Rheumatic fever electrocardiogram: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Varun Kumar (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{Rheumatic fever}} {{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief:''' Varun Kumar, M.B.B.S. ==Electrocardiogram== ECG changes depend on the structures involved and the extent. Fo...") |
Varun Kumar (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category:Bacterial diseases]] | [[Category:Bacterial diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Rheumatology]] | [[Category:Rheumatology]] | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Up-To-Date cardiology]] | |||
Revision as of 21:21, 30 September 2011
|
Rheumatic fever Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Rheumatic fever electrocardiogram On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Rheumatic fever electrocardiogram |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Rheumatic fever electrocardiogram |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief: Varun Kumar, M.B.B.S.
Electrocardiogram
ECG changes depend on the structures involved and the extent. Following ECG changes may be noted in patients with rhumatic fever[1].
- Sinus tachycardia or bradycardia depending on vagal tone.
- Prolongation of PR interval may be noted in some patients.
- Variable degree of AV conduction block may be noted. But they generally resolve with the resolution of rheumatic fever.
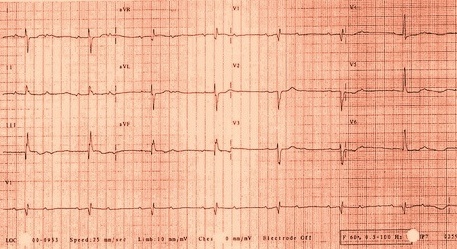
- P mitrale may be noted, which is suggestive of left atrial enlargement secondary to mitral valve abnormalities.
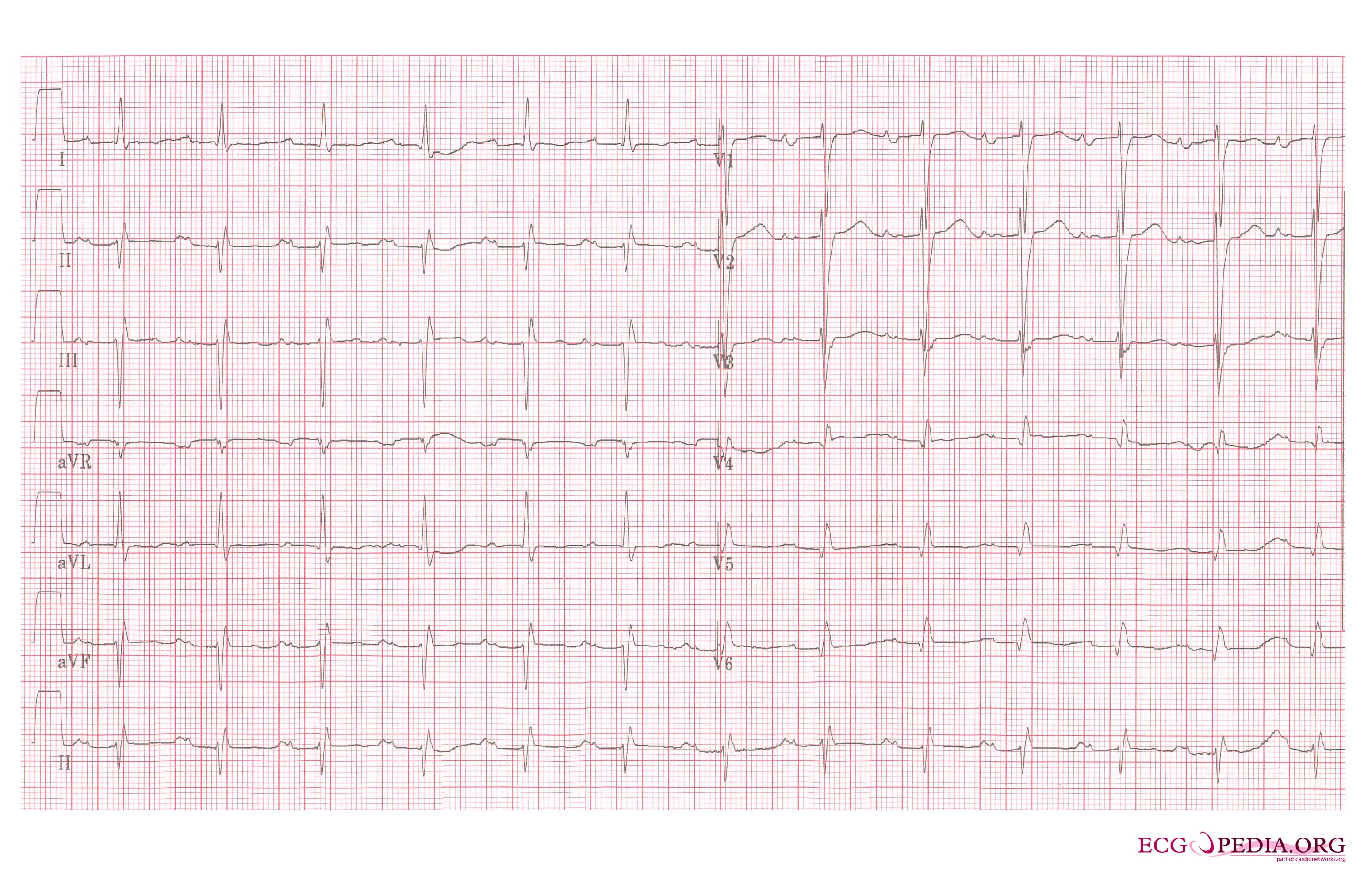
- Mital valve abnormalities may lead to development of atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation.
- T-wave inversions in may be noted in leads I, II and IV suggestive of pericardial invlovement.
- ST segment elevation may also be present in leads II, III, aVF and V4 to V6 in patients with acute pericarditis.