Secondary hyperaldosteronism pathophysiology
| https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JBfkGNr01V8%7C350}} |
|
Secondary hyperaldosteronism Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Secondary Hyperaldosteronism from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Secondary hyperaldosteronism pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Secondary hyperaldosteronism pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Secondary hyperaldosteronism pathophysiology |
Overview
Secondary hyperaldosteronism is a disease of increasing aldosterone or other mineralocorticoid levels. The resulting Na+ retention produces hypertension, and elevated K+ excretion may cause hypokalemia.
Pathophysiology
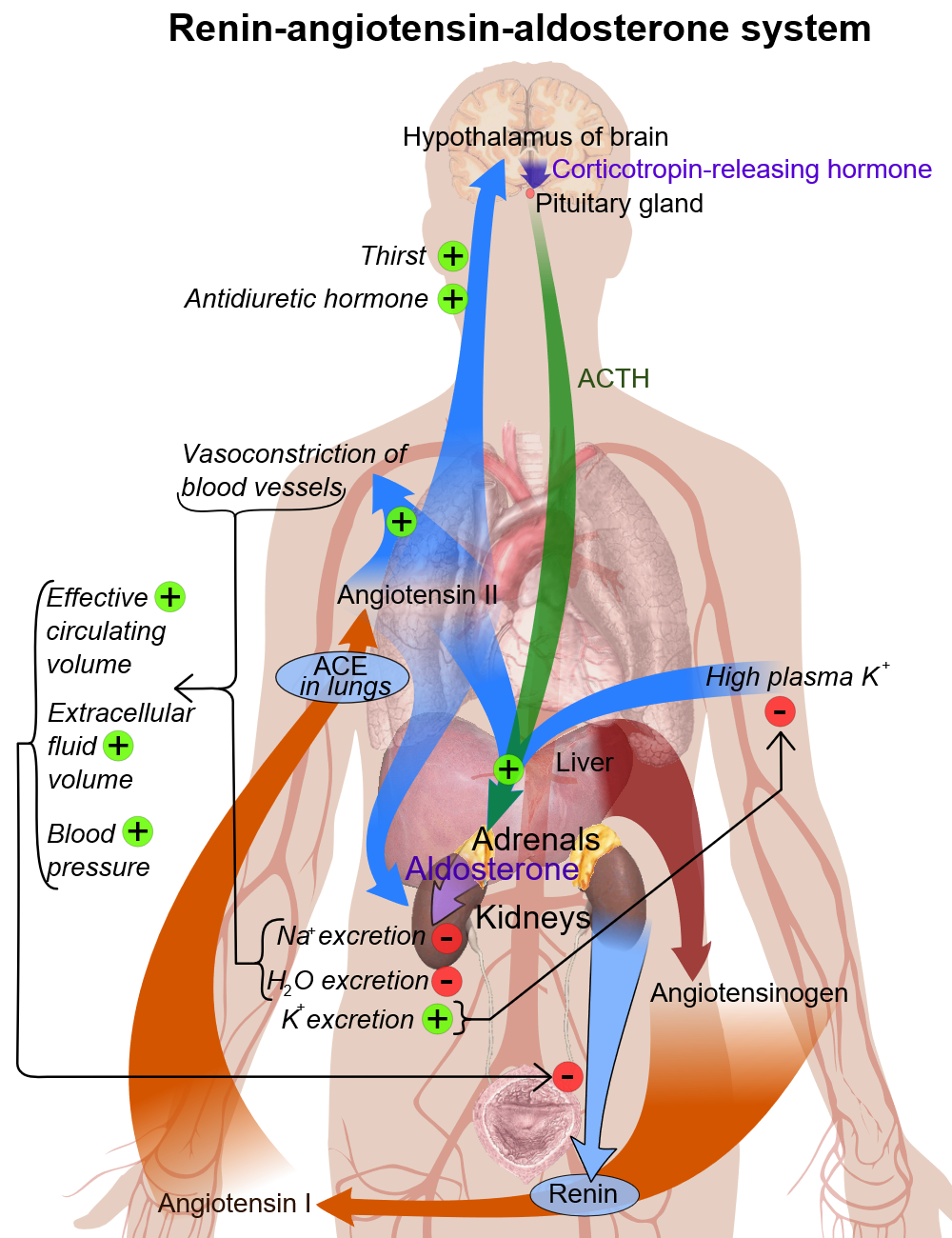
Basic physiology of aldosterone
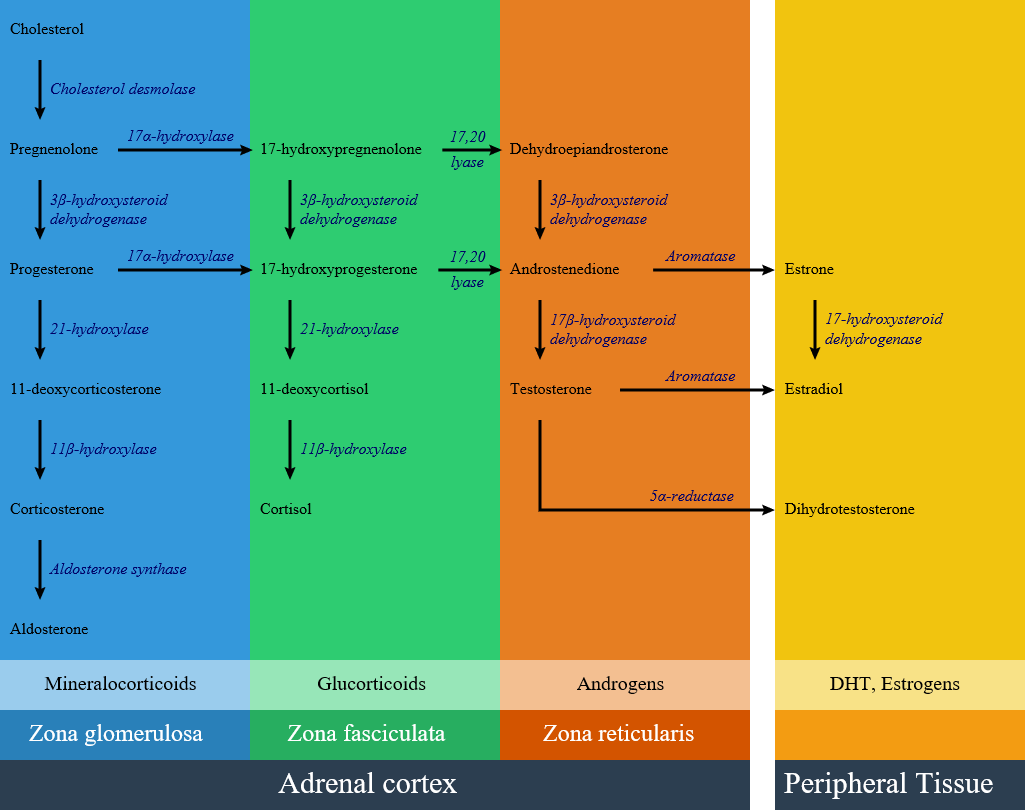
Circulating aldosterone is principally made in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex (outer layer of the cortex) by a cascade of enzyme steps leading to the conversion of cholesterol to aldosterone.
- Aldosterone's production is regulated at two critical enzyme steps:
- (1) early in its biosynthetic pathway (the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone by cholesterol side chain cleavage enzyme) and
- (2) late (the conversion of corticosterone to aldosterone by aldosterone synthase).
- A variety of factors modify aldosterone secretion--the most important are angiotensin II (AngII), the end-product of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), and potassium. However ACTH, neural mediators and natriuretic factors also play part in the feedback mechanism.
- Aldosterone's classical epithelial effect is to increase the transport of sodium across the cell in exchange for potassium and hydrogen ions. [1]
Pathogenesis
Secondary hyperaldosteronism syndrome is a disease of increasing aldosterone or other mineralocorticoid levels. The resulting Na+ retention produces hypertension, and elevated K+ excretion may cause hypokalemia. Patients with Secondary hyperaldosertonism may have:
- Renin-producing tumors
- Renal artery stenosis
- Cushing syndrome
- Liddle's syndrome
- Ectopic ACTH production
- Licorice ingestion
- Other mineralocorticoids excess:
Genetics
References
- ↑ Williams GH (2005). "Aldosterone biosynthesis, regulation, and classical mechanism of action". Heart Fail Rev. 10 (1): 7–13. doi:10.1007/s10741-005-2343-3. PMID 15947886.
- ↑ "File:Adrenal Steroids Pathways.svg - Wikimedia Commons".