ==[[Subdural empyema overview|Overview]]== | ||
== | ==[[Subdural empyema historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | ||
==[[Subdural empyema classification|Classification]]== | |||
==[[Subdural empyema pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== | |||
==[[Subdural empyema causes|Causes]]== | |||
==[[Subdural empyema differential diagnosis|Differentiating Subdural Empyema from other diseases]]== | |||
==[[Subdural empyema epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== | |||
==[[Subdural empyema risk factors|Risk Factors]]== | |||
==[[Subdural empyema natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis]]== | |||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
[[Subdural empyema history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Subdural empyema physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Subdural empyema laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Subdural empyema lumbar puncture|Lumbar Puncture]] | [[Subdural empyema x ray|X Ray]] | [[Subdural empyema CT|CT]] | [[Subdural empyema MRI|MRI]] | [[Subdural empyema other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
== | [[Subdural empyema medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Subdural empyema surgery|Surgery]] | [[Subdural empyema prevention|Prevention]] | [[Subdural empyema cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Subdural empyema future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] | ||
==Case Studies== | |||
[[Subdural empyema case study one|Case #1]] | |||
[[ | [[Category:Neurology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:53, 18 September 2017
| Subdural Empyema | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| |
|---|---|
| Subdural empyema with skin abscess as seen on CT |
For patient information, click here.
|
Subdural empyema Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Subdural empyema On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Subdural empyema |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: João André Alves Silva, M.D. [2]; Anthony Gallo, B.S. [3]
Synonyms and keywords: Circumscript meningitis; Pachymeningitis interna; Purulent pachymeningitis; Subdural abscess; SDE
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differentiating Subdural Empyema from other diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
Diagnosis
History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | Lumbar Puncture | X Ray | CT | MRI | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Surgery | Prevention | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies