Pancreatic pseudocyst: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
{{SI}} | {{SI}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} | ||
'''Contributors:''' [[User:zorkun|Cafer Zorkun]] M.D., PhD. | |||
{{Editor Help}} | {{Editor Help}} | ||
Revision as of 18:17, 15 March 2009
| Pancreatic pseudocyst | |
| ICD-10 | K86.3 |
|---|---|
| ICD-9 | 577.2 |
| DiseasesDB | 9530 |
| MedlinePlus | 000272 |
| eMedicine | med/2674 radio/576 |
| MeSH | D010192 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Contributors: Cafer Zorkun M.D., PhD.
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Overview
A pancreatic pseudocyst is a circumscribed collection of fluid rich in amylase and other pancreatic enzymes, blood and necrotic tissue typically located in the lesser sac. It has a non-epithelialised lining made of granulation tissue and hence the name pseudocyst (pseudo - false). By contrast, true cysts have an epithelial lining. This is typically a complication of acute pancreatitis, but may also occur following abdominal trauma.
Pancreatic pseudocysts account for approximately 75% of all pancreatic masses.
Etiopathogenesis
Acute pancreatitis results amongst other things in the disruption of pancreatic parenchyma and the ductal system. This results in extravasation of pancreatic enzymes which in turn digest the adjoining tissues. This results in a collection of fluid containing pancreatic enzymes, hemolysed blood and necrotic debris around the pancreas. The lesser sac being a potential space, the fluid collects here preferentially. This is called an acute pancreatic collection. Some of these collections resolve on their own as the patient recovers from the acute episode. However, others become more organised and get walled-off within a thick wall of granulation tissue and fibrosis. This takes several weeks to occur and results in a pancreatic pseudocyst.
Diagnosis
The questions that need to be answered are:
- where, how big and how many?
- is there a communication with the pancreatic ductal system? Draining such a pseudocyst carries an increased risk of pancreatic fistula.
The most useful imaging tools are;
- Ultrasonography - The role of ultrasonography in imaging the pancreas is limited by patient habitus, operator experience and the fact that the pancreas lies behind the stomach (and so a gas-filled stomach will obscure the pancreas).
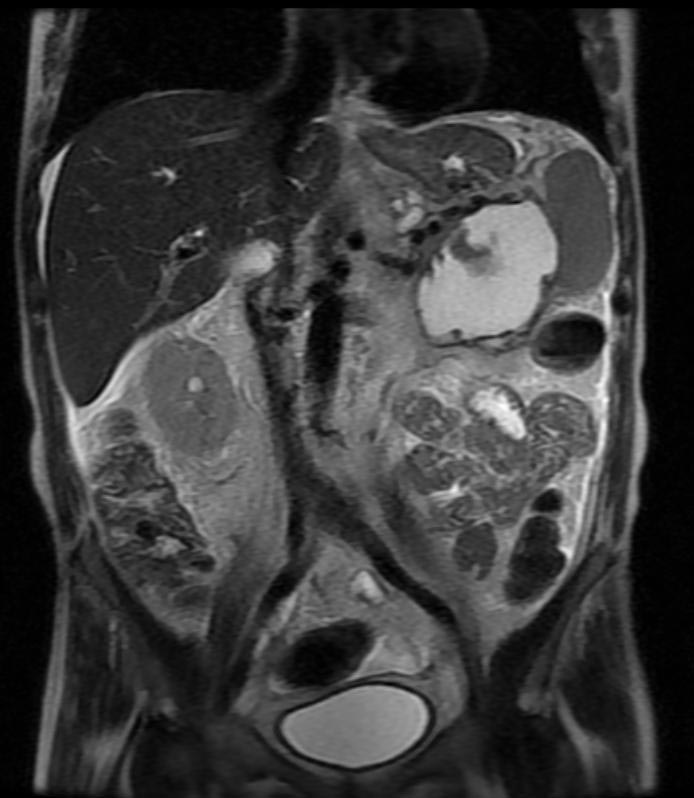
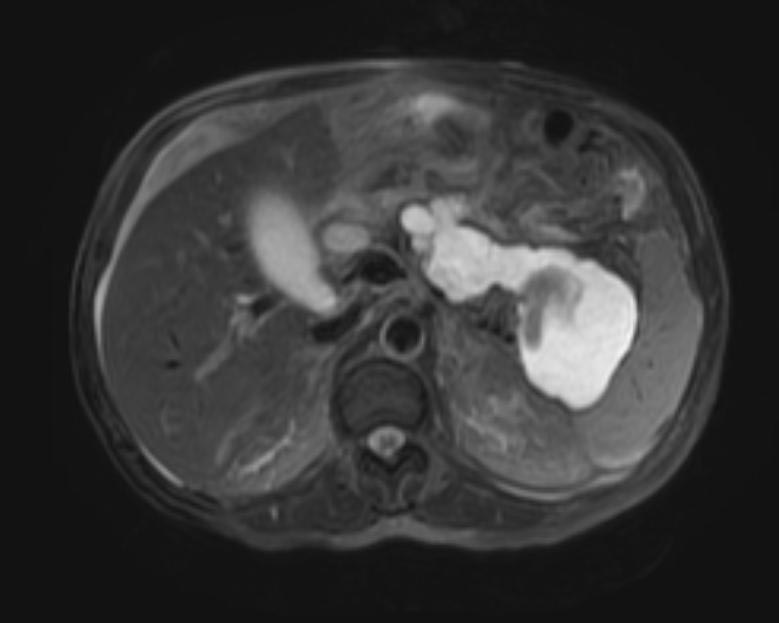
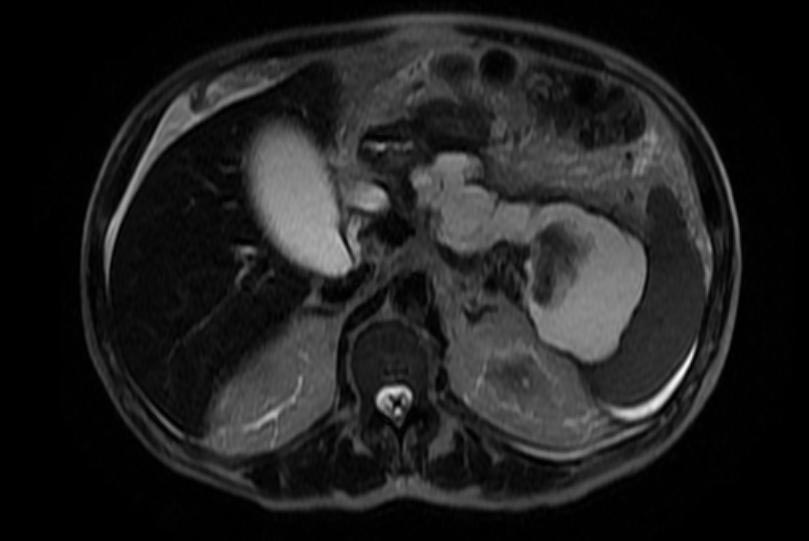
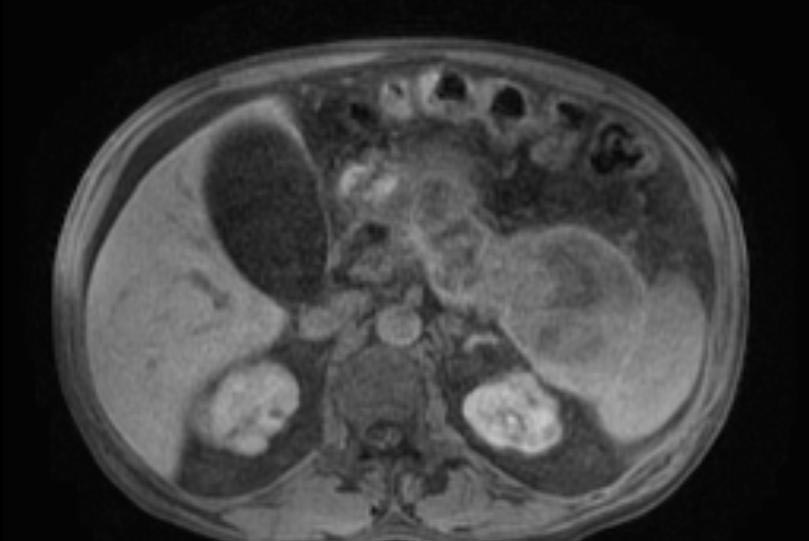
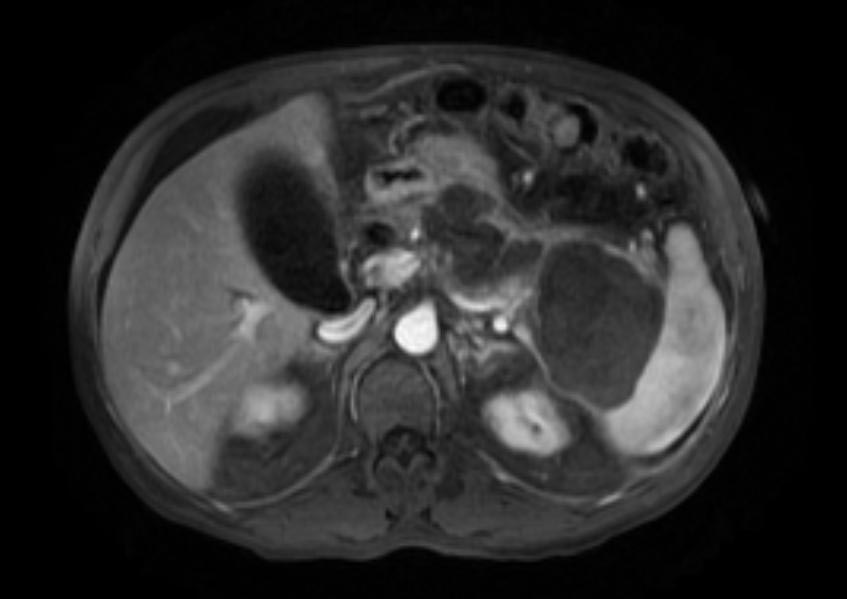
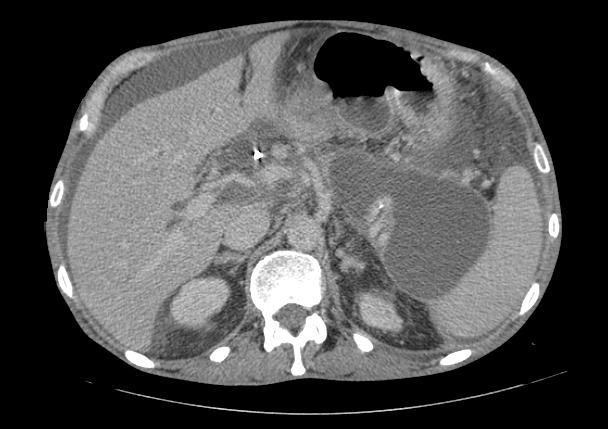
- Computerized tomography - This is the gold standard for initial assessment and follow-up
-
Computerized tomography: Pancreatic pseudocyst
-
Computerized tomography: Pancreatic pseudocyst
-
Computerized tomography: Pancreatic pseudocyst
-
Computerized tomography: Pancreatic pseudocyst
-
Computerized tomography: Pancreatic pseudocyst
-
Computerized tomography: Pancreatic pseudocyst
- Magnetic Resonance Cholangio-pancreatography - to establish the relationship of the pseudocyst to the pancreatic ducts
Treatment
A small pseudocyst that is not causing any symptoms may be managed conservatively. However, a large proportion of them will need some form of treatment, The interventions available are:
- Endoscopic trans-gastric drainage
- Imaging guided percutaneous drainage
- Laparoscopic/open cystogastrostomy