|
|
| (36 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| | {| class="infobox" style="float:right;" |
| | |- |
| | | [[File:Siren.gif|30px|link= Bradycardia resident survival guide]]|| <br> || <br> |
| | | [[Bradycardia resident survival guide|'''Resident'''<br>'''Survival'''<br>'''Guide''']] |
| | |} |
| {{Infobox_Disease | | | {{Infobox_Disease | |
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |
| Image = SSS for right up.jpg| | | Image = SSS for right up.jpg| |
| Caption = Sick sinus syndrome| | | Caption = Sick sinus syndrome| |
| Width = 250px| | | Width = 250px| |
| DiseasesDB = 12066 |
| |
| ICD10 = {{ICD10|I|49|5|i|30}} |
| |
| ICD9 = {{ICD9|427.81}} |
| |
| ICDO = |
| |
| OMIM = 163800 |
| |
| MedlinePlus = |
| |
| eMedicineSubj = |
| |
| eMedicineTopic = |
| |
| MeshID = |
| |
| }} | | }} |
| {{SI}}
| |
| {{CMG}}
| |
|
| |
|
| '''''Key words and synonyms:''''' Bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome, tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, tachy-brady syndrome, sinus node dysfunction, SND, SSS. [[Sinus arrest]], [[sinus bradycardia]], are forms or variants of sick sinus syndrome.
| | {{Sick sinus syndrome}} |
|
| |
|
| ==Overview==
| | '''For patient information click [[Sick sinus syndrome (patient information)|here]]''' |
| '''Sick sinus syndrome''', also called '''Sinus node dysfunction''', is a group of abnormal heart rhythms ([[arrhythmia]]s) caused by a malfunction of the [[sinus node]], the heart's "natural" pacemaker. It encompasses disorder causing reduced automaticity of the sinoatrial node, exit block, and sinus arrest. The syndrome primarily affects the elderly, and is associated with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation | |
| or flutter in approximately 50% of patients and with distal conduction disease in up to 11% of patients. It is also sometimes called as tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, characterized by periods of bradycardia alternating with periods of atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. Management of the syndrome usually requires an implanted pacemaker
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Subclassification of variants of sinus node dysfunction==
| | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Sahar}} |
| #'''Bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome''' is a variant of sick sinus syndrome where atrial tachyarrhythmias such as atrial flutter and fibrillation alternate with prolonged periods of [[asystole]].
| |
| #'''Chronotropic incompetence'''
| |
| #'''[[Sinus bradycardia]]'''
| |
| #'''[[Sinus arrest]]'''
| |
| #'''Sinus node exit block'''
| |
| #'''Sinus pause'''
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Common Causes==
| | {{SK}} Bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome, tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome, tachy-brady syndrome, sinus node dysfunction, sinoatrial arrest, SND, SSS, Sinus arrest, sinus bradycardia, are forms or variants of sick sinus syndrome. |
| Sick sinus syndrome can result in many abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias), including sinus arrest, sinus node exit block, [[sinus bradycardia]], and other types of [[bradycardia]] (slow heart rate).
| |
|
| |
|
| Sick sinus syndrome may also be associated with tachycardias (fast heart rate) such as [[paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia ]] (PSVT) and atrial fibrillation. Tachycardias that occur with sick sinus syndrome are characterized by a long pause after the tachycardia. | | == [[Sick sinus syndrome overview|Overview]] == |
|
| |
|
| Abnormal rhythms are often caused or worsened by medications such as [[digitalis]], [[calcium channel blocker]]s, [[beta-blocker]]s, sympatholytic medications, and anti-arrhythmics. Disorders that cause scarring, degeneration, or damage to the conduction system can cause sick sinus syndrome, including [[sarcoidosis]], amyloidosis, [[Chagas' disease]], and cardiomyopathies.
| | == [[Sick sinus syndrome historical perspective|Historical Perspective]] == |
|
| |
|
| Sick sinus syndrome is more common in elderly adults, where the cause is often a non-specific, scar-like degeneration of the [[Electrical conduction system of the heart|cardiac conduction system]]. Cardiac surgery, especially to the [[atria]], is a common cause of sick sinus syndrome in children. | | == [[Sick sinus syndrome classification|Classification]] == |
|
| |
|
| [[Coronary artery disease]], high blood pressure, and aortic and mitral valve diseases may be associated with sick sinus syndrome, although this association may only be incidental. | | == [[Sick sinus syndrome pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]] == |
|
| |
|
| ==Symptoms== | | == [[Sick sinus syndrome causes|Causes]] == |
| Even though many types of sick sinus syndrome produce no symptoms, patients may present with:
| |
| * [[Stokes-Adams attack]]s - fainting due to [[asystole]] or [[ventricular fibrillation]]
| |
| * [[Dizziness]] or light-headedness
| |
| * [[Palpitations]]
| |
| * [[Chest pain]] or [[Angina pectoris|angina]]
| |
| * [[Shortness of breath]]
| |
| * [[Fatigue]]
| |
| * [[Headache]]
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Diagnosis== | | == [[Sick sinus syndrome differential diagnosis|Differential Diagnosis]] == |
| Ambulatory monitoring of the [[electrocardiogram]] (ECG) may be necessary because arrhythmias are transient. The ECG may show any of the following
| |
| * Inappropriate [[sinus bradycardia]]
| |
| * [[Sinus arrest]]
| |
| * [[Sinoatrial block]]
| |
| * [[Atrial fibrillation]] with slow ventricular response
| |
| * A prolonged [[asystolic]] period after a period of tachycardias
| |
| * [[Atrial flutter]]
| |
| * [[Ectopic atrial tachycardia]]
| |
| * [[Sinus node reentrant tachycardia]]
| |
|
| |
|
| Electrophysiologic tests are no longer used for diagnostic purposes because of their low specificity and sensitivity. Cardioinhibitory and vasodepressor forms of sick sinus syndrome may be revealed by [[tilt table test]]ing.
| | == [[Sick sinus syndrome epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]] == |
|
| |
|
| | == [[Sick sinus syndrome screening|Screening]] == |
|
| |
|
| <div align="left">
| | == [[Sick sinus syndrome natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]] == |
| <gallery heights="175" widths="275">
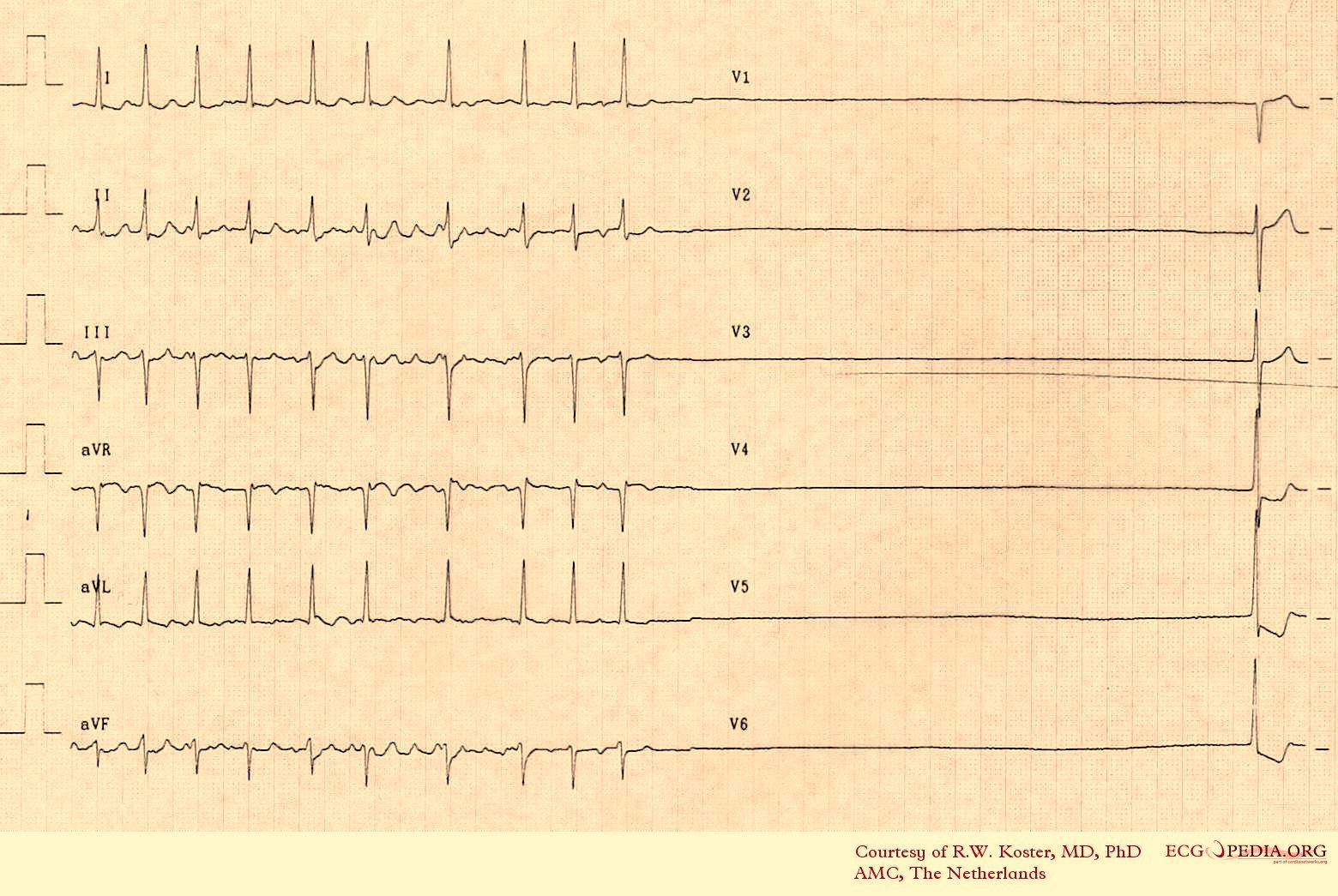
| |
| Image:SSS ecg 001.jpg|Sick Sinus Syndrome
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| </div>
| |
|
| |
|
| | == Diagnosis == |
|
| |
|
| ==Treatment==
| | [[Sick sinus syndrome history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome electrocardiogram|Electrocardiogram]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome EKG examples|EKG Examples]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome echocardiography or ultrasound|Echocardiography]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome x ray|X-ray]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome CT scan|CT scan]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome MRI|MRI]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome other imaging findings|Other Imaging Findings]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] |
|
| |
|
| Bradyarrhythmias are well controlled with pacemakers, while tachyarrhythmias respond well to medical therapy. However, because both bradyarrhythmias and tachyarrhythmias may be present, drugs to control tachyarrhythmia may exacerbate bradyarrhythmia. Therefore, a pacemaker is implanted before drug therapy is begun for the tachyarrhythmia.
| | == Treatment == |
|
| |
|
| ==ACC / AHA Guidelines- Recommendations for Permanent Pacing in Sinus Node Dysfunction (DO NOT EDIT) <ref name="Epstein"> Epstein AE, DiMarco JP, Ellenbogen KA, Estes NAM III, Freedman RA, Gettes LS, Gillinov AM, Gregoratos G, Hammill SC, Hayes DL, Hlatky MA, Newby LK, Page RL, Schoenfeld MH, Silka MJ, Stevenson LW, Sweeney MO. ACC/AHA/HRS 2008 guidelines for device-based therapy of cardiac rhythm abnormalities: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the ACC/AHA/NASPE 2002 Guideline Update for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices). Circulation. 2008; 117: 2820–2840. PMID 18483207 </ref>==
| | [[Sick sinus syndrome medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome surgery|Surgery]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Sick sinus syndrome future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] |
| {{cquote|
| |
| ===Class I===
| |
| 1. Permanent [[pacemaker]] implantation is indicated for [[SND]] with documented symptomatic [[bradycardia]], including frequent sinus pauses that produce symptoms. ''(Level of Evidence: C)''
| |
|
| |
|
| 2. Permanent [[pacemaker]] implantation is indicated for symptomatic chronotropic incompetence. ''(Level of Evidence: C)''
| | == Case Studies == |
|
| |
|
| 3. Permanent [[pacemaker]] implantation is indicated for symptomatic [[sinus bradycardia]] that results from required drug therapy for medical conditions. ''(Level of Evidence: C)''
| | [[Sick sinus syndrome case study one|Case #1]] |
|
| |
|
| ===Class IIa===
| |
| 1. Permanent [[pacemaker]] implantation is reasonable for [[SND]] with heart rate less than 40 bpm when a clear association between significant symptoms consistent with [[bradycardia]] and the actual presence of [[bradycardia]] has not been documented. ''(Level of Evidence: C)''
| |
|
| |
| 2. Permanent [[pacemaker]] implantation is reasonable for [[syncope]] of unexplained origin when clinically significant abnormalities of [[sinus node]] function are discovered or provoked in electrophysiological studies. ''(Level of Evidence: C)''
| |
|
| |
| ===Class IIb===
| |
| 1. Permanent [[pacemaker]] implantation may be considered in minimally symptomatic patients with chronic heart rate less than 40 bpm while awake. ''(Level of Evidence: C)''
| |
|
| |
| ===Class III===
| |
| 1. Permanent [[pacemaker]] implantation is not indicated for [[SND]] in asymptomatic patients. ''(Level of Evidence: C)''
| |
|
| |
| 2. Permanent [[pacemaker]] implantation is not indicated for [[SND]] in patients for whom the symptoms suggestive of [[bradycardia]] have been clearly documented to occur in the absence of [[bradycardia]]. ''(Level of Evidence: C)''
| |
|
| |
| 3. Permanent [[pacemaker]] implantation is not indicated for [[SND]] with symptomatic [[bradycardia]] due to nonessential drug therapy. ''(Level of Evidence: C)''}}
| |
|
| |
| ==Sources==
| |
| * The ACC/AHA/HRS 2008 Guidelines for Device-Based Therapy of Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities <ref name="Epstein"> Epstein AE, DiMarco JP, Ellenbogen KA, Estes NAM III, Freedman RA, Gettes LS, Gillinov AM, Gregoratos G, Hammill SC, Hayes DL, Hlatky MA, Newby LK, Page RL, Schoenfeld MH, Silka MJ, Stevenson LW, Sweeney MO. ACC/AHA/HRS 2008 guidelines for device-based therapy of cardiac rhythm abnormalities: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the ACC/AHA/NASPE 2002 Guideline Update for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices). Circulation. 2008; 117: 2820–2840. PMID 18483207 </ref>
| |
|
| |
| ==External links==
| |
| *[http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000161.htm NIH website]
| |
|
| |
| ==References==
| |
| * {{cite journal | author=Adan V, Crown LA | title=Diagnosis and treatment of sick sinus syndrome | journal=Am Fam Physician | year=2003 | pages=1725-32 | volume=67 | issue=8 | id=PMID 12725451}}
| |
| {{Reflist|2}}
| |
|
| |
| [[de:Sick-Sinus-Syndrom]]
| |
| [[ja:洞不全症候群]]
| |
| [[sv:Taky-brady-syndrom]]
| |
|
| |
|
| [[Category:Electrophysiology]] | | [[Category:Electrophysiology]] |
| [[Category:Syndromes]] | | [[Category:Syndromes]] |
| [[Category:Cardiology]] | | [[Category:Cardiology]] |
| | [[Category:Arrhythmia]] |
|
| |
|
| {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | | {{WH}} |
| {{WikiDoc Sources}} | | {{WS}} |