Rheumatoid arthritis x ray: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[[Category:Needs content]] | [[Category:Needs content]] | ||
Revision as of 20:38, 10 April 2018
|
Rheumatoid arthritis Microchapters | |
|
Diagnosis | |
|---|---|
|
Treatment | |
|
Case Studies | |
|
Rheumatoid arthritis x ray On the Web | |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Rheumatoid arthritis x ray | |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Rheumatoid arthritis x ray | |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Manpreet Kaur, MD [2]
Overview
X Ray
Hallmark of rheumatoid arthritis are :
- Soft tissue swelling:
- This is an early finding in the course of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Soft tissue swelling is fusiform and periarticular which is due to the combination of joint effusion, edema, and tenosynovitis.
- Joint space narrowing can be symmetrical or concentric.
- Marginal erosions can result from the erosion by pannus of the bony “bare areas”
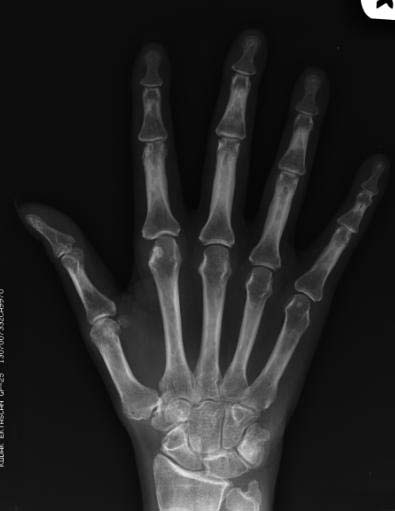
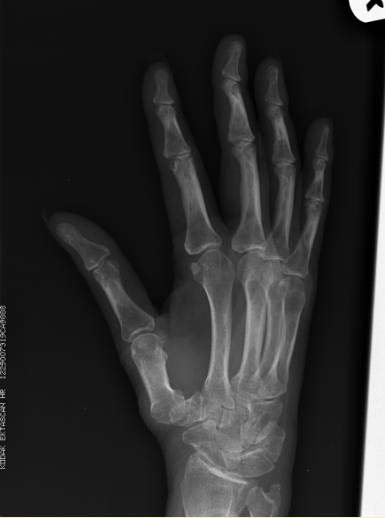
Hand and wrist findings
- Common joints involved are:
- PIP and MCP joints (especially 2nd and 3rd MCP)
- Ulnar styloid
- Triquetrum
- Findings seen are:
- Subchondral cysts
- Ulnar deviation of the MCP joints
- Boutonniere and swan neck deformities
- Hitchhiker’s thumb deformity
- Scapholunate dissociation, ulnar translocation
- Ankylosis
Feet
- Various radiological findings are:
- Subtalar joint involvement
- Posterior calcaneal tubercle erosion
- Hammertoe deformity
- Hallux valgus
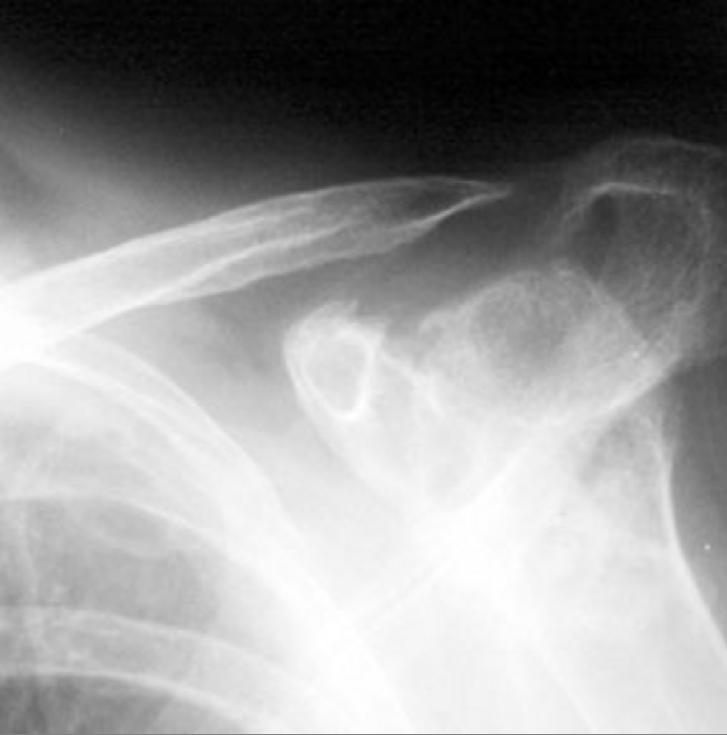
Shoulder
- Distal clavicle erosions
- Erosions of the superolateral aspect of the head of the humerus
- High riding shoulder due to subacromial-subdeltoid bursitis
Knee
- Joint effusions
- Loss of joint space
- Prepatellar bursitis
Hip
- Concentric loss of joint space
- Acetabular protrusio
Spine
- Atlantoaxial subluxation
- Atlantoaxial impaction: cephalad migration of C2
- Osteoporosis and osteoporotic fractures
- Erosion of spinous processes
-
-
-
-
-
Distal clavicle erosion
References
Template:WH {[WS}}