Pefloxacin: Difference between revisions
Gerald Chi (talk | contribs) m (Changed protection level for "Pefloxacin" ([Edit=Allow only autoconfirmed users] (expires 20:36, 22 January 2014 (UTC)) [Move=Allow only autoconfirmed users] (expires 20:36, 22 January 2014 (UTC)))) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{drugbox | {{drugbox | ||
| IUPAC_name = 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)- 4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid | | Watchedfields = changed | ||
| image = Pefloxacin. | | verifiedrevid = 464197549 | ||
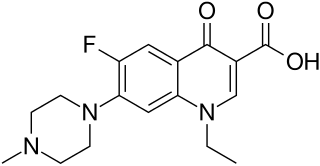
| IUPAC_name = 1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid | |||
| image = Pefloxacin.png | |||
| width = 220 | |||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 46291 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = 2H52Z9F2Q5 | |||
| InChI = 1/C17H20FN3O3/c1-3-20-10-12(17(23)24)16(22)11-8-13(18)15(9-14(11)20)21-6-4-19(2)5-7-21/h8-10H,3-7H2,1-2H3,(H,23,24) | |||
| InChIKey = FHFYDNQZQSQIAI-UHFFFAOYAD | |||
| smiles = O=C(O)\C2=C\N(c1cc(c(F)cc1C2=O)N3CCN(C)CC3)CC | |||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEMBL = 267648 | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C17H20FN3O3/c1-3-20-10-12(17(23)24)16(22)11-8-13(18)15(9-14(11)20)21-6-4-19(2)5-7-21/h8-10H,3-7H2,1-2H3,(H,23,24) | |||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChIKey = FHFYDNQZQSQIAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| CAS_number = 70458-92-3 | | CAS_number = 70458-92-3 | ||
| ATC_prefix = J01 | | ATC_prefix = J01 | ||
| ATC_suffix = MA03 | | ATC_suffix = MA03 | ||
| ATC_supplemental = | | ATC_supplemental = | ||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEBI = 50199 | |||
| PubChem = 51081 | | PubChem = 51081 | ||
| DrugBank = | | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | ||
| DrugBank = DB00487 | |||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| KEGG = D02306 | |||
| C=17 | H=20 | F=1 | N=3 | O=3 | | C=17 | H=20 | F=1 | N=3 | O=3 | ||
| molecular_weight = 333.358 g/mol | | molecular_weight = 333.358 g/mol | ||
| Line 24: | Line 47: | ||
| routes_of_administration = | | routes_of_administration = | ||
}} | }} | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{SI}} | {{SI}} | ||
{{CMG}} | |||
'''Pefloxacin''' is | ==Overview== | ||
'''Pefloxacin''' is a [[quinolone]] drug used to treat bacterial infections. It is an analog of [[norfloxacin]], belonging to the 3rd generation of quinolones. Pefloxacin has not been approved for use in the United States. | |||
=== | ==History== | ||
Pefloxacin was developed in 1979 and approved in France for human use in 1985.<ref> http://www.bailii.org/ew/cases/EWHC/Patents/2008/2413.html</ref> | |||
== | ==Licensed uses== | ||
* | *Uncomplicated gonococcal urethritis in males.<ref name=p_usage>http://www.pefloxacin.com/pefloxacin_usage.htm</ref> | ||
= | *Bacterial infections in the gastrointestinal system.<ref name=p_usage/> | ||
= | *Genitourinary tract infections.<ref name=p_usage/> | ||
=== | *Gonorrhoeae. however this indication is no longer effective due to bacterial resistance.<ref>{{cite journal |author= |title=Update to CDC's sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2006: fluoroquinolones no longer recommended for treatment of gonococcal infections |journal=MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. |volume=56 |issue=14 |pages=332–6 |date=April 2007 |pmid=17431378 |url=http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5614a3.htm |author1= Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)}}</ref> | ||
Pefloxacin has been increasingly used as a veterinary medicine to treat microbial infections.<ref> http://www.pefloxacin.com/pefloxacin_other.html</ref> | |||
=== | ==Mode of action== | ||
== | Pefloxacin is a [[broad-spectrum antibiotic]] that is active against both [[Gram-positive]] and [[Gram-negative]] bacteria. It functions by inhibiting [[DNA gyrase]], a type II [[topoisomerase]], and topoisomerase IV,<ref>{{cite journal |author=Drlica K, Zhao X |title=DNA gyrase, topoisomerase IV, and the 4-quinolones |journal=Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. |volume=61 |issue=3 |pages=377–92 |date=1 September 1997|pmid=9293187 |pmc=232616 |url=http://mmbr.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=9293187 }}</ref> which is an enzyme necessary to separate, replicated DNA, thereby inhibiting cell division. | ||
==Adverse effects== | |||
Tendinitis and rupture, usually of the Achilles tendon, are a class-effects of the fluoroquinolones, most frequently reported with pefloxacin.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Khaliq Y, Zhanel GG |title=Musculoskeletal injury associated with fluoroquinolone antibiotics |journal=Clin Plast Surg |volume=32 |issue=4 |pages=495–502, vi |date=October 2005 |pmid=16139623 |doi=10.1016/j.cps.2005.05.004 |url=http://journals.elsevierhealth.com/retrieve/pii/S0094-1298(05)00043-X}} | |||
</ref> The estimated risk of tendon damage during pefloxacin therapy has been estimated by the French authorities in 2000 to be 1 case per 23,130 treatment days as compared to ciprofloxacin where it has been estimated to be 1 case per 779,600.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Casparian JM, Luchi M, Moffat RE, Hinthorn D |title=Quinolones and tendon ruptures |journal=South. Med. J. |volume=93 |issue=5 |pages=488–91 |date=May 2000 |pmid=10832946 |url=http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0038-4348&volume=93&issue=5&spage=488 |doi=10.1097/00007611-200093050-00008}}</ref> | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
{{QuinoloneAntiBiotics}} | {{QuinoloneAntiBiotics}} | ||
[[Category:Fluoroquinolone antibiotics]] | [[Category:Fluoroquinolone antibiotics]] | ||
[[Category:Piperazines]] | |||
[[Category:Drug]] | |||
Revision as of 15:35, 13 April 2015
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 100% |
| Protein binding | 20–30% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 8.6 hours |
| Excretion | Mostly renal, also biliary |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H20FN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 333.358 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Pefloxacin |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Pefloxacin |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Pefloxacin at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Pefloxacin at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Pefloxacin
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Pefloxacin Discussion groups on Pefloxacin Patient Handouts on Pefloxacin Directions to Hospitals Treating Pefloxacin Risk calculators and risk factors for Pefloxacin
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Pefloxacin |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Pefloxacin is a quinolone drug used to treat bacterial infections. It is an analog of norfloxacin, belonging to the 3rd generation of quinolones. Pefloxacin has not been approved for use in the United States.
History
Pefloxacin was developed in 1979 and approved in France for human use in 1985.[1]
Licensed uses
- Uncomplicated gonococcal urethritis in males.[2]
- Bacterial infections in the gastrointestinal system.[2]
- Genitourinary tract infections.[2]
- Gonorrhoeae. however this indication is no longer effective due to bacterial resistance.[3]
Pefloxacin has been increasingly used as a veterinary medicine to treat microbial infections.[4]
Mode of action
Pefloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It functions by inhibiting DNA gyrase, a type II topoisomerase, and topoisomerase IV,[5] which is an enzyme necessary to separate, replicated DNA, thereby inhibiting cell division.
Adverse effects
Tendinitis and rupture, usually of the Achilles tendon, are a class-effects of the fluoroquinolones, most frequently reported with pefloxacin.[6] The estimated risk of tendon damage during pefloxacin therapy has been estimated by the French authorities in 2000 to be 1 case per 23,130 treatment days as compared to ciprofloxacin where it has been estimated to be 1 case per 779,600.[7]
References
- ↑ http://www.bailii.org/ew/cases/EWHC/Patents/2008/2413.html
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 http://www.pefloxacin.com/pefloxacin_usage.htm
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (April 2007). "Update to CDC's sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2006: fluoroquinolones no longer recommended for treatment of gonococcal infections". MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 56 (14): 332–6. PMID 17431378.
- ↑ http://www.pefloxacin.com/pefloxacin_other.html
- ↑ Drlica K, Zhao X (1 September 1997). "DNA gyrase, topoisomerase IV, and the 4-quinolones". Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 61 (3): 377–92. PMC 232616. PMID 9293187.
- ↑ Khaliq Y, Zhanel GG (October 2005). "Musculoskeletal injury associated with fluoroquinolone antibiotics". Clin Plast Surg. 32 (4): 495–502, vi. doi:10.1016/j.cps.2005.05.004. PMID 16139623.
- ↑ Casparian JM, Luchi M, Moffat RE, Hinthorn D (May 2000). "Quinolones and tendon ruptures". South. Med. J. 93 (5): 488–91. doi:10.1097/00007611-200093050-00008. PMID 10832946.