Repaglinide
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
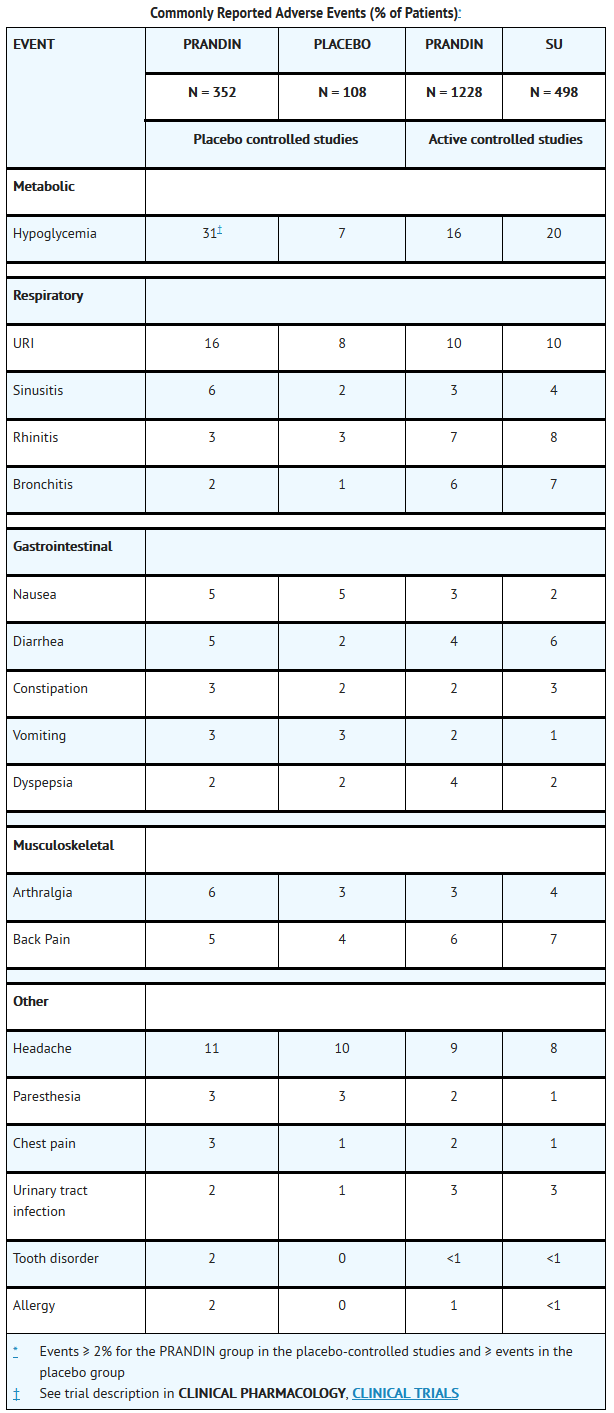
Repaglinide is an antidiabetic agent that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Common adverse reactions include hypoglycemia, diarrhea, arthralgia, headache, sinusitis, upper respiratory infection.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Starting Dose
- For patients not previously treated or whose HbA1c is < 8%, the starting dose should be 0.5 mg with each meal. For patients previously treated with blood glucose-lowering drugs and whose HbA1c is ≥ 8%, the initial dose is 1 or 2 mg with each meal preprandially.
- Dose Adjustment
- Dosing adjustments should be determined by blood glucose response, usually fasting blood glucose. Postprandial glucose levels testing may be clinically helpful in patients whose pre-meal blood glucose levels are satisfactory but whose overall glycemic control (HbA1c) is inadequate. The preprandial dose should be doubled up to 4 mg with each meal until satisfactory blood glucose response is achieved. At least one week should elapse to assess response after each dose adjustment.
- The recommended dose range is 0.5 mg to 4 mg taken with meals. PRANDIN may be dosed preprandially 2, 3, or 4 times a day in response to changes in the patient’s meal pattern. The maximum recommended daily dose is 16 mg.
- Patient Management
- Long-term efficacy should be monitored by measurement of HbA1c levels approximately every 3 months. Failure to follow an appropriate dosage regimen may precipitate hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Patients who do not adhere to their prescribed dietary and drug regimen are more prone to exhibit unsatisfactory response to therapy including hypoglycemia. When hypoglycemia occurs in patients taking a combination of PRANDIN and a thiazolidinedione or PRANDIN and metformin, the dose of PRANDIN should be reduced.
- Patients Receiving Other Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
- When PRANDIN is used to replace therapy with other oral hypoglycemic agents, PRANDIN may be started on the day after the final dose is given. Patients should then be observed carefully for hypoglycemia due to potential overlapping of drug effects. When transferred from longer half-life sulfonylurea agents (e.g., chlorpropamide) to repaglinide, close monitoring may be indicated for up to one week or longer.
- Combination Therapy
- If PRANDIN monotherapy does not result in adequate glycemic control, metformin or a thiazolidinedione may be added. If metformin or thiazolidinedione monotherapy does not provide adequate control, PRANDIN may be added. The starting dose and dose adjustments for PRANDIN combination therapy is the same as for PRANDIN monotherapy. The dose of each drug should be carefully adjusted to determine the minimal dose required to achieve the desired pharmacologic effect. Failure to do so could result in an increase in the incidence of hypoglycemic episodes. Appropriate monitoring of FPG and HbA1c measurements should be used to ensure that the patient is not subjected to excessive drug exposure or increased probability of secondary drug failure.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Repaglinide in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Repaglinide in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Repaglinide in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Repaglinide in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Repaglinide in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Diabetic ketoacidosis, with or without coma. This condition should be treated with insulin.
- Type 1 diabetes.
- Co-administration of gemfibrozil.
- Known hypersensitivity to the drug or its inactive ingredients.
Warnings
Precautions
- General:
- PRANDIN is not indicated for use in combination with NPH-insulin (See ADVERSE REACTIONS, Cardiovascular Events).
- Macrovascular Outcomes:
- There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with PRANDIN or any other anti-diabetic drug.
- Hypoglycemia
- All oral blood glucose-lowering drugs including repaglinide are capable of producing hypoglycemia. Proper patient selection, dosage, and instructions to the patients are important to avoid hypoglycemic episodes. Hepatic insufficiency may cause elevated repaglinide blood levels and may diminish gluconeogenic capacity, both of which increase the risk of serious hypoglycemia. Elderly, debilitated, or malnourished patients, and those with adrenal, pituitary, hepatic, or severe renal insufficiency may be particularly susceptible to the hypoglycemic action of glucose-lowering drugs.
- Hypoglycemia may be difficult to recognize in the elderly and in people taking beta-adrenergic blocking drugs. Hypoglycemia is more likely to occur when caloric intake is deficient, after severe or prolonged exercise, when alcohol is ingested, or when more than one glucose-lowering drug is used.
- The frequency of hypoglycemia is greater in patients with type 2 diabetes who have not been previously treated with oral blood glucose-lowering drugs (naïve) or whose HbA1c is less than 8%. PRANDIN should be administered with meals to lessen the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Loss of Control of Blood Glucose: When a patient stabilized on any diabetic regimen is exposed to stress such as fever, trauma, infection, or surgery, a loss of glycemic control may occur. At such times, it may be necessary to discontinue PRANDIN and administer insulin. The effectiveness of any hypoglycemic drug in lowering blood glucose to a desired level decreases in many patients over a period of time, which may be due to progression of the severity of diabetes or to diminished responsiveness to the drug. This phenomenon is known as secondary failure, to distinguish it from primary failure in which the drug is ineffective in an individual patient when the drug is first given. Adequate adjustment of dose and adherence to diet should be assessed before classifying a patient as a secondary failure.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Repaglinide in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Repaglinide in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Repaglinide in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Repaglinide during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Repaglinide with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Repaglinide with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Repaglinide with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Repaglinide with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Repaglinide with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Repaglinide in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Repaglinide in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Repaglinide in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Repaglinide in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Repaglinide in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Repaglinide in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Repaglinide in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Repaglinide Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Repaglinide in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Repaglinide in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Repaglinide in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Repaglinide in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Repaglinide Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Repaglinide |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Repaglinide |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Patients should be informed of the potential risks and advantages of PRANDIN and of alternative modes of therapy. They should also be informed about the importance of adherence to dietary instructions, of a regular exercise program, and of regular testing of blood glucose and HbA1c. The risks of hypoglycemia, its symptoms and treatment, and conditions that predispose to its development and concomitant administration of other glucose-lowering drugs should be explained to patients and responsible family members. Primary and secondary failure should also be explained.
- Patients should be instructed to take PRANDIN before meals (2, 3, or 4 times a day preprandially). Doses are usually taken within 15 minutes of the meal but time may vary from immediately preceding the meal to as long as 30 minutes before the meal. Patients who skip a meal (or add an extra meal) should be instructed to skip (or add) a dose for that meal.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Repaglinide interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Repaglinide |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Repaglinide |Label Name=Repaglinide11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Repaglinide |Label Name=Repaglinide11.png
}}