Reserpine: Difference between revisions
Gerald Chi (talk | contribs) m (Changed protection level for "Reserpine" ([Edit=Allow only autoconfirmed users] (expires 23:39, 20 March 2014 (UTC)) [Move=Allow only autoconfirmed users] (expires 23:39, 20 March 2014 (UTC)))) |
m (Protected "Reserpine": Bot: Protecting all pages from category Drug ([Edit=Allow only administrators] (indefinite) [Move=Allow only administrators] (indefinite))) |
||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage | |||
|authorTag= | |||
Gerald Chi | |||
{{ | <!--Overview--> | ||
| | |||
' | |genericName= | ||
| | |||
| CAS_number=50-55-5 | Reserpine | ||
| ATC_prefix=C02 | |||
| ATC_suffix=AA02 | |aOrAn= | ||
| PubChem=5770 | |||
| DrugBank= | a | ||
|drugClass= | |||
[[catecholamine]]-depleting [[sympatholytic]] | |||
|indication= | |||
[[hypertension|mild essential hypertension]] | |||
|hasBlackBoxWarning= | |||
|adverseReactions= | |||
[[abdominal pain]], [[diarrhea]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[xerostomia]], [[dizziness]], [[headache]], [[lethargy]], [[somnolence]], [[vertigo]], [[depression]], and [[nasal congestion]] | |||
<!--Black Box Warning--> | |||
|blackBoxWarningTitle= | |||
Title | |||
|blackBoxWarningBody= | |||
<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span></i> | |||
* Content | |||
<!--Adult Indications and Dosage--> | |||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | |||
|fdaLIADAdult= | |||
=====Mild Essential Hypertension===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Initial Dosage | |||
::* In the average patient not receiving other antihypertensive agents, the usual initial dosage is '''0.5 mg daily for 1 or 2 weeks.''' | |||
:* Maintenance Dosage | |||
::* For maintenance, reduce to '''0.1–0.25 mg daily'''. | |||
::* Higher dosages should be used cautiously, because occurrence of serious mental depression and other side effects may increase considerably. | |||
=====Psychiatric Disorders===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
:* Dosage | |||
::* The usual initial dosage is '''0.5 mg daily''', but may range from '''0.1 mg to 1.0 mg'''. Adjust dosage upward or downward according to the patient's response. | |||
* Reserpine is also useful as adjunctive therapy with other [[antihypertensive]] agents in the more severe forms of [[hypertension]]; relief of symptoms in agitated psychotic states (e.g., [[schizophrenia]]), primarily in those individuals unable to tolerate [[phenothiazine]] derivatives or in those who also require [[antihypertensive]] medication. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
<!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | |||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
|fdaLIADPed= | |||
* Reserpine is '''not''' recommended for use in children. | |||
* If it is to be used in treating a child, the usual recommended starting dose is 20 µg/kg daily. The maximum recommended dose is 0.25 mg (total) daily. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Contraindications--> | |||
|contraindications= | |||
* [[Hypersensitivity]] | |||
* Mental [[depression]] or history of mental [[depression]] (especially with suicidal tendencies) | |||
* Active [[peptic ulcer]] | |||
* [[Ulcerative colitis]] | |||
* [[Electroconvulsive therapy]] | |||
<!--Warnings--> | |||
|warnings= | |||
* Extreme caution should be exercised in treating patients with a history of mental [[depression]]. Reserpine may cause mental [[depression]]. Recognition of depression may be difficult because this condition may often be disguised by somatic complaints (''masked depression''). The drug should be discontinued at first signs of [[depression]] such as despondency, early morning [[insomnia]], [[loss of appetite]], [[impotence]], or self-deprecation. Drug-induced depression may persist for several months after drug withdrawal and may be severe enough to result in [[suicide]]. | |||
====Precautions==== | |||
* General | |||
:* Since reserpine increases gastrointestinal motility and secretion, it should be used cautiously in patients with a history of [[peptic ulcer]], [[ulcerative colitis]], or [[gallstone]]s ([[biliary colic]] may be precipitated). | |||
:* Caution should be exercised when treating [[hypertensive]] patients with [[renal insufficiency]], since they adjust poorly to lowered [[blood pressure]] levels. | |||
:* Preoperative withdrawal of reserpine does not assure that circulatory instability will not occur. It is important that the anesthesiologist be aware of the patient’s drug intake and consider this in the overall management, since hypotension has occurred in patients receiving rauwolfia preparations. Anticholinergic and/or adrenergic drugs (e.g., metaraminol, [[norepinephrine]]) have been employed to treat adverse vagocirculatory effects. | |||
<!--Adverse Reactions--> | |||
<!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | |||
|clinicalTrials= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Clinical Trial Experience</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Postmarketing Experience--> | |||
|postmarketing= | |||
* The following adverse reactions have been observed with rauwolfia preparations, but there has not been enough systematic collection of data to support an estimate of their frequency. Consequently the reactions are categorized by organ system and are listed in decreasing order of severity and not frequency. | |||
======Neurologic====== | |||
Rare [[parkinsonian syndrome]] and other extrapyramidal tract symptoms; [[dizziness]]; [[headache]]; paradoxical [[anxiety]]; [[depression]]; [[nervousness]]; nightmares; dull sensorium; [[drowsiness]]. | |||
======Cardiovascular====== | |||
[[Arrhythmia]]s (particularly when used concurrently with [[digitalis]] or [[quinidine]]), [[syncope]], [[angina]]-like symptoms, [[bradycardia]], [[edema]]. | |||
======Respiratory====== | |||
[[Dyspnea]], [[epistaxis]], [[nasal congestion]]. | |||
======Gastrointestinal====== | |||
[[Vomiting]], [[diarrhea]], [[nausea]], [[anorexia]], dryness of mouth, hypersecretion. | |||
======Musculoskeletal====== | |||
Muscular aches. | |||
======Genitourinary====== | |||
Pseudolactation, [[impotence]], [[dysuria]], [[gynecomastia]], decreased [[libido]], breast engorgement. | |||
======Metabolic====== | |||
Weight gain. | |||
======Hypersensitive Reactions====== | |||
[[Purpura]], [[rash]], [[pruritus]]. | |||
======Special Senses====== | |||
[[Deafness]], [[optic atrophy]], [[glaucoma]], [[uveitis]], conjunctival injection. | |||
<!--Drug Interactions--> | |||
|drugInteractions= | |||
* [[MAO inhibitor]]s | |||
:* MAO inhibitors should be avoided or used with extreme caution. | |||
* [[TCA|Tricyclic antidepressants]] | |||
:* Concurrent use of [[TCA|tricyclic antidepressants]] may decrease the [[antihypertensive]] effect of reserpine. | |||
* Reserpine and sympathomimetics | |||
:* Concurrent use of reserpine and direct-or-indirect acting [[sympathomimetic]]s should be closely monitored. The action of direct-acting amines ([[epinephrine]], [[isoproterenol]], [[phenylephrine]], metaraminol) may be prolonged when given to patients taking reserpine. The action of indirect-acting amines ([[ephedrine]], [[tyramine]], [[amphetamine]]s) is inhibited. | |||
:* Reserpine should be used cautiously with [[digitalis]] and [[quinidine]], since cardiac [[arrhythmia]]s have occurred with rauwolfia preparations. | |||
:* Concomitant use of reserpine with other [[antihypertensive]] agents necessitates careful titration of dosage with each agent. | |||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | |||
|useInPregnancyFDA= | |||
* '''Pregnancy Category C''' | |||
:* Reserpine administered parenterally has been shown to be teratogenic in rats at doses up to 2 mg/kg and to have an embryocidal effect in guinea pigs given dosages of 0.5 mg daily. | |||
:* There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of reserpine in pregnant women. Reserpine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. | |||
* Nonteratogenic Effects | |||
:* Reserpine crosses the placental barrier, and increased respiratory tract secretions, [[nasal congestion]], [[cyanosis]], and [[anorexia]] may occur in neonates of reserpine-treated mothers. | |||
|useInPregnancyAUS= | |||
* '''Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category''' | |||
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of {{PAGENAME}} in women who are pregnant. | |||
|useInLaborDelivery= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on use of {{PAGENAME}} during labor and delivery. | |||
|useInNursing= | |||
* Reserpine is excreted in maternal breast milk, and increased respiratory tract secretions, [[nasal congestion]], [[cyanosis]], and [[anorexia]] may occur in breast-fed infants. Because of the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants and the potential for tumorigenicity shown for reserpine in animal studies, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. | |||
|useInPed= | |||
* Safety and effectiveness in children have not been established by means of controlled clinical trials, although there is experience with the use of reserpine in children. Because of adverse effects such as emotional [[depression]] and lability, [[sedation]], and stuffy nose, reserpine is not usually recommended as a step-2 drug in the treatment of hypertension in children. | |||
|useInGeri= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to geriatric patients. | |||
|useInGender= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific gender populations. | |||
|useInRace= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific racial populations. | |||
|useInRenalImpair= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with renal impairment. | |||
|useInHepaticImpair= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with hepatic impairment. | |||
|useInReproPotential= | |||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in women of reproductive potentials and males. | |||
|useInImmunocomp= | |||
There is no FDA guidance one the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients who are immunocompromised. | |||
<!--Administration and Monitoring--> | |||
|administration= | |||
* Oral | |||
|monitoring= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--IV Compatibility--> | |||
|IVCompat= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>IV Compatibility</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Overdosage--> | |||
|overdose= | |||
===Acute Overdose=== | |||
====Signs and Symptoms==== | |||
* No deaths due to acute poisoning with reserpine have been reported. | |||
* Highest known doses survived: children, 1000 mg (age and sex not specified); young children, 200 mg (20-month-old boy). | |||
* Oral LD50's in animals (mg/kg): rat, 2993; mouse, 47 and 500. | |||
* The clinical picture of acute poisoning is characterized chiefly by signs and symptoms due to the reflex parasympathomimetic effect of reserpine. | |||
* Impairment of consciousness may occur and may range from drowsiness to coma, depending upon the severity of overdosage. Flushing of the skin, conjunctival injection, and [[miosis|pupillary constriction]] are to be expected. [[Hypotension]], [[hypothermia]], central respiratory depression, and [[bradycardia]] may develop in cases of severe overdosage. Increased salivary and gastric secretion and [[diarrhea]] may also occur. | |||
====Management==== | |||
* There is no specific antidote. | |||
* Stomach contents should be evacuated, taking adequate precautions against aspiration and for protection of the airway. Activated charcoal slurry should be instilled. | |||
* The effects of reserpine overdosage should be treated symptomatically. If hypotension is severe enough to require treatment with a vasopressor, one having a direct action upon vascular smooth muscle (e.g., [[phenylephrine]], levarterenol, metaraminol) should be used. Since reserpine is long-acting, the patient should be observed carefully for at least 72 hours, and treatment administered as required. | |||
===Chronic Overdose=== | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Chronic Overdose</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Pharmacology--> | |||
<!--Drugbox2--> | |||
|drugBox= | |||
{{Drugbox2 | |||
| Watchedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 460779417 | |||
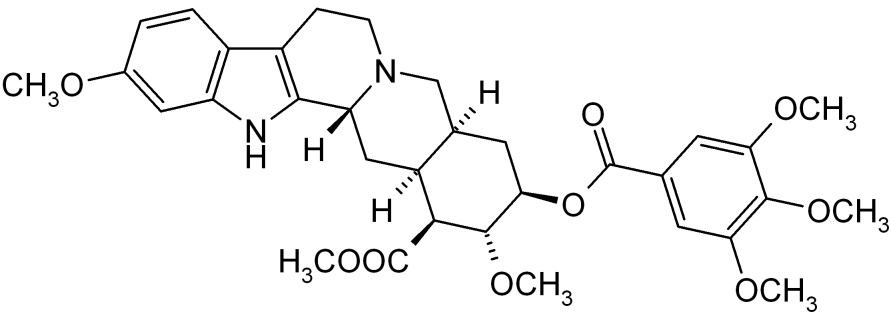
| IUPAC_name = Methyl (3β,16β,17α,18β,20α)-11,17-dimethoxy-18-[(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]yohimban-16-carboxylate | |||
| image = Reserpine.png | |||
| width = 350px | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | |||
| tradename = | |||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|CDI|reserpine}} | |||
| MedlinePlus = a601107 | |||
| licence_US = Reserpine | |||
| pregnancy_category = C Risk cannot be ruled out, US | |||
| legal_status = Rx-only (some countries banned/discontinued) | |||
| routes_of_administration = oral | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| bioavailability = 50% | |||
| metabolism = gut/liver | |||
| elimination_half-life = phase 1 = 4.5h,<br> phase 2 = 271h, <br> average = 33h | |||
| excretion = 62% feces / 8% urine | |||
<!--Identifiers--> | |||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| CAS_number = 50-55-5 | |||
| ATC_prefix = C02 | |||
| ATC_suffix = AA02 | |||
| PubChem = 5770 | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| DrugBank = DB00206 | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 5566 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = 8B1QWR724A | |||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| KEGG = D00197 | |||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEBI = 28487 | |||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEMBL = 772 | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | |||
| C=33 | H=40 | N=2 | O=9 | | C=33 | H=40 | N=2 | O=9 | ||
| molecular_weight = 608.68 g/mol | | molecular_weight = 608.68 g/mol | ||
| | | exact mass = 608.27283 | ||
| | | smiles = O=C(OC)[C@H]6[C@H]4C[C@@H]3c2nc1cc(OC)ccc1c2CCN3C[C@H]4C[C@@H](OC(=O)c5cc(OC)c(OC)c(OC)c5)[C@@H]6OC | ||
| | | InChI = 1/C33H40N2O9/c1-38-19-7-8-20-21-9-10-35-16-18-13-27(44-32(36)17-11-25(39-2)30(41-4)26(12-17)40-3)31(42-5)28(33(37)43-6)22(18)15-24(35)29(21)34-23(20)14-19/h7-8,11-12,14,18,22,24,27-28,31,34H,9-10,13,15-16H2,1-6H3/t18-,22+,24-,27-,28+,31+/m1/s1 | ||
| | | InChIKey = QEVHRUUCFGRFIF-MDEJGZGSBW | ||
| | | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| StdInChI = 1S/C33H40N2O9/c1-38-19-7-8-20-21-9-10-35-16-18-13-27(44-32(36)17-11-25(39-2)30(41-4)26(12-17)40-3)31(42-5)28(33(37)43-6)22(18)15-24(35)29(21)34-23(20)14-19/h7-8,11-12,14,18,22,24,27-28,31,34H,9-10,13,15-16H2,1-6H3/t18-,22+,24-,27-,28+,31+/m1/s1 | |||
| | | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | | StdInChIKey = QEVHRUUCFGRFIF-MDEJGZGSSA-N | ||
}} | }} | ||
<!--Mechanism of Action--> | |||
|mechAction= | |||
* Reserpine depletes stores of [[catecholamine]]s and [[serotonin|5-hydroxytryptamine]] in many organs, including the [[brain]] and [[adrenal medulla]]. Most of its pharmacological effects have been attributed to this action. Depletion is slower and less complete in the [[adrenal medulla]] than in other tissues. The depression of sympathetic nerve function results in a decreased [[heart rate]] and a lowering of arterial [[blood pressure]]. The sedative and tranquilizing properties of reserpine are thought to be related to depletion of [[catecholamine]]s and [[serotonin|5-hydroxytryptamine]] from the brain. | |||
<!--Structure--> | |||
= | |structure= | ||
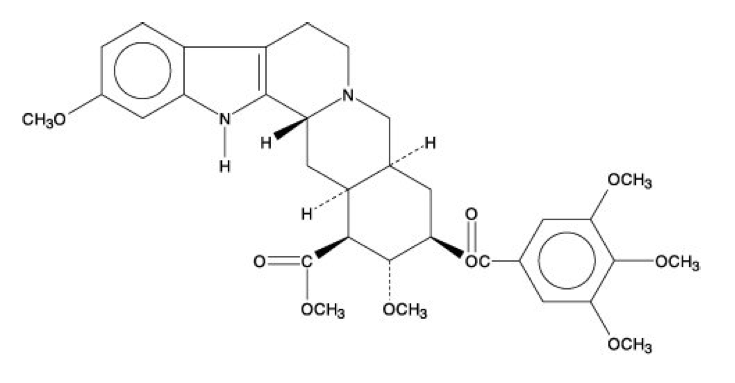
* Reserpine, USP is an antihypertensive, available as 0.1 mg and 0.25 mg tablets for oral administration. Its chemical name is methyl 18β-hydroxy-11,17 α-dimethoxy-3β, 20α-yohimban-16β-carboxylate 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate (ester) and its structural formula is: | |||
Reserpine | |||
[[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
Reserpine | * Reserpine USP, a pure crystalline alkaloid of rauwolfia, is a white or pale buff to slightly yellowish, odorless crystalline powder. It darkens slowly on exposure to light, but more rapidly when in solution. It is insoluble in water, freely soluble in acetic acid and in chloroform, slightly soluble in benzene, and very slightly soluble in alcohol and in ether. Its molecular weight is 608.69. | ||
* Inactive Ingredients: Acacia, confectioner’s sugar, corn starch, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate. | |||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | |||
|PD= | |||
* Reserpine, like other rauwolfia compounds, is characterized by slow onset of action and sustained effects. Both cardiovascular and central nervous system effects may persist for a period of time following withdrawal of the drug. | |||
* Mean maximum plasma levels of plasma concentrations after a single dose of 0.5 mg of reserpine, administered as two 0.25 mg tablets or as an aqueous solution, peaked after 2.5 hours. The mean peak level was approximately 1.1 ng/ml. The two formulations were found to be bioequivalent. Absolute bioavailability of reserpine, as established by comparison to an intravenous dose, has been reported to be approximately 50%. | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetics--> | |||
= | |PK= | ||
* Reserpine is extensively bound (95%) to plasma proteins. Reserpine is almost completely metabolized in the body, and only about 1% is excreted as unchanged drug in the urine. No definitive studies on the human metabolism of reserpine have been made. After oral administration, an initial half-life of approximately 5 hours is followed by a terminal half-life of the order of 200 hours. Plasma levels may be measurable 14 days after a single dose. The clinical significance of the long terminal half-life is unknown. | |||
<!--Nonclinical Toxicology--> | |||
|nonClinToxic= | |||
=====Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility===== | |||
[[ | * Animal Tumorigenicity | ||
[[ | :* Rodent studies have shown that reserpine is an animal tumorigen, causing an increased incidence of mammary fibroadenomas in female mice, malignant tumors of the seminal vesicles in male mice, and malignant adrenal medullary tumors in male rats. These findings arose in 2-year studies in which the drug was administered in the feed at concentrations of 5 to 10 ppm – about 100 to 300 times the usual human dose. The breast neoplasms are thought to be related to reserpine’s prolactin-elevating effect. Several other prolactin-elevating drugs have also been associated with an increased incidence of mammary [[neoplasia]] in rodents. | ||
[ | :* The extent to which these findings indicate a risk to humans is uncertain. Tissue culture experiments show that about one third of human breast tumors are prolactin-dependent in vitro, a factor of considerable importance if the use of the drug is contemplated in a patient with previously detected breast cancer. The possibility of an increased risk of [[breast cancer]] in reserpine users has been studied extensively; however, no firm conclusion has emerged. Although a few epidemiologic studies have suggested a slightly increased risk (less than twofold in all studies except one) in women who have used reserpine, other studies of generally similar design have not confirmed this. Epidemiologic studies conducted using other drugs (neuroleptic agents) that, like reserpine, increase prolactin levels and therefore would be considered rodent mammary carcinogens have not shown an association between chronic administration of the drug and human mammary tumorigenesis. While long-term clinical observation has not suggested such as association, the available evidence is considered too limited to be conclusive at this time. An association of reserpine intake with pheochromocytoma or tumors of the seminal vesicles has not been explored. | ||
<!--Clinical Studies--> | |||
|clinicalStudies= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Clinical Studies</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--How Supplied--> | |||
|howSupplied= | |||
* Reserpine Tablets, USP for oral administration are available as: | |||
:* 0.1 mg: round, white, scored tablets, debossed SZ 71 on one side and plain on the reverse side and supplied as: | |||
:: NDC 0185-0032-01 bottles of 100 | |||
:: NDC 0185-0032-10 bottles of 1000 | |||
:* 0.25 mg: round, white, scored tablets, debossed SZ 77 on one side and plain on the reverse side and supplied as: | |||
:: NDC 0185-0134-01 bottles of 100 | |||
:: NDC 0185-0134-10 bottles of 1000 | |||
* Storage | |||
:* Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture. | |||
:* Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers. | |||
<!--Patient Counseling Information--> | |||
|fdaPatientInfo= | |||
* Patients should be informed of possible side effects and advised to take the medication regularly and continuously as directed. | |||
<!--Precautions with Alcohol--> | |||
|alcohol= | |||
* Alcohol-{{PAGENAME}} interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |||
<!--Brand Names--> | |||
|brandNames= | |||
* Resa® | |||
* Serpalan®<ref>{{Cite web | title = RESERPINE tablet | url = http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=3a4d74d7-2e63-4789-b50e-af17ced92462 }}</ref> | |||
<!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | |||
|lookAlike= | |||
* N/A<ref name="www.ismp.org">{{Cite web | last = | first = | title = http://www.ismp.org | url = http://www.ismp.org | publisher = | date = }}</ref> | |||
<!--Drug Shortage Status--> | |||
|drugShortage= | |||
}} | |||
<!--Pill Image--> | |||
{{PillImage | |||
|fileName=No image.jpg|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
|drugName= | |||
|NDC= | |||
|drugAuthor= | |||
|ingredients= | |||
|pillImprint= | |||
|dosageValue= | |||
|dosageUnit= | |||
|pillColor= | |||
|pillShape= | |||
|pillSize= | |||
|pillScore= | |||
}} | |||
<!--Label Display Image--> | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}02.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}03.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}04.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
<!--Category--> | |||
[[Category:Cardiovascular Drugs]] | |||
[[Category:Drug]] | |||
[[Category:Antihypertensive agents]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:03, 20 August 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Reserpine is a catecholamine-depleting sympatholytic that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of mild essential hypertension. Common adverse reactions include abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, xerostomia, dizziness, headache, lethargy, somnolence, vertigo, depression, and nasal congestion.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Mild Essential Hypertension
- Dosing Information
- Initial Dosage
- In the average patient not receiving other antihypertensive agents, the usual initial dosage is 0.5 mg daily for 1 or 2 weeks.
- Maintenance Dosage
- For maintenance, reduce to 0.1–0.25 mg daily.
- Higher dosages should be used cautiously, because occurrence of serious mental depression and other side effects may increase considerably.
Psychiatric Disorders
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
- The usual initial dosage is 0.5 mg daily, but may range from 0.1 mg to 1.0 mg. Adjust dosage upward or downward according to the patient's response.
- Reserpine is also useful as adjunctive therapy with other antihypertensive agents in the more severe forms of hypertension; relief of symptoms in agitated psychotic states (e.g., schizophrenia), primarily in those individuals unable to tolerate phenothiazine derivatives or in those who also require antihypertensive medication.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Reserpine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Reserpine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Reserpine is not recommended for use in children.
- If it is to be used in treating a child, the usual recommended starting dose is 20 µg/kg daily. The maximum recommended dose is 0.25 mg (total) daily.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Reserpine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Reserpine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity
- Mental depression or history of mental depression (especially with suicidal tendencies)
- Active peptic ulcer
- Ulcerative colitis
- Electroconvulsive therapy
Warnings
- Extreme caution should be exercised in treating patients with a history of mental depression. Reserpine may cause mental depression. Recognition of depression may be difficult because this condition may often be disguised by somatic complaints (masked depression). The drug should be discontinued at first signs of depression such as despondency, early morning insomnia, loss of appetite, impotence, or self-deprecation. Drug-induced depression may persist for several months after drug withdrawal and may be severe enough to result in suicide.
Precautions
- General
- Since reserpine increases gastrointestinal motility and secretion, it should be used cautiously in patients with a history of peptic ulcer, ulcerative colitis, or gallstones (biliary colic may be precipitated).
- Caution should be exercised when treating hypertensive patients with renal insufficiency, since they adjust poorly to lowered blood pressure levels.
- Preoperative withdrawal of reserpine does not assure that circulatory instability will not occur. It is important that the anesthesiologist be aware of the patient’s drug intake and consider this in the overall management, since hypotension has occurred in patients receiving rauwolfia preparations. Anticholinergic and/or adrenergic drugs (e.g., metaraminol, norepinephrine) have been employed to treat adverse vagocirculatory effects.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Reserpine in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
- The following adverse reactions have been observed with rauwolfia preparations, but there has not been enough systematic collection of data to support an estimate of their frequency. Consequently the reactions are categorized by organ system and are listed in decreasing order of severity and not frequency.
Neurologic
Rare parkinsonian syndrome and other extrapyramidal tract symptoms; dizziness; headache; paradoxical anxiety; depression; nervousness; nightmares; dull sensorium; drowsiness.
Cardiovascular
Arrhythmias (particularly when used concurrently with digitalis or quinidine), syncope, angina-like symptoms, bradycardia, edema.
Respiratory
Dyspnea, epistaxis, nasal congestion.
Gastrointestinal
Vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, anorexia, dryness of mouth, hypersecretion.
Musculoskeletal
Muscular aches.
Genitourinary
Pseudolactation, impotence, dysuria, gynecomastia, decreased libido, breast engorgement.
Metabolic
Weight gain.
Hypersensitive Reactions
Special Senses
Deafness, optic atrophy, glaucoma, uveitis, conjunctival injection.
Drug Interactions
- MAO inhibitors should be avoided or used with extreme caution.
- Concurrent use of tricyclic antidepressants may decrease the antihypertensive effect of reserpine.
- Reserpine and sympathomimetics
- Concurrent use of reserpine and direct-or-indirect acting sympathomimetics should be closely monitored. The action of direct-acting amines (epinephrine, isoproterenol, phenylephrine, metaraminol) may be prolonged when given to patients taking reserpine. The action of indirect-acting amines (ephedrine, tyramine, amphetamines) is inhibited.
- Reserpine should be used cautiously with digitalis and quinidine, since cardiac arrhythmias have occurred with rauwolfia preparations.
- Concomitant use of reserpine with other antihypertensive agents necessitates careful titration of dosage with each agent.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C
- Reserpine administered parenterally has been shown to be teratogenic in rats at doses up to 2 mg/kg and to have an embryocidal effect in guinea pigs given dosages of 0.5 mg daily.
- There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of reserpine in pregnant women. Reserpine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
- Nonteratogenic Effects
- Reserpine crosses the placental barrier, and increased respiratory tract secretions, nasal congestion, cyanosis, and anorexia may occur in neonates of reserpine-treated mothers.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Reserpine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Reserpine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Reserpine is excreted in maternal breast milk, and increased respiratory tract secretions, nasal congestion, cyanosis, and anorexia may occur in breast-fed infants. Because of the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants and the potential for tumorigenicity shown for reserpine in animal studies, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in children have not been established by means of controlled clinical trials, although there is experience with the use of reserpine in children. Because of adverse effects such as emotional depression and lability, sedation, and stuffy nose, reserpine is not usually recommended as a step-2 drug in the treatment of hypertension in children.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Reserpine with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Reserpine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Reserpine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Reserpine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Reserpine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Reserpine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Reserpine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Reserpine in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Reserpine in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- No deaths due to acute poisoning with reserpine have been reported.
- Highest known doses survived: children, 1000 mg (age and sex not specified); young children, 200 mg (20-month-old boy).
- Oral LD50's in animals (mg/kg): rat, 2993; mouse, 47 and 500.
- The clinical picture of acute poisoning is characterized chiefly by signs and symptoms due to the reflex parasympathomimetic effect of reserpine.
- Impairment of consciousness may occur and may range from drowsiness to coma, depending upon the severity of overdosage. Flushing of the skin, conjunctival injection, and pupillary constriction are to be expected. Hypotension, hypothermia, central respiratory depression, and bradycardia may develop in cases of severe overdosage. Increased salivary and gastric secretion and diarrhea may also occur.
Management
- There is no specific antidote.
- Stomach contents should be evacuated, taking adequate precautions against aspiration and for protection of the airway. Activated charcoal slurry should be instilled.
- The effects of reserpine overdosage should be treated symptomatically. If hypotension is severe enough to require treatment with a vasopressor, one having a direct action upon vascular smooth muscle (e.g., phenylephrine, levarterenol, metaraminol) should be used. Since reserpine is long-acting, the patient should be observed carefully for at least 72 hours, and treatment administered as required.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Reserpine in the drug label.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- Reserpine depletes stores of catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in many organs, including the brain and adrenal medulla. Most of its pharmacological effects have been attributed to this action. Depletion is slower and less complete in the adrenal medulla than in other tissues. The depression of sympathetic nerve function results in a decreased heart rate and a lowering of arterial blood pressure. The sedative and tranquilizing properties of reserpine are thought to be related to depletion of catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine from the brain.
Structure
- Reserpine, USP is an antihypertensive, available as 0.1 mg and 0.25 mg tablets for oral administration. Its chemical name is methyl 18β-hydroxy-11,17 α-dimethoxy-3β, 20α-yohimban-16β-carboxylate 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate (ester) and its structural formula is:
- Reserpine USP, a pure crystalline alkaloid of rauwolfia, is a white or pale buff to slightly yellowish, odorless crystalline powder. It darkens slowly on exposure to light, but more rapidly when in solution. It is insoluble in water, freely soluble in acetic acid and in chloroform, slightly soluble in benzene, and very slightly soluble in alcohol and in ether. Its molecular weight is 608.69.
- Inactive Ingredients: Acacia, confectioner’s sugar, corn starch, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate.
Pharmacodynamics
- Reserpine, like other rauwolfia compounds, is characterized by slow onset of action and sustained effects. Both cardiovascular and central nervous system effects may persist for a period of time following withdrawal of the drug.
- Mean maximum plasma levels of plasma concentrations after a single dose of 0.5 mg of reserpine, administered as two 0.25 mg tablets or as an aqueous solution, peaked after 2.5 hours. The mean peak level was approximately 1.1 ng/ml. The two formulations were found to be bioequivalent. Absolute bioavailability of reserpine, as established by comparison to an intravenous dose, has been reported to be approximately 50%.
Pharmacokinetics
- Reserpine is extensively bound (95%) to plasma proteins. Reserpine is almost completely metabolized in the body, and only about 1% is excreted as unchanged drug in the urine. No definitive studies on the human metabolism of reserpine have been made. After oral administration, an initial half-life of approximately 5 hours is followed by a terminal half-life of the order of 200 hours. Plasma levels may be measurable 14 days after a single dose. The clinical significance of the long terminal half-life is unknown.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Animal Tumorigenicity
- Rodent studies have shown that reserpine is an animal tumorigen, causing an increased incidence of mammary fibroadenomas in female mice, malignant tumors of the seminal vesicles in male mice, and malignant adrenal medullary tumors in male rats. These findings arose in 2-year studies in which the drug was administered in the feed at concentrations of 5 to 10 ppm – about 100 to 300 times the usual human dose. The breast neoplasms are thought to be related to reserpine’s prolactin-elevating effect. Several other prolactin-elevating drugs have also been associated with an increased incidence of mammary neoplasia in rodents.
- The extent to which these findings indicate a risk to humans is uncertain. Tissue culture experiments show that about one third of human breast tumors are prolactin-dependent in vitro, a factor of considerable importance if the use of the drug is contemplated in a patient with previously detected breast cancer. The possibility of an increased risk of breast cancer in reserpine users has been studied extensively; however, no firm conclusion has emerged. Although a few epidemiologic studies have suggested a slightly increased risk (less than twofold in all studies except one) in women who have used reserpine, other studies of generally similar design have not confirmed this. Epidemiologic studies conducted using other drugs (neuroleptic agents) that, like reserpine, increase prolactin levels and therefore would be considered rodent mammary carcinogens have not shown an association between chronic administration of the drug and human mammary tumorigenesis. While long-term clinical observation has not suggested such as association, the available evidence is considered too limited to be conclusive at this time. An association of reserpine intake with pheochromocytoma or tumors of the seminal vesicles has not been explored.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Reserpine in the drug label.
How Supplied
- Reserpine Tablets, USP for oral administration are available as:
- 0.1 mg: round, white, scored tablets, debossed SZ 71 on one side and plain on the reverse side and supplied as:
- NDC 0185-0032-01 bottles of 100
- NDC 0185-0032-10 bottles of 1000
- 0.25 mg: round, white, scored tablets, debossed SZ 77 on one side and plain on the reverse side and supplied as:
- NDC 0185-0134-01 bottles of 100
- NDC 0185-0134-10 bottles of 1000
- Storage
- Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture.
- Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Reserpine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Reserpine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Reserpine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Patients should be informed of possible side effects and advised to take the medication regularly and continuously as directed.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Reserpine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Resa®
- Serpalan®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- N/A[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "RESERPINE tablet".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Reserpine |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Reserpine |Label Name=Reserpine02.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Reserpine |Label Name=Reserpine03.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Reserpine |Label Name=Reserpine04.png
}}