Paroxysmal AV block Vagal Maneuvers :Carotid Sinus Massage and Tilt Table testing: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "==Vagal Maneuvers : Carotid Sinus massage and Tilt Table testing== *Though not specific,tilt table testing (TT) and other vagal maneuvers such as the vasalva maneuver, eye bal...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[Image:Carotid Sinus Massage.JPG|thumb|center|500px|Carotid Sinus Massage- {{cite web |url=https://www.escardio.org/Guidelines/Clinical-Practice-Guidelines/Syncope-Guidelines-on-Diagnosis-and-Management-of |title=ESC Guidelines on Syncope (Diagnosis and Management of) |format= |work= |accessdate=}}]] | [[Image:Carotid Sinus Massage.JPG|thumb|center|500px|Carotid Sinus Massage- {{cite web |url=https://www.escardio.org/Guidelines/Clinical-Practice-Guidelines/Syncope-Guidelines-on-Diagnosis-and-Management-of |title=ESC Guidelines on Syncope (Diagnosis and Management of) |format= |work= |accessdate=}}]] | ||
==2018 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Patients With Bradycardia and Cardiac Conduction Delay== | |||
===Treatment of Vagally Mediated Atrioventricular Block=== | |||
*Vagally mediated atrioventricular block observed with ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring may be an incidental finding that occurred while the patient was sleeping or in other cases be associated with syncope. | |||
*Vagally mediated atrioventricular block is felt to be attributable to neural reflexes, which result in simultaneous bradycardia and hypotension. | |||
*There is typically sinus rate slowing in conjunction with the onset of atrioventricular block and the atrioventricular block can be high grade or complete. | |||
*Atrioventricular block attributable to high vagal tone, such as during sleep, is almost always asymptomatic. | |||
*The level of the block is at the atrioventricular node, and there is normal atrioventricular nodal function when tested at EPS. | |||
*If asymptomatic, medical treatment or pacemaker implantation is not warranted for atrioventricular block attributable to high vagal tone or vagally mediated atrioventricular block. | |||
*If the patient is having frequent syncopal episodes, treatment may be warranted if bradycardia appears to be the dominant factor in these episodes. | |||
*Although PPM implantation is a relatively low-risk cardiac procedure, procedural complications and death directly related to implant can occur, and implanted leads have long-term management implications. | |||
Revision as of 19:48, 27 June 2020
Vagal Maneuvers : Carotid Sinus massage and Tilt Table testing
- Though not specific,tilt table testing (TT) and other vagal maneuvers such as the vasalva maneuver, eye ball pressure and immersing one's face in cold water can be used in the diagnosis of EV-AVB.
- The Syncope Unit Project-2 study found an increase recurrence rate in patients who did not undergo tilt table testing. This highlights the utility of TT as a screening test for reflex syncope.
- A positive response is indicated as a marker of hypotensive susceptibility which involves a decrease in both preload and afterload. [1]
- Having said that, a negative test does not rule out the possibility of an extrinsic vagal paroxysmal AV block.
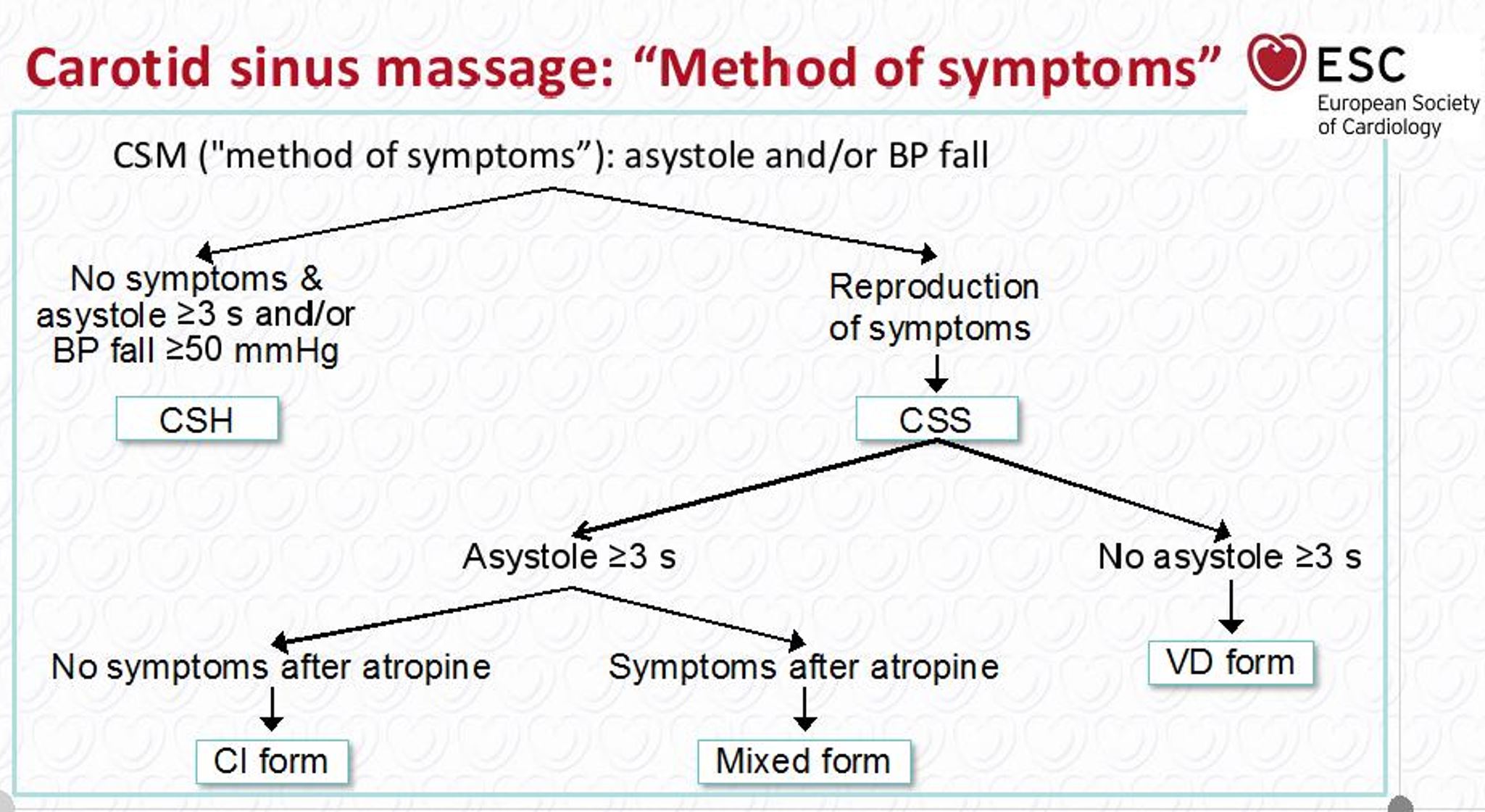
- A carotid sinus massage is indicated in patients more than 40 years of age with syncope of unknown origin compatible with reflex mechanism.
- Carotid sinus sensitivity is confirmed if carotid sinus massage causes bradycardia (asystole) and/or hypotension that reproduce spontaneous symptoms and patients have clinical features compatible with reflex mechanism of syncope. "ESC Guidelines on Syncope (Diagnosis and Management of)".
2018 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Patients With Bradycardia and Cardiac Conduction Delay
Treatment of Vagally Mediated Atrioventricular Block
- Vagally mediated atrioventricular block observed with ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring may be an incidental finding that occurred while the patient was sleeping or in other cases be associated with syncope.
- Vagally mediated atrioventricular block is felt to be attributable to neural reflexes, which result in simultaneous bradycardia and hypotension.
- There is typically sinus rate slowing in conjunction with the onset of atrioventricular block and the atrioventricular block can be high grade or complete.
- Atrioventricular block attributable to high vagal tone, such as during sleep, is almost always asymptomatic.
- The level of the block is at the atrioventricular node, and there is normal atrioventricular nodal function when tested at EPS.
- If asymptomatic, medical treatment or pacemaker implantation is not warranted for atrioventricular block attributable to high vagal tone or vagally mediated atrioventricular block.
- If the patient is having frequent syncopal episodes, treatment may be warranted if bradycardia appears to be the dominant factor in these episodes.
- Although PPM implantation is a relatively low-risk cardiac procedure, procedural complications and death directly related to implant can occur, and implanted leads have long-term management implications.
- ↑ Brignole M, Arabia F, Ammirati F, Tomaino M, Quartieri F, Rafanelli M; et al. (2016). "Standardized algorithm for cardiac pacing in older patients affected by severe unpredictable reflex syncope: 3-year insights from the Syncope Unit Project 2 (SUP 2) study". Europace. 18 (9): 1427–33. doi:10.1093/europace/euv343. PMID 26612880.