Right ventricular hypertrophy: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
* [[Pulmonic regurgitation]] | * [[Pulmonic regurgitation]] | ||
* [[Pulmonic stenosis]] | * [[Pulmonic stenosis]] | ||
* [[Scoliosis] | * [[Scoliosis]] | ||
* [[Tetralogy of Fallot]] | * [[Tetralogy of Fallot]] | ||
* [[Transposition of the Great Vessels]] | * [[Transposition of the Great Vessels]] | ||
Revision as of 00:13, 24 September 2012
| Right ventricular hypertrophy | |
 | |
|---|---|
| Right Ventricular hypertrophy | |
| ICD-10 | I51.7 |
| ICD-9 | 429.3 |
| DiseasesDB | 11623 |
| MeSH | D017380 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Synonyms and keywords: RVH
Overview
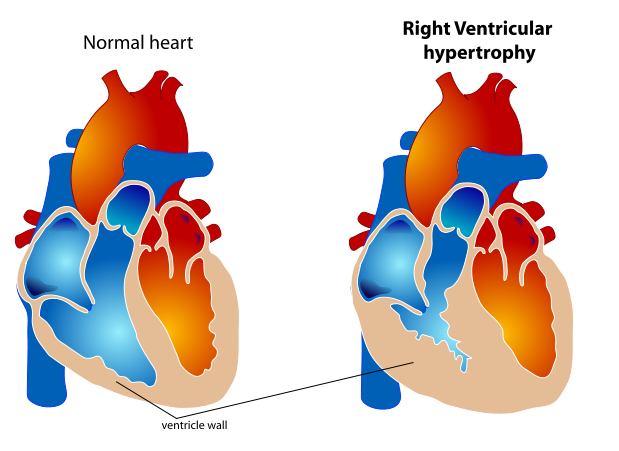
Right ventricular hypertrophy is a form of ventricular hypertrophy affecting the right ventricle.
Pathophysiology
Blood travels through the right ventricle to the lungs. If conditions occur which decrease pulmonary circulation, meaning blood does not flow well from the heart to the lungs, extra stress can be placed on the right ventricle. This can lead to right ventricular hypertrophy.
Causes of Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Atrial septal defect ddb1090.htm ostium primum] and ddb1107.htm ostium secundum]
- Bronchiectasis
- Cardiac fibrosis
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Churg-Strauss syndrome
- Coal worker pneumoconiosis
- Cor pulmonale
- Cystic fibrosis
- Eisenmenger's Syndrome
- High altitude[1]
- Left ventricular hypertrophy or dilation
- Mitral stenosis
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Pickwickian Syndrome
- Primary pulmonary hypertension
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Pulmonic regurgitation
- Pulmonic stenosis
- Scoliosis
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Transposition of the Great Vessels
- Tricuspid regurgitation
- Ventricular septal defect
Diagnosis
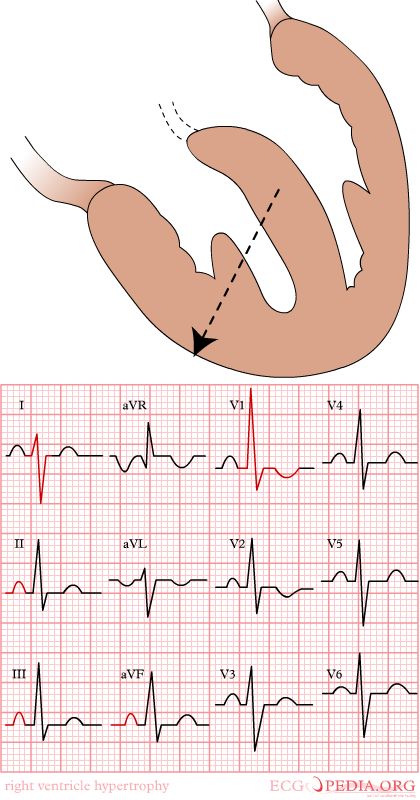
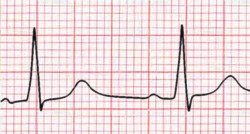
EKG Findings in Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
-
Right ventricular hypertrophy
-
Right ventricular hypertrohpy, the R wave > the S wave in V1
Diagnostic Criteria for Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Right axis deviation of +90 degrees or more
- RV1 = 7 mm or more
- RV1 + SV5 or SV6 = 10 mm or more
- R/S ratio in V1 = 1.0 or more
- S/R ratio in V6 = 1.0 or more
- Late intrinsicoid deflection in V1 (0.035+)
- Incomplete RBBB pattern
- ST T strain pattern in 2,3,aVF
- P pulmonale or Right atrial enlargement or P congenitale
- S1 S2 S3 pattern in children
- Tall R wave in V1 or qR in V1
- R wave greater than S wave in V1
- R wave progression reversal
- Inverted T wave in the anterior precordial leads
Differential Diagnosis of R>S in V1
- RVH
- Posterior MI
- WPW
- HCM (septal hypertrophy)
- Kulbertus' block (septal fascicular block)
- Duchennes Muscular Dystrophy
- Normal variant
- V4r may be a more useful and reliable than lead V1 in that it often reveals an r>s while v1 remains normal
- An incomplete right bundle branch block in the right precordial chest leads may signal the development of RVH
- In the limb leads right axis deviation develops and at times prominent Q waves simulating an IMI appear in leads 2,3, and aVF.
- In children an S1 S2 S3 pattern (i.e. an S wave deeper than R in all 3 standard leads) is a reliable index of RVH
- RV strain can be seen in leads V1 and V2 but also in leads 2,3, aVF