|
|
| Line 10: |
Line 10: |
| OMIM = | | | OMIM = | |
| MedlinePlus = 000084 | | | MedlinePlus = 000084 | |
| eMedicineSubj = ped |
| |
| eMedicineTopic = 1832 |
| |
| eMedicine_mult = {{eMedicine2|emerg|469}} |
| |
| MeshID = D008478 | | | MeshID = D008478 | |
| }} | | }} |
| Line 18: |
Line 15: |
| {{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor In Chief:''' {{CZ}} | | {{CMG}}; '''Associate Editor In Chief:''' {{CZ}} |
|
| |
|
| ==Overview== | | ==[[Pneumomediastinum overview|Overview]]== |
| | ==[[Pneumomediastinum historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== |
| | ==[[Pneumomediastinum pathophysiology |Pathophysiology]]== |
| | ==[[Pneumomediastinum causes|Causes]]== |
| | ==[[Pneumomediastinum differential diagnosis|Differentiating Pneumomediastinum from other Diseases]]== |
| | ==[[Pneumomediastinum epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== |
| | ==[[Pneumomediastinum natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== |
| | ==Diagnosis== |
| | [[Pneumomediastinum history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Pneumomediastinum physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Pneumomediastinum laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Pneumomediastinum electrocardiogram|Electrocardiogram]] | [[Pneumomediastinum chest x ray|Chest X Ray]] | [[Pneumomediastinum CT|CT]] | [[Pneumomediastinum MRI|MRI]] | [[Pneumomediastinum echocardiography or ultrasound|Echocardiography or Ultrasound]] | [[Pneumomediastinum other imaging findings|Other Imaging Findings]] | [[Pneumomediastinum other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] |
|
| |
|
| '''Pneumomediastinum''' (from [[Greek language|Greek]] ''pneuma'' - "air", also known as '''mediastinal emphysema''') is a condition in which air is present in the [[mediastinum]].
| | ==Treatment== |
| | | [[Pneumomediastinum medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Pneumomediastinum surgery|Surgery]] | [[Pneumomediastinum primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Pneumomediastinum secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] |
| First described in 1819 by [[René Laennec]],<ref>Laënnec RTH. De l’auscultation médiate ou Traité du Diagnostic des Maladies des Poumon et du Coeur. 1st ed. Paris: Brosson & Chaudé; 1819.</ref><ref name="pmid17048358">{{cite journal |author=Roguin A |title=Rene Theophile Hyacinthe Laënnec (1781-1826): the man behind the stethoscope |journal=Clinical medicine & research |volume=4 |issue=3 |pages=230–5 |year=2006 |pmid=17048358 |doi=}}</ref> the condition can result from [[physical trauma]] or other situations that lead to high pressure within the [[alveoli]] of the [[lung]], causing them to burst and leak air into the [[chest cavity]].
| | ==Case Studies== |
| | | :[[Pneumomediastinum case study one|Case #1]] |
| ==Differential diagnosis of causes of pneumomediastinum==
| |
| | |
| It is most commonly caused by:
| |
| | |
| * Oesophageal rupture, for example in [[Boerhaave syndrome]]
| |
| | |
| * [[Asthma]] or other conditions leading to alveolar rupture
| |
| | |
| It has also been associated with:
| |
| * [[Mycoplasma pneumoniae]] [[pneumonia]]<ref name="pmid17899058">{{cite journal |author=Vázquez JL, Vázquez I, González ML, García-Tejedor JL, Repáraz A |title=Pneumomediastinum and pneumothorax as presenting signs in severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia |journal= |volume= |issue= |pages= |year=2007 |pmid=17899058 |doi=10.1007/s00247-007-0611-1}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| * [[anorexia]]<ref name="pmid17909893">{{cite journal |author=Hatzitolios A, Ntaios G |title=Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum May Be Associated with Both Anorexia Nervosa and Obesity |journal= |volume= |issue= |pages= |year=2007 |pmid=17909893 |doi=10.1007/s00408-007-9037-7}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| * [[obesity]]<ref name="pmid17909893">{{cite journal |author=Hatzitolios A, Ntaios G |title=Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum May Be Associated with Both Anorexia Nervosa and Obesity |journal= |volume= |issue= |pages= |year=2007 |pmid=17909893 |doi=10.1007/s00408-007-9037-7}}</ref>
| |
| | |
| It can be induced to assist thoracoscopic surgery.<ref name="pmid17669882">{{cite journal |author=Utsumi T, Shiono H, Fukai I, Akashi A |title=Artificial pneumomediastinum facilitates thoracoscopic surgery in anterior mediastinum |journal=Interactive cardiovascular and thoracic surgery |volume=6 |issue=3 |pages=411–2 |year=2007 |pmid=17669882 |doi=10.1510/icvts.2006.147355}}
| |
| </ref>
| |
| | |
| It can be caused by a pulmonary [[barotrauma]] resulting when a person moves to or from a higher pressure environment, such as when a Scuba diver<ref>{{cite journal |author=Tetzlaff K, Reuter M |title=Recurrent pulmonary barotrauma (PBT) in a previously healthy male scuba diver who suffered from repeated pneumomediastinum after shallow-water scuba dives |journal=Undersea Hyperb Med |volume=25 |issue=2 |pages=127–8 |year=1998 |pmid=9670439 |doi= |url=http://archive.rubicon-foundation.org/2412 |accessdate=2008-06-05}}</ref><ref>Dr. Richard Moon, Diver's Alert Network Vice President and Medical Director, http://www.diversalertnetwork.org/medical/articles/article.asp?articleid=40 </ref>, a free-diver<ref>{{cite journal |author=Jacobson FL, Loring SH, Ferrigno M |title=Pneumomediastinum after lung packing |journal=Undersea Hyperb Med |volume=33 |issue=5 |pages=313–6 |year=2006 |pmid=17091828 |doi= |url=http://archive.rubicon-foundation.org/5045 |accessdate=2008-06-05}}</ref> or an airplane passenger<ref>{{cite journal |author=Nicol E, Davies G, Jayakumar P, Green ND |title=Pneumopericardium and pneumomediastinum in a passenger on a commercial flight |journal=Aviat Space Environ Med |volume=78 |issue=4 |pages=435–9 |year=2007 |month=April |pmid=17484349 |doi= |url=http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/asma/asem/2007/00000078/00000004/art00014 |accessdate=2008-06-05 }}</ref> ascends or descends.
| |
| | |
| ==Clinical Presentation & Diagnosis== | |
| | |
| | |
| Pneumomediastinum is uncommon, it occurs when air leaks from any part of the lung or airways into the mediastinum and is often recognized on [[auscultation]] by a "crunching" sound timed with the cardiac cycle ([[Hamman's crunch]]). [[Subcutaneous emphysema]] is one of the symptoms of pneumomediastinum.
| |
| | |
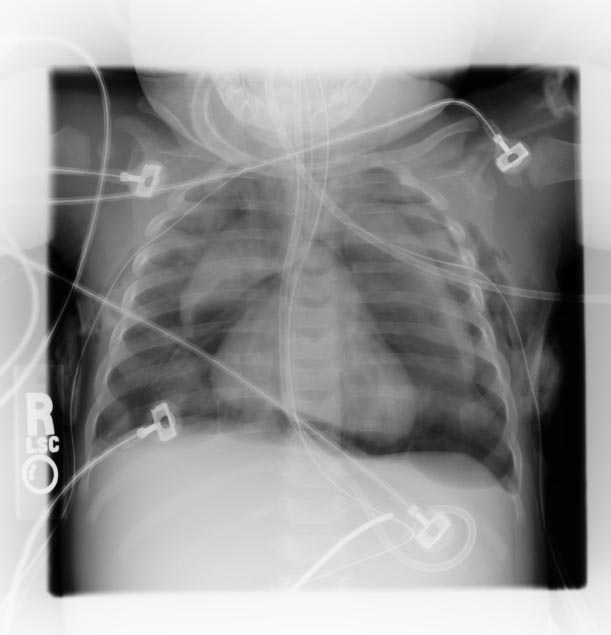
| The diagnosis can be confirmed via [[chest X-ray]] showing a radiolucent outline around the heart and mediastinum or via [[ct scan|CT scanning]] of the [[thorax]].
| |
| | |
| ==== Chest X Ray ====
| |
| | |
| <gallery>
| |
| Image:Pneumomediastinum-003.jpg|Pneumomediastinum: Spinnaker sail sign (Image courtesy of RadsWiki)
| |
| Image:PneumoMediastinum2008.jpg|Pneumomediastinum and right sided pneumothorax post first rib fracture in a mountain biking accident.
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
| ====Computerized Tomography ====
| |
| | |
| <gallery>
| |
| Image:Subcutaneous emphysema chest cropped.jpg|A CT scan showing air in the mediastinum
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
| Images shown below are courtesy of RadsWiki.
| |
| | |
| <gallery>
| |
| Image:Pneumomediastinum-001.jpg|Pneumomediastinum
| |
| Image:Pneumomediastinum-002.jpg|Pneumomediastinum
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
| | |
| <gallery>
| |
| Image:Pneumomediastinum-101.jpg|Pneumomediastinum and pneumothorax
| |
| Image:Pneumomediastinum-102.jpg|Pneumomediastinum and pneumothorax
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
| <gallery>
| |
| Image:Pneumo3010775.jpg|Pneumomediastinum and pneumothorax and subcutaneous emphysema
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| | |
| == References ==
| |
| {{reflist|2}}
| |
|
| |
|
| ==External links== | | ==External links== |
| Line 89: |
Line 35: |
| == Acknowledgements == | | == Acknowledgements == |
| The content on this page was first contributed by: [[C. Michael Gibson]] M.S., M.D. | | The content on this page was first contributed by: [[C. Michael Gibson]] M.S., M.D. |
| <!--
| |
| List of contributors:
| |
|
| |
| == Suggested Reading and Key General References ==
| |
|
| |
| == Suggested Links and Web Resources ==
| |
|
| |
| == For Patients ==
| |
|
| |
| -->
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| {{Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period}} | | {{Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period}} |