Pyelonephritis CT scan: Difference between revisions
Usama Talib (talk | contribs) (→CT) |
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Pyelonephritis}} | {{Pyelonephritis}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{USAMA}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
A CT scan can be used to detect pyelonephritis | A [[CT scan]] can be used to detect diffuse or complicated pyelonephritis and its suspected complications. It is used when the suspicion of pyelonephritis is accompanied by other differentials. CT scan is very sensitive and [[CT]] urography is sometimes used for imaging of the [[urinary tract]]. The extent of damage to the parenchymal tissue can also be witnessed in detail with a [[CT scan]]. | ||
==CT== | ==CT== | ||
Findings on a CT scan may vary with respect to the type of pyelonephritis. A CT scan usually | Findings on a [[CT scan]] may vary with respect to the type of pyelonephritis. A [[CT scan]] usually demonstrates:<ref name="pmid2651759">{{cite journal| author=Meyrier A, Condamin MC, Fernet M, Labigne-Roussel A, Simon P, Callard P et al.| title=Frequency of development of early cortical scarring in acute primary pyelonephritis. | journal=Kidney Int | year= 1989 | volume= 35 | issue= 2 | pages= 696-703 | pmid=2651759 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=2651759 }} </ref><ref name="pmid2798873">{{cite journal| author=Soulen MC, Fishman EK, Goldman SM| title=Sequelae of acute renal infections: CT evaluation. | journal=Radiology | year= 1989 | volume= 173 | issue= 2 | pages= 423-6 | pmid=2798873 | doi=10.1148/radiology.173.2.2798873 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=2798873 }} </ref><ref name="pmid17318482">{{cite journal| author=Demertzis J, Menias CO| title=State of the art: imaging of renal infections. | journal=Emerg Radiol | year= 2007 | volume= 14 | issue= 1 | pages= 13-22 | pmid=17318482 | doi=10.1007/s10140-007-0591-3 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=17318482 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8126807">{{cite journal| author=Fowler JE, Perkins T| title=Presentation, diagnosis and treatment of renal abscesses: 1972-1988. | journal=J Urol | year= 1994 | volume= 151 | issue= 4 | pages= 847-51 | pmid=8126807 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8126807 }} </ref><ref name="pmid21292654">{{cite journal| author=Gupta K, Hooton TM, Naber KG, Wullt B, Colgan R, Miller LG et al.| title=International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. | journal=Clin Infect Dis | year= 2011 | volume= 52 | issue= 5 | pages= e103-20 | pmid=21292654 | doi=10.1093/cid/ciq257 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21292654 }} </ref><ref name="pmid12848478">{{cite journal| author=Kawashima A, LeRoy AJ| title=Radiologic evaluation of patients with renal infections. | journal=Infect Dis Clin North Am | year= 2003 | volume= 17 | issue= 2 | pages= 433-56 | pmid=12848478 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12848478 }} </ref> | ||
*Round swollen kidneys | *Round swollen [[Kidney|kidneys]] | ||
* | *Hypodense appearance | ||
* | *[[Abscess]]es may not be present | ||
===Acute Pyelonephritis=== | ===Acute Pyelonephritis=== | ||
[http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki] | [[CT scan]] in case of acute pyelonephritis may demonstrate:<ref name="pmid2651759">{{cite journal| author=Meyrier A, Condamin MC, Fernet M, Labigne-Roussel A, Simon P, Callard P et al.| title=Frequency of development of early cortical scarring in acute primary pyelonephritis. | journal=Kidney Int | year= 1989 | volume= 35 | issue= 2 | pages= 696-703 | pmid=2651759 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=2651759 }} </ref><ref name="pmid2388315">{{cite journal| author=Tsugaya M, Hirao N, Sakagami H, Iwase Y, Watase H, Ohtaguro K et al.| title=Computerized tomography in acute pyelonephritis: the clinical correlations. | journal=J Urol | year= 1990 | volume= 144 | issue= 3 | pages= 611-3 | pmid=2388315 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=2388315 }} </ref> | ||
'''[http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki]''' | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Acute | Image:CT Acute Pyelonephritis.gif|CT: Acute pyelonephritis | ||
Image:Acute pyelonephritis 002.jpg|CT: Acute pyelonephritis | Image:Acute pyelonephritis 002.jpg|CT: Acute pyelonephritis | ||
Image:Acute pyelonephritis 003.jpg|CT: Acute pyelonephritis | Image:Acute pyelonephritis 003.jpg|CT: Acute pyelonephritis | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
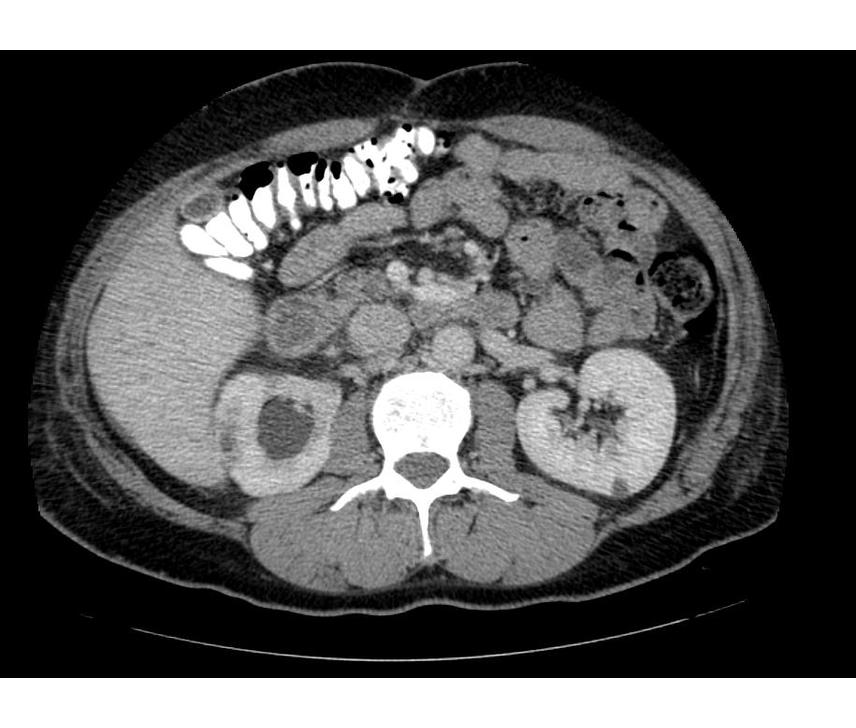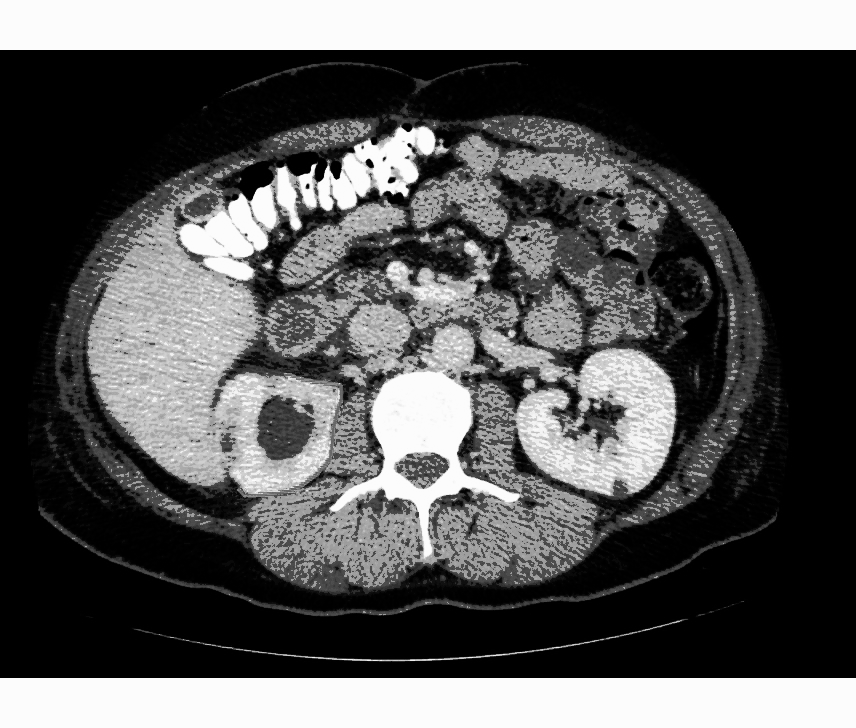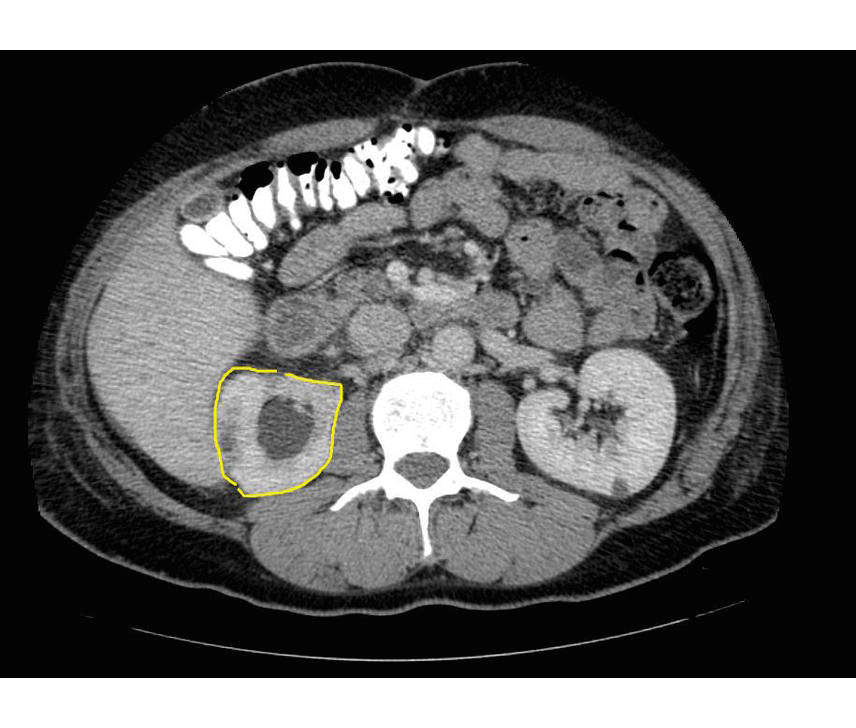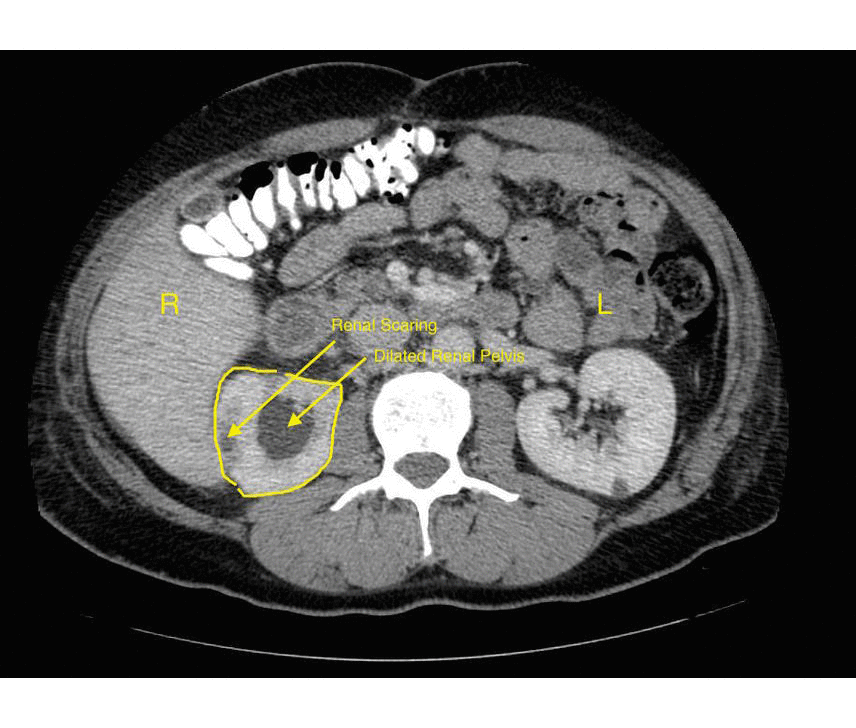
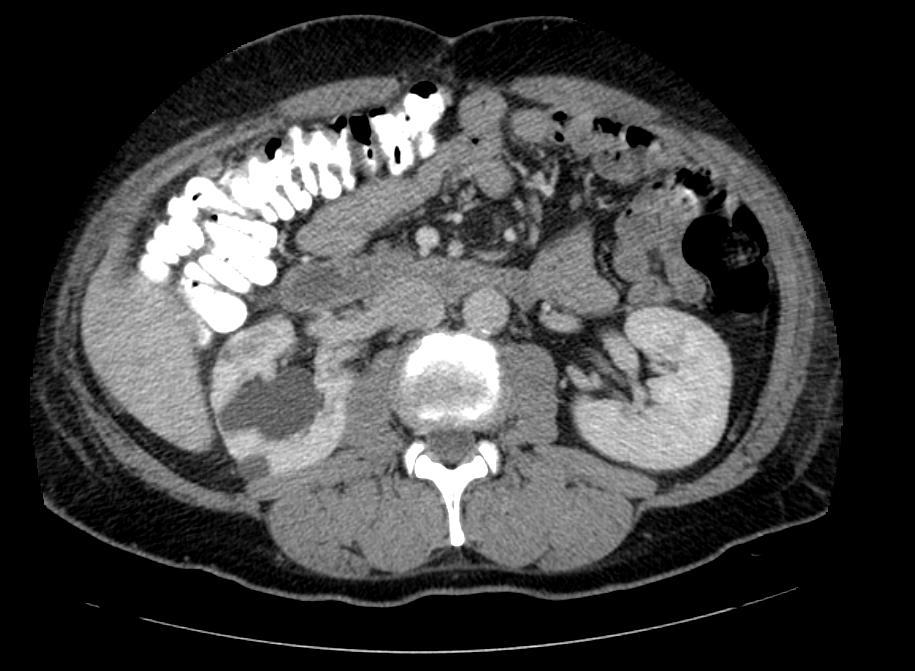
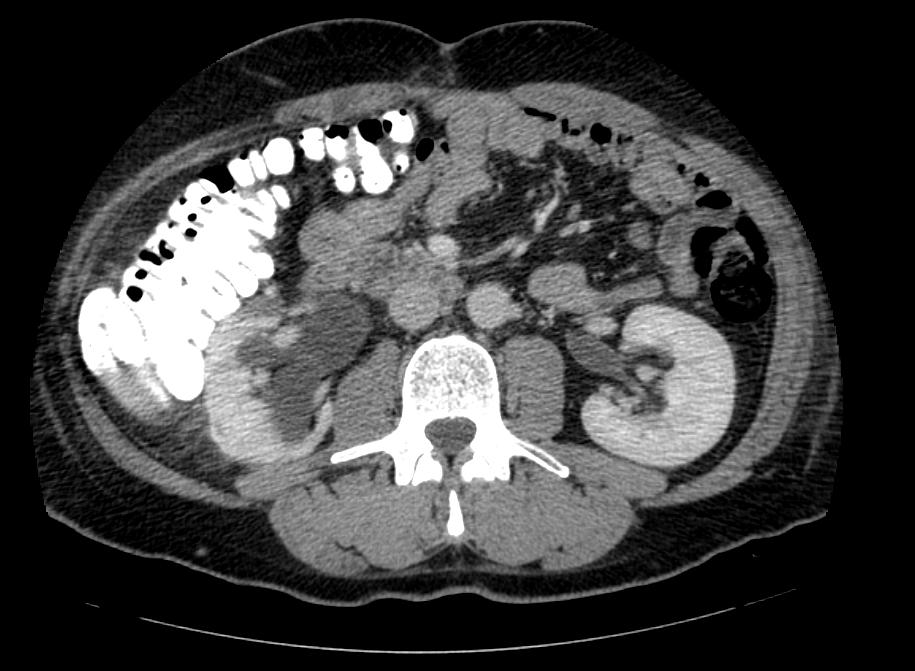
===Chronic Pyelonephritis=== | ===Chronic Pyelonephritis=== | ||
Imaging findings are characterized by renal scarring, [[atrophy]] and cortical thinning, [[hypertrophy]] of residual normal tissue, caliceal clubbing secondary to retraction of the [[papilla]] from overlying scar, thickening and dilatation of the caliceal system, and overall renal asymmetry. | Imaging findings are characterized by renal scarring, [[atrophy]] and cortical thinning, [[hypertrophy]] of residual normal tissue, caliceal clubbing secondary to retraction of the [[papilla]] from overlying scar, thickening and dilatation of the caliceal system, and overall renal asymmetry. | ||
[http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki] | '''[http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki]''' | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Chronic | Image:Chronic Pyelo CT.gif|CT image demonstrates chronic pyelonephritis on the right | ||
Image:Chronic-pyelonephritis-002.jpg|CT image demonstrates chronic pyelonephritis on the right | Image:Chronic-pyelonephritis-002.jpg|CT image demonstrates chronic pyelonephritis on the right | ||
Image:Chronic-pyelonephritis-003.jpg|CT image demonstrates chronic pyelonephritis on the right | Image:Chronic-pyelonephritis-003.jpg|CT image demonstrates chronic pyelonephritis on the right | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
===Emphysematous Pyelonephritis=== | ===Emphysematous Pyelonephritis=== | ||
*Additional evaluation with CT will confirm the presence and extent of parenchymal gas and will often allow identification of the source of obstruction when present. | *Additional evaluation with [[CT]] will confirm the presence and extent of parenchymal gas and will often allow identification of the source of obstruction when present. | ||
*The use of intravenous contrast material will often reveal asymmetric renal enhancement or delayed excretion, and, during the [[nephrographic]] phase, will help identify areas of focal tissue [[necrosis]] or abscess formation. | *The use of intravenous contrast material will often reveal asymmetric renal enhancement or delayed excretion, and, during the [[nephrographic]] phase, will help identify areas of focal tissue [[necrosis]] or abscess formation. | ||
[http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki] | '''[http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki]''' | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Emphysematous Pyelo.gif|CT: Emphysematous pyelonephritis | |||
Image:Emphysematous-pyelonephritis-001.jpg|CT: Emphysematous pyelonephritis | Image:Emphysematous-pyelonephritis-001.jpg|CT: Emphysematous pyelonephritis | ||
Image:Emphysematous-pyelonephritis-002.jpg|CT: Emphysematous pyelonephritis | Image:Emphysematous-pyelonephritis-002.jpg|CT: Emphysematous pyelonephritis | ||
Image:Emphysematous-pyelonephritis-003.jpg|CT: Emphysematous pyelonephritis | Image:Emphysematous-pyelonephritis-003.jpg|CT: Emphysematous pyelonephritis | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
===Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis=== | ===Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis=== | ||
The CT findings of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis are pathognomonic in most cases: diffuse [[reniform]] enlargement with ill-defined central low attenuation, apparent cortical thinning, and central calculi. <ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/9931">rID: 9931</ref> | The [[CT]] findings of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis are pathognomonic in most cases: diffuse [[reniform]] enlargement with ill-defined central low attenuation, apparent cortical thinning, and central calculi.<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/9931">rID: 9931</ref> | ||
*Extension into the [[perinephric space]] and beyond the [[Gerota fascia]] is not uncommon. | *Extension into the [[perinephric space]] and beyond the [[Gerota fascia]] is not uncommon. | ||
*Central areas of low [[attenuation]] represent [[nonenhancing]] xanthomatous material that may demonstrate attenuation values less than those of water. | *Central areas of low [[attenuation]] represent [[nonenhancing]] xanthomatous material that may demonstrate attenuation values less than those of water. | ||
[http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki] | '''[http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki]''' | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:XP Dilated renal calyces.gif|CT image demonstrates right xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis | |||
Image:Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis 001.jpg|CT image demonstrates right xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis | Image:Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis 001.jpg|CT image demonstrates right xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis | ||
Image:Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis 003.jpg|CT image demonstrates right xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis | Image:Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis 003.jpg|CT image demonstrates right xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis | ||
Image:Xanthogranulomatous-pyelonephritis-2.jpg|CT image demonstrates right xanthogranuomatous pyelonephritis with dilated calyces | Image:Xanthogranulomatous-pyelonephritis-2.jpg|CT image demonstrates right xanthogranuomatous pyelonephritis with dilated calyces | ||
| Line 51: | Line 55: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{WH}} | |||
{{WS}} | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Infectious disease]] | |||
[[Category:Nephrology]] | [[Category:Nephrology]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Urology]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Up-To-Date]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Radiology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:54, 29 July 2020
|
Pyelonephritis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pyelonephritis CT scan On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pyelonephritis CT scan |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Pyelonephritis CT scan |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Usama Talib, BSc, MD [2]
Overview
A CT scan can be used to detect diffuse or complicated pyelonephritis and its suspected complications. It is used when the suspicion of pyelonephritis is accompanied by other differentials. CT scan is very sensitive and CT urography is sometimes used for imaging of the urinary tract. The extent of damage to the parenchymal tissue can also be witnessed in detail with a CT scan.
CT
Findings on a CT scan may vary with respect to the type of pyelonephritis. A CT scan usually demonstrates:[1][2][3][4][5][6]
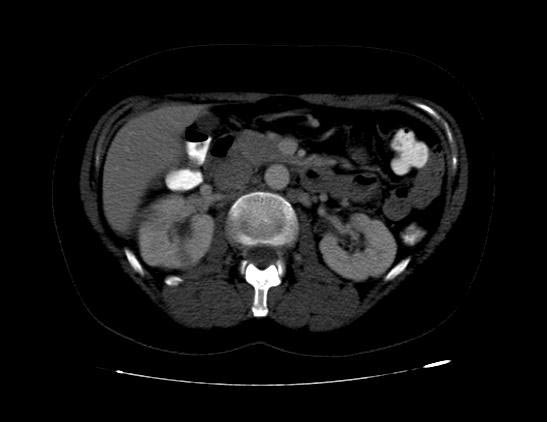
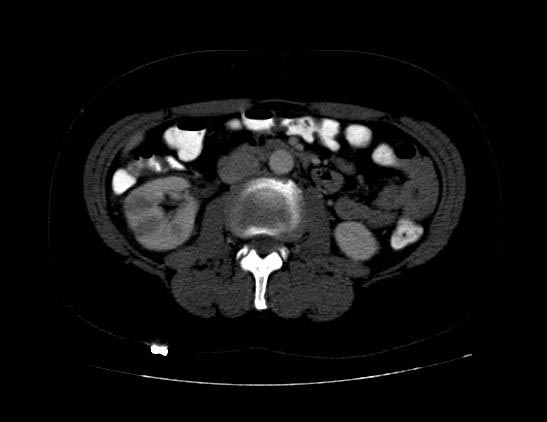
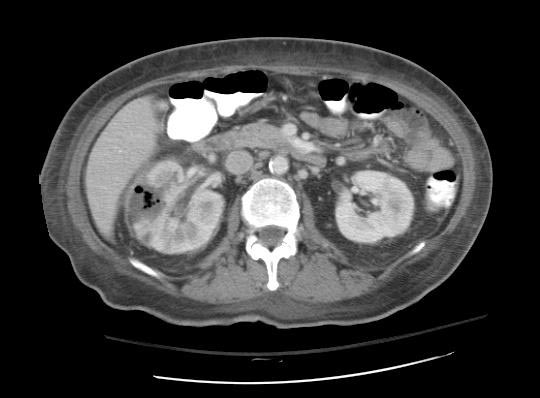
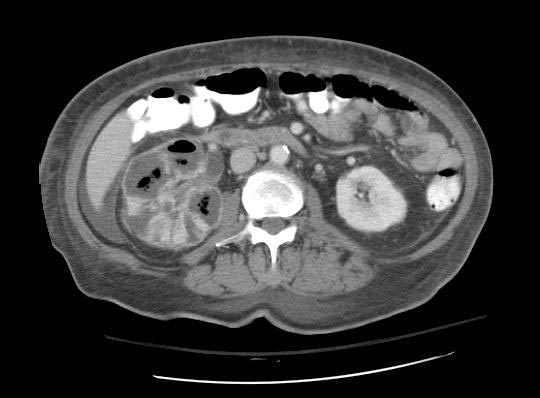
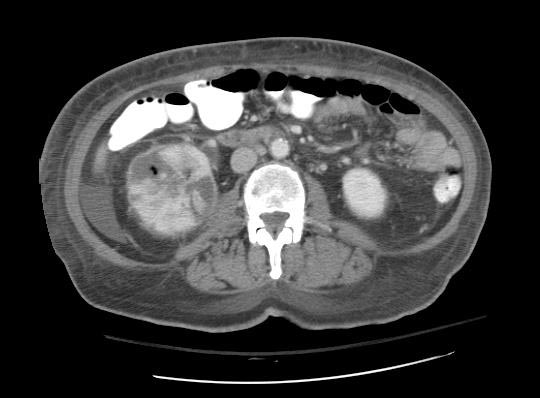
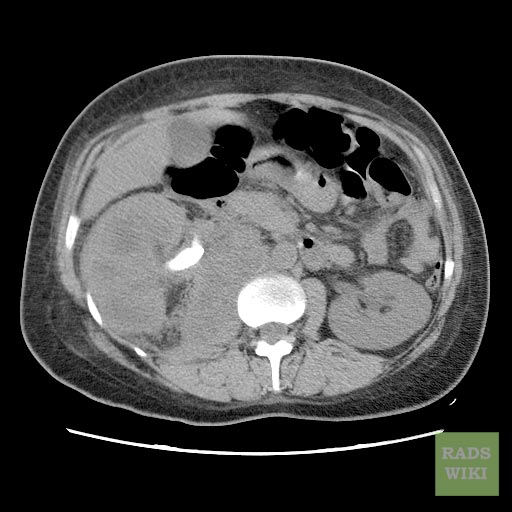
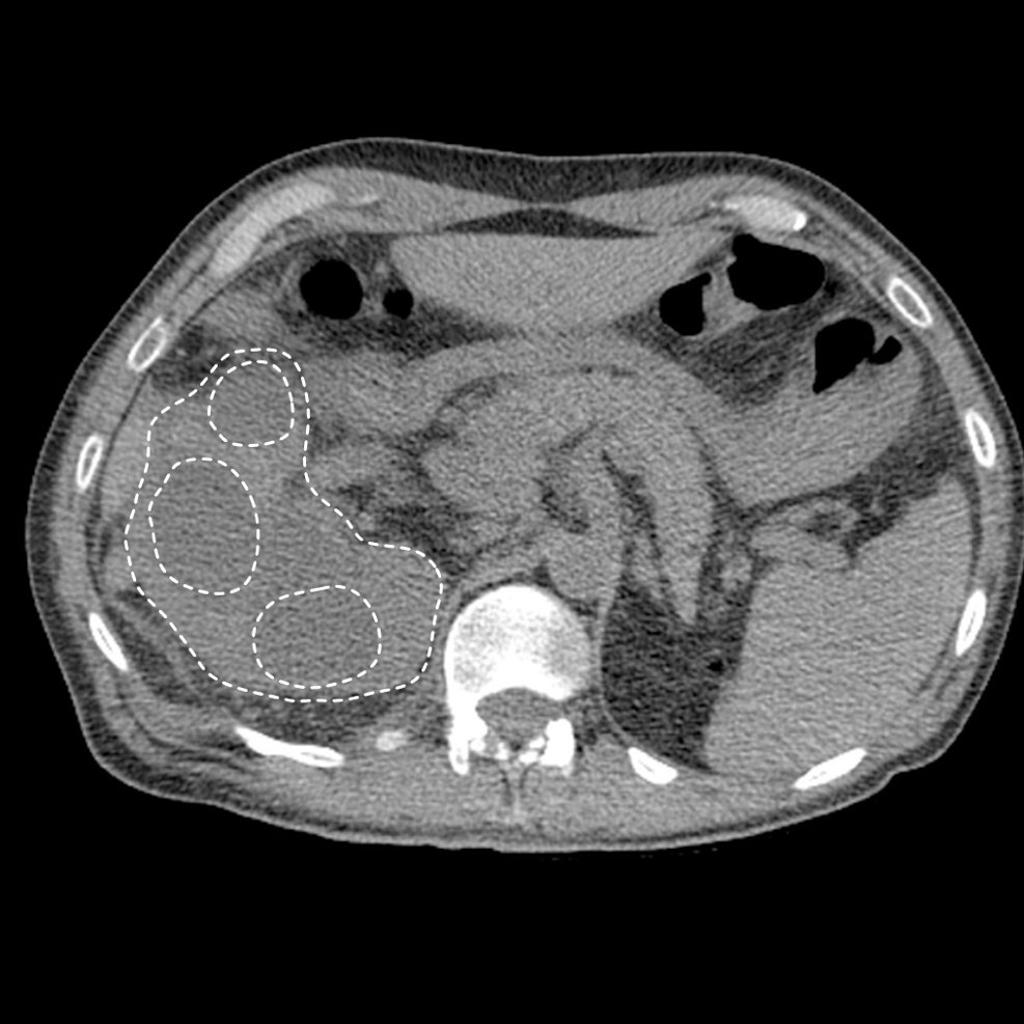
Acute Pyelonephritis
CT scan in case of acute pyelonephritis may demonstrate:[1][7] Images courtesy of RadsWiki
-
CT: Acute pyelonephritis
-
CT: Acute pyelonephritis
-
CT: Acute pyelonephritis
Chronic Pyelonephritis
Imaging findings are characterized by renal scarring, atrophy and cortical thinning, hypertrophy of residual normal tissue, caliceal clubbing secondary to retraction of the papilla from overlying scar, thickening and dilatation of the caliceal system, and overall renal asymmetry. Images courtesy of RadsWiki
-
CT image demonstrates chronic pyelonephritis on the right
-
CT image demonstrates chronic pyelonephritis on the right
-
CT image demonstrates chronic pyelonephritis on the right
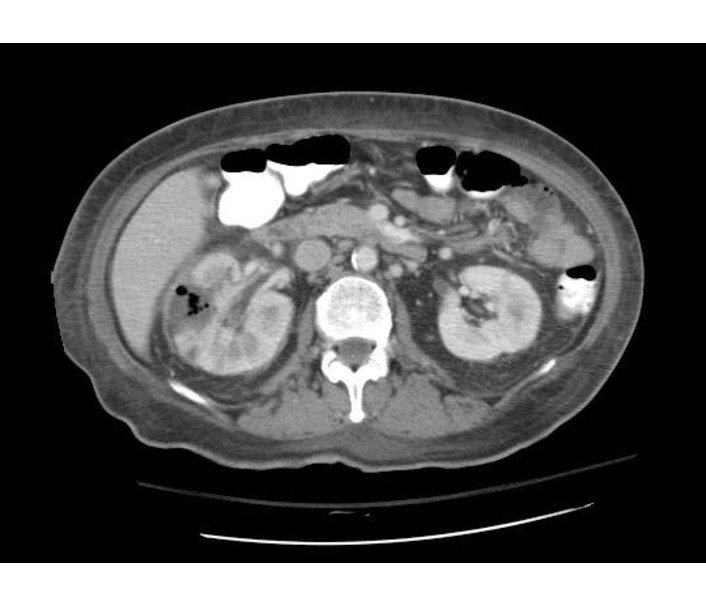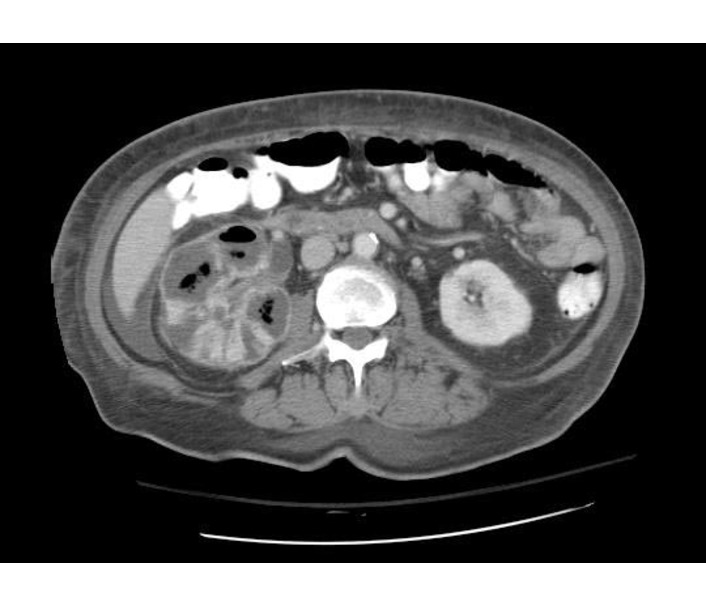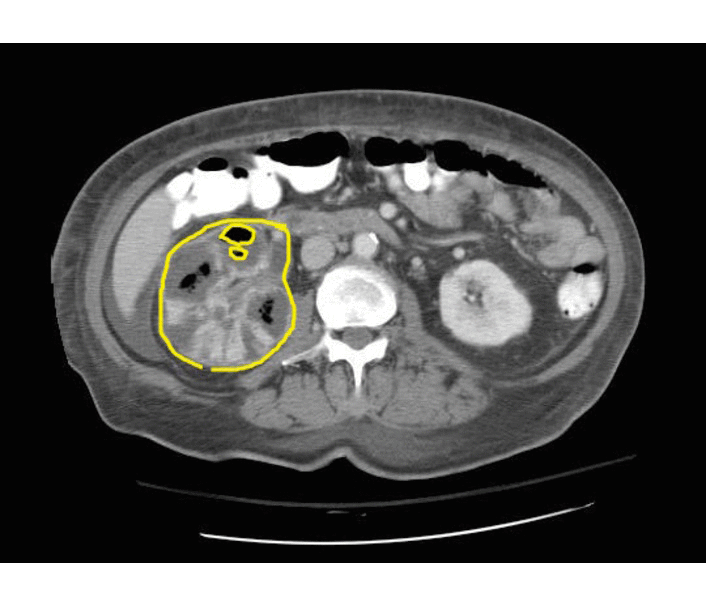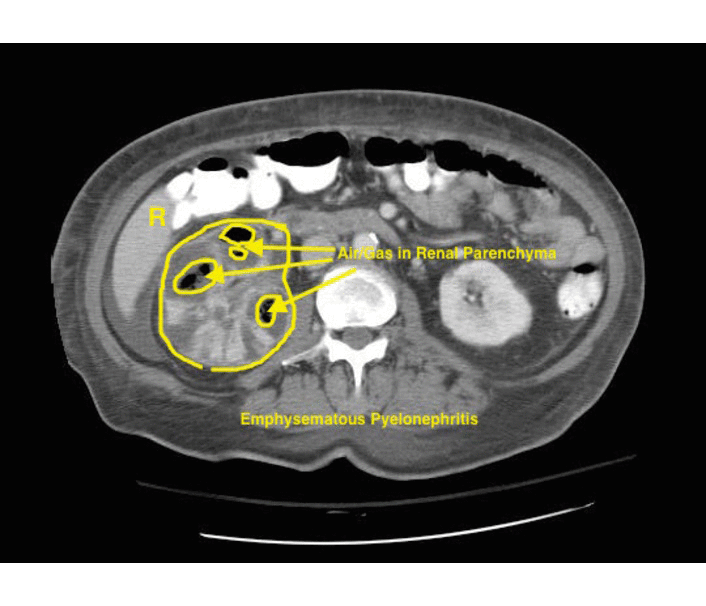
Emphysematous Pyelonephritis
- Additional evaluation with CT will confirm the presence and extent of parenchymal gas and will often allow identification of the source of obstruction when present.
- The use of intravenous contrast material will often reveal asymmetric renal enhancement or delayed excretion, and, during the nephrographic phase, will help identify areas of focal tissue necrosis or abscess formation.
-
CT: Emphysematous pyelonephritis
-
CT: Emphysematous pyelonephritis
-
CT: Emphysematous pyelonephritis
-
CT: Emphysematous pyelonephritis
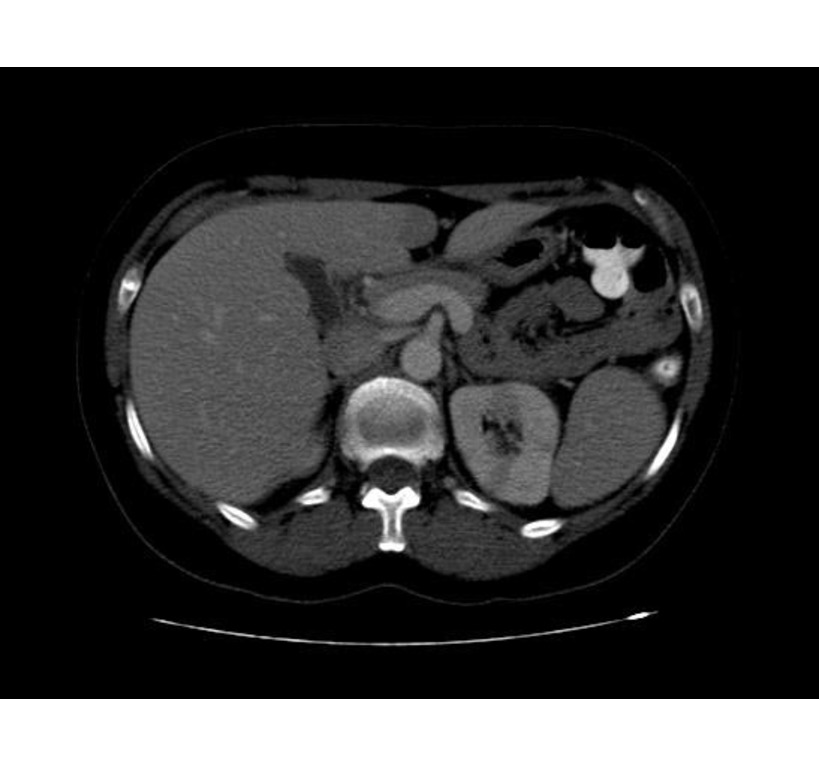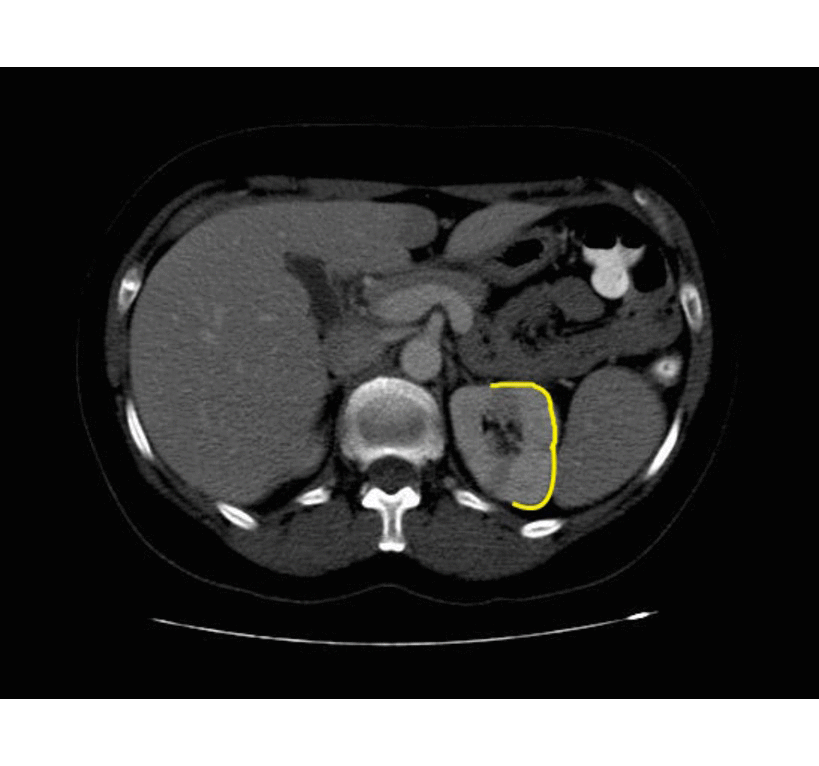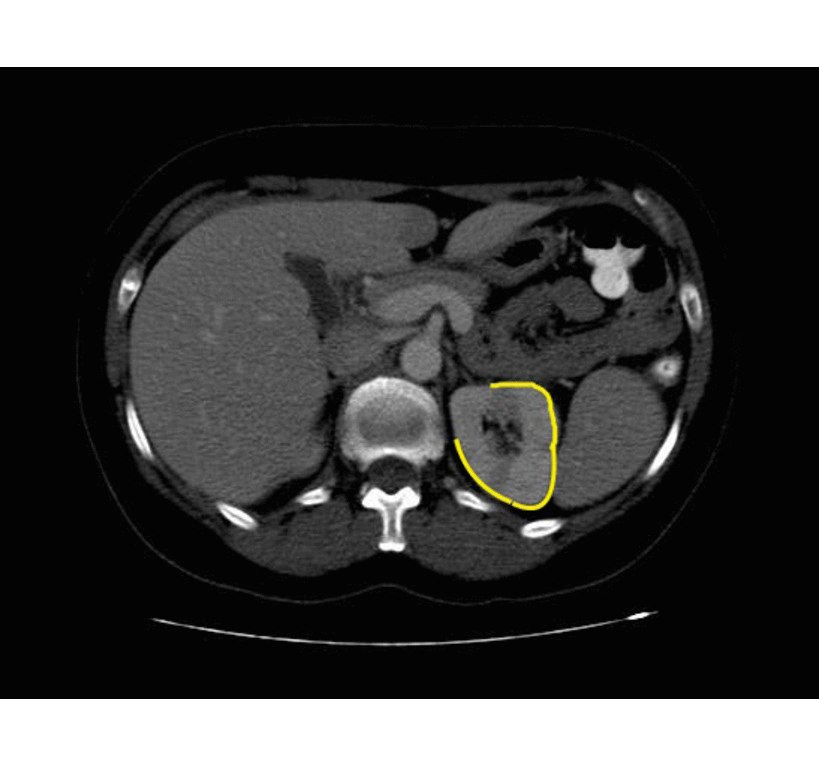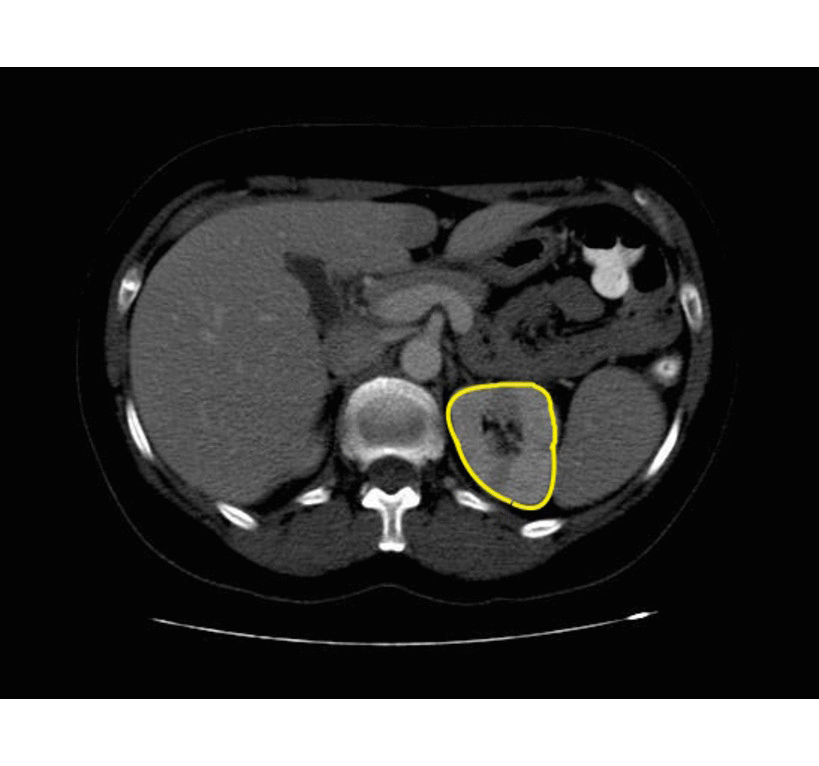
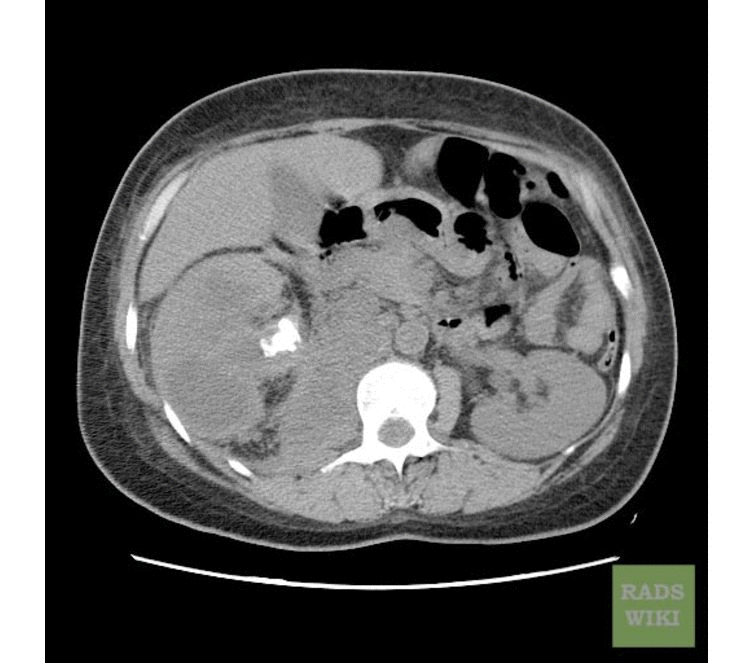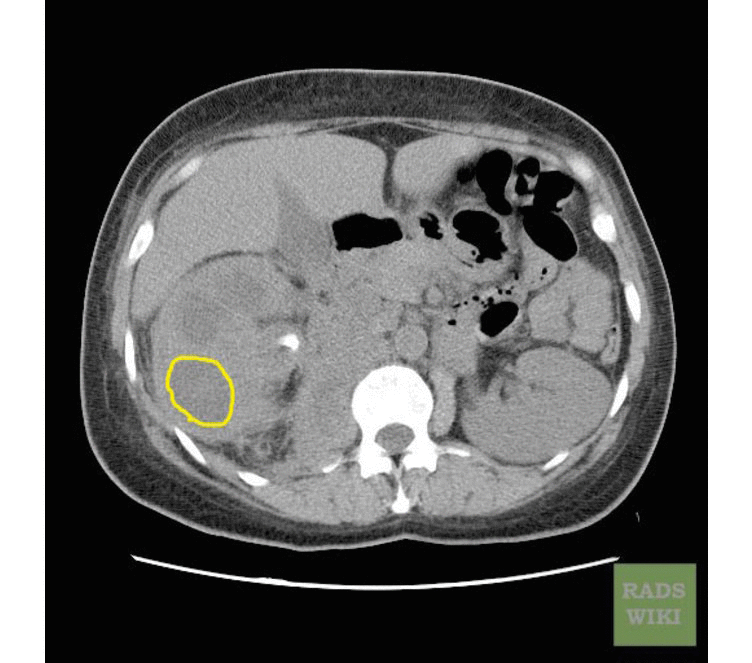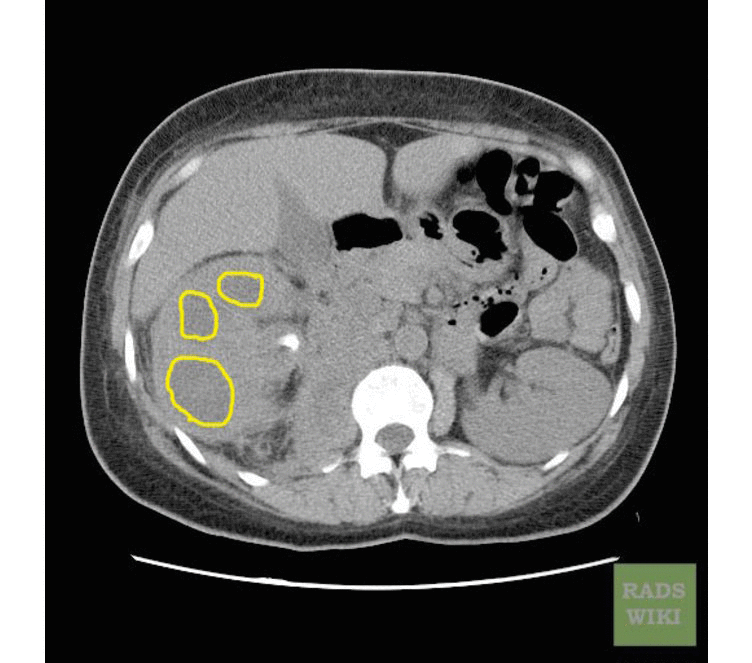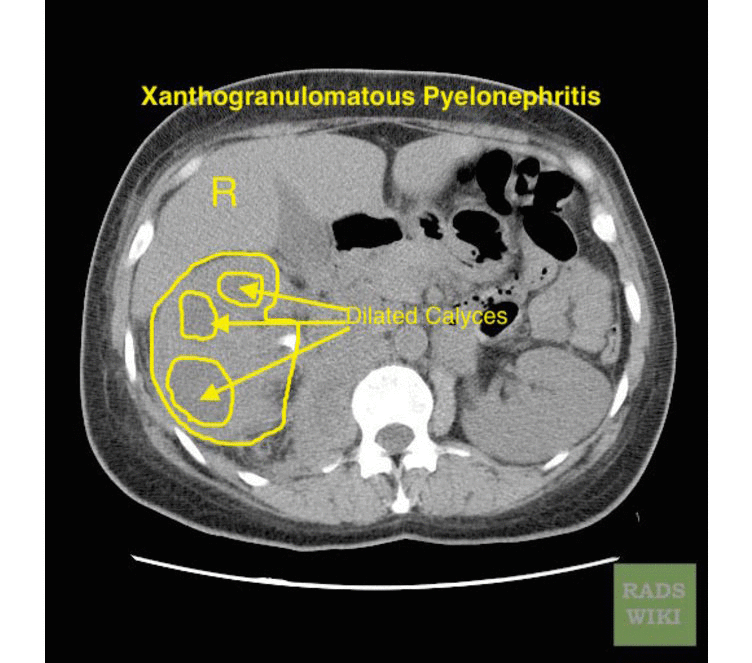
Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis
The CT findings of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis are pathognomonic in most cases: diffuse reniform enlargement with ill-defined central low attenuation, apparent cortical thinning, and central calculi.[8]
- Extension into the perinephric space and beyond the Gerota fascia is not uncommon.
- Central areas of low attenuation represent nonenhancing xanthomatous material that may demonstrate attenuation values less than those of water.
-
CT image demonstrates right xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
-
CT image demonstrates right xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
-
CT image demonstrates right xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
-
CT image demonstrates right xanthogranuomatous pyelonephritis with dilated calyces
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Meyrier A, Condamin MC, Fernet M, Labigne-Roussel A, Simon P, Callard P; et al. (1989). "Frequency of development of early cortical scarring in acute primary pyelonephritis". Kidney Int. 35 (2): 696–703. PMID 2651759.
- ↑ Soulen MC, Fishman EK, Goldman SM (1989). "Sequelae of acute renal infections: CT evaluation". Radiology. 173 (2): 423–6. doi:10.1148/radiology.173.2.2798873. PMID 2798873.
- ↑ Demertzis J, Menias CO (2007). "State of the art: imaging of renal infections". Emerg Radiol. 14 (1): 13–22. doi:10.1007/s10140-007-0591-3. PMID 17318482.
- ↑ Fowler JE, Perkins T (1994). "Presentation, diagnosis and treatment of renal abscesses: 1972-1988". J Urol. 151 (4): 847–51. PMID 8126807.
- ↑ Gupta K, Hooton TM, Naber KG, Wullt B, Colgan R, Miller LG; et al. (2011). "International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases". Clin Infect Dis. 52 (5): e103–20. doi:10.1093/cid/ciq257. PMID 21292654.
- ↑ Kawashima A, LeRoy AJ (2003). "Radiologic evaluation of patients with renal infections". Infect Dis Clin North Am. 17 (2): 433–56. PMID 12848478.
- ↑ Tsugaya M, Hirao N, Sakagami H, Iwase Y, Watase H, Ohtaguro K; et al. (1990). "Computerized tomography in acute pyelonephritis: the clinical correlations". J Urol. 144 (3): 611–3. PMID 2388315.
- ↑ Radiopaedia.org. Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/9931">rID: 9931