Orlistat: Difference between revisions
Kiran Singh (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Kiran Singh (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 250: | Line 250: | ||
Revision as of 17:24, 23 December 2014
{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage |authorTag=Kiran Singh, M.D. [1] |genericName=orlistat |aOrAn=a |indicationType=treatment |indication=a list of indications, separated by commas. |adverseReactions=a list of adverse reactions, separated by commas. |blackBoxWarningTitle=Warning Title |blackBoxWarningBody=Condition Name: (Content) |fdaLIADAdult===Indications==
- XENICAL is indicated for obesity management including weight loss and weight maintenance when used in conjunction with a reduced-calorie diet. XENICAL is also indicated to reduce the risk for weight regain after prior weight loss. XENICAL is indicated for obese patients with an initial body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m2 or ≥27 kg/m2 in the presence of other risk factors (e.g., hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia).
- TABLE 1 illustrates body mass index (BMI) according to a variety of weights and heights. The BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. For example, a person who weighs 180 lbs and is 5'5" would have a BMI of 30.

Dosing
- The recommended dose of XENICAL is one 120-mg capsule three times a day with each main meal containing fat (during or up to 1 hour after the meal).
- The patient should be on a nutritionally balanced, reduced-calorie diet that contains approximately 30% of calories from fat. The daily intake of fat, carbohydrate, and protein should be distributed over three main meals. If a meal is occasionally missed or contains no fat, the dose of XENICAL can be omitted.
- Because XENICAL has been shown to reduce the absorption of some fat-soluble vitamins and beta-carotene, patients should be counseled to take a multivitamin containing fat-soluble vitamins to ensure adequate nutrition. The vitamin supplement should be taken at least 2 hours before or after the administration of XENICAL, such as at bedtime.
- For patients receiving both XENICAL and cyclosporine therapy, administer cyclosporine 3 hours after XENICAL.
- For patients receiving both XENICAL and levothyroxine therapy, administer levothyroxine and XENICAL at least 4 hours apart. Patients treated concomitantly with XENICAL and levothyroxine should be monitored for changes in thyroid function.
- Doses above 120 mg three times a day have not been shown to provide additional benefit.
- Based on fecal fat measurements, the effect of XENICAL is seen as soon as 24 to 48 hours after dosing. Upon discontinuation of therapy, fecal fat content usually returns to pretreatment levels within 48 to 72 hours.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- XENICAL 120 mg turquoise capsules imprinted with ROCHE and XENICAL 120 in black ink.
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport===Indications and Dosing==
- Concomitant nutritionally-balanced meal with 30% calories from fat is recommended
- Concomitant daily multivitamin supplement is recommended
- Obesity: 120 mg ORALLY 3 times daily during or within 1 hour of each fat-containing meal
- Obesity: over-the-counter dose: 60 mg ORALLY 3 times daily during or within 1 hour of each fat-containing meal[1]
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Orlistat in adult patients. |offLabelPedGuideSupport===Indications and Dosing==
- Concomitant nutritionally-balanced meal with 30% calories from fat is recommended.
- Concomitant daily multivitamin supplement is recommended.
- Obesity: (12 to 16 years) 120 mg ORALLY 3 times daily during or within 1 hour of each fat-containing meal.
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Orlistat in pediatric patients. |contraindications=* Pregnancy
- Patients with chronic malabsorption syndrome
- Patients with cholestasis
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to XENICAL or to any component of this product
|warnings===Concomitant Drug and Vitamin Use==
- Data from a XENICAL and cyclosporine drug interaction study indicate a reduction in cyclosporine plasma levels when XENICAL was coadministered with cyclosporine. Therefore, XENICAL and cyclosporine should not be simultaneously coadministered. To reduce the chance of a drug-drug interaction, cyclosporine should be taken at least 3 hours before or after XENICAL in patients taking both drugs. In addition, in those patients whose cyclosporine levels are being measured, more frequent monitoring should be considered.
- Patients should be strongly encouraged to take a multivitamin supplement that contains fat-soluble vitamins to ensure adequate nutrition because XENICAL has been shown to reduce the absorption of some fat-soluble vitamins and beta-carotene. In addition, the levels of vitamin D and beta-carotene may be low in obese patients compared with non-obese subjects. The supplement should be taken once a day at least 2 hours before or after the administration of XENICAL, such as at bedtime.
- TABLE 2 illustrates the percentage of adult patients on XENICAL and placebo who developed a low vitamin level on two or more consecutive visits during 1 and 2 years of therapy in studies in which patients were not previously receiving vitamin supplementation.

- TABLE 3 illustrates the percentage of adolescent patients on XENICAL and placebo who developed a low vitamin level on two or more consecutive visits during the 1-year study.

- Weight-loss may affect glycemic control in patients with diabetes mellitus. A reduction in dose of oral hypoglycemic medication (e.g., sulfonylureas) or insulin may be required in some patients
Liver Injury
- There have been rare postmarketing reports of severe liver injury with hepatocellular necrosis or acute hepatic failure in patients treated with XENICAL, with some of these cases resulting in liver transplant or death. Patients should be instructed to report any symptoms of hepatic dysfunction (anorexia, pruritus, jaundice, dark urine, light-colored stools, or right upper quadrant pain) while taking XENICAL. When these symptoms occur, XENICAL and other suspect medications should be discontinued immediately and liver function tests and ALT and AST levels obtained.
Increases in Urinary Oxalate
- Some patients may develop increased levels of urinary oxalate following treatment with XENICAL. Cases of oxalate nephrolithiasis and oxalate nephropathy with renal failure have been reported. Monitor renal function when prescribing XENICAL to patients at risk for renal impairment and use with caution in those with a history of hyperoxaluria or calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis.
Cholelithiasis
Substantial weight loss can increase the risk of cholelithiasis. In a clinical trial of XENICAL for the prevention of type 2 diabetes, the rates of cholelithiasis as an adverse event were 2.9% (47/1649) for patients randomized to XENICAL and 1.8% (30/1655) for patients randomized to placebo.
Miscellaneous
- Organic causes of obesity (e.g., hypothyroidism) should be excluded before prescribing XENICAL.
- Patients should be advised to adhere to dietary guidelines. Gastrointestinal events may increase when XENICAL is taken with a diet high in fat (>30% total daily calories from fat). The daily intake of fat should be distributed over three main meals. If XENICAL is taken with any one meal very high in fat, the possibility of gastrointestinal effects increases.
|clinicalTrials===Clinical Trials==
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in patients.
- Commonly Observed (based on first year and second year data)
- Gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms were the most commonly observed treatment-emergent adverse events associated with the use of XENICAL in the seven double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials and are primarily a manifestation of the mechanism of action. (Commonly observed is defined as an incidence of ≥5% and an incidence in the XENICAL 120 mg group that is at least twice that of placebo.)

In general, the first occurrence of these events was within 3 months of starting therapy. Overall, approximately 50% of all episodes of GI adverse events associated with XENICAL treatment lasted for less than 1 week, and a majority lasted for no more than 4 weeks. However, GI adverse events may occur in some individuals over a period of 6 months or longer.
Discontinuation of Treatment
In controlled clinical trials, 8.8% of patients treated with XENICAL discontinued treatment due to adverse events, compared with 5.0% of placebo-treated patients. For XENICAL, the most common adverse events resulting in discontinuation of treatment were gastrointestinal.
Other Adverse Clinical Events
The following table lists other treatment-emergent adverse events from seven multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials that occurred at a frequency of ≥2% among patients treated with XENICAL 120 mg three times a day and with an incidence that was greater than placebo during year 1 and year 2, regardless of relationship to study medication.

In the 4-year XENDOS study, the general pattern of adverse events was similar to that reported for the 1- and 2-year studies with the total incidence of gastrointestinal-related adverse events occurring in year 1 decreasing each year over the 4-year period.
In clinical trials in obese diabetic patients, hypoglycemia and abdominal distension were also observed.
Pediatric Patients
In clinical trials with XENICAL in adolescent patients ages 12 to 16 years, the profile of adverse reactions was generally similar to that observed in adults. |postmarketing=The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of XENICAL. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to XENICAL exposure.
- Rare cases of increase in transaminases and in alkaline phosphatase and hepatitis that may be serious have been reported. There have been reports of hepatic failure observed with the use of XENICAL in postmarketing surveillance, with some of these cases resulting in liver transplant or death.
- Cases of reduced concentrations of cyclosporine have been reported when cyclosporine was co-administered with XENICAL.
- Rare cases of hypersensitivity have been reported with the use of XENICAL. Signs and symptoms have included pruritus, rash, urticaria, angioedema, bronchospasm and anaphylaxis. Very rare cases of bullous eruption have been reported.
- Reports of decreased prothrombin, increased INR and unbalanced anticoagulant treatment resulting in change of hemostatic parameters have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with XENICAL and anticoagulants.
- Hypothyroidism has been reported in patients treated concomitantly with XENICAL and levothyroxine.
- Acute oxalate nephropathy after treatment with XENICAL has been reported in patients with or at risk for renal disease.
- Pancreatitis has been reported with the use of XENICAL in postmarketing surveillance. No causal relationship or physiopathological mechanism between pancreatitis and obesity therapy has been definitively established.
- Lower gastrointestinal bleeding has been reported in patients treated with XENICAL. Most reports are nonserious; severe or persistent cases should be investigated further.
- Convulsions have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with orlistat and antiepileptic drugs.
|drugInteractions=Cyclosporine
Data from a XENICAL and cyclosporine drug interaction study indicate a reduction in cyclosporine plasma levels when XENICAL was coadministered with cyclosporine. XENICAL and cyclosporine should not be simultaneously coadministered. Cyclosporine should be administered 3 hours after the administration of XENICAL.
Fat-soluble Vitamin Supplements and Analogues
Data from a pharmacokinetic interaction study showed that the absorption of beta-carotene supplement is reduced when concomitantly administered with XENICAL. XENICAL inhibited absorption of a vitamin E acetate supplement. The effect of XENICAL on the absorption of supplemental vitamin D, vitamin A, and nutritionally-derived vitamin K is not known at this time
Levothyroxine
Hypothyroidism has been reported in patients treated concomitantly with XENICAL and levothyroxine postmarketing . Patients treated concomitantly with XENICAL and levothyroxine should be monitored for changes in thyroid function. Administer levothyroxine and XENICAL at least 4 hours apart .
Warfarin
Vitamin K absorption may be decreased with XENICAL. Patients on chronic stable doses of warfarin who are prescribed XENICAL should be monitored closely for changes in coagulation parameters.
Antiepileptic Drugs
Convulsions have been reported in patients treated concomitantly with orlistat and antiepileptic drugs. Patients should be monitored for possible changes in the frequency and/or severity of convulsions |useInPregnancyFDA=Pregnancy Category X
XENICAL is contraindicated during pregnancy, because weight loss offers no potential benefit to a pregnant woman and may result in fetal harm. A minimum weight gain, and no weight loss, is currently recommended for all pregnant women, including those who are already overweight or obese, due to the obligatory weight gain that occurs in maternal tissues during pregnancy. No embryotoxicity or teratogenicity was seen in animals that received orlistat at doses much higher than the recommended human dose. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard of maternal weight loss to the fetus.
Animal Data
Reproduction studies were conducted in rats and rabbits at doses up to 800 mg/kg/day. Neither study showed embryotoxicity or teratogenicity. This dose is 23 and 47 times the daily human dose calculated on a body surface area (mg/m2) basis for rats and rabbits, respectively. |useInPregnancyAUS=(Description) |useInLaborDelivery=(Description) |useInNursing=It is not known if XENICAL is present in human milk. Caution should be exercised when XENICAL is administered to a nursing woman. |useInPed=* Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 12 have not been established.
- The safety and efficacy of XENICAL have been evaluated in obese adolescent patients aged 12 to 16 years. Use of XENICAL in this age group is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of XENICAL in adults with additional data from a 54-week efficacy and safety study and a 21-day mineral balance study in obese adolescent patients aged 12 to 16 years. Patients treated with XENICAL in the 54-week efficacy and safety study (64.8% female, 75% Caucasians, 18.8% Blacks, and 6.3% Other) had a mean reduction in BMI of 0.55 kg/m2 compared with an average increase of 0.31 kg/m2 in placebo-treated patients (p=0.001). In both adolescent studies, adverse effects were generally similar to those described in adults and included fatty/oily stool, oily spotting, and oily evacuation. In a subgroup of 152 XENICAL and 77 placebo patients from the 54-week study, changes in body composition measured by DEXA were similar in both treatment groups with the exception of fat mass, which was significantly reduced in patients treated with XENICAL compared to patients treated with placebo (-2.5 kg vs -0.6 kg, p=0.033). Because XENICAL can interfere with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, all patients should take a daily multivitamin that contains vitamins A, D, E, K, and beta-carotene. The vitamin supplement should be taken at least 2 hours before or after XENICAL .
- Plasma concentrations of orlistat and its metabolites M1 and M3 were similar to those found in adults at the same dose level. Daily fecal fat excretions were 27% and 7% of dietary intake in XENICAL and placebo treatment groups, respectively.
|useInGeri=Clinical studies of XENICAL did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. |useInGender=(Description) |useInRace=(Description) |useInRenalImpair=(Description) |useInHepaticImpair=(Description) |useInReproPotential=(Description) |useInImmunocomp=(Description) |othersTitle=Others |useInOthers=(Description) |administration=(Oral/Intravenous/etc) |monitoring======Condition 1=====
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 2
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 3
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section) |overdose=Single doses of 800 mg XENICAL and multiple doses of up to 400 mg three times a day for 15 days have been studied in normal weight and obese subjects without significant adverse findings.
Should a significant overdose of XENICAL occur, it is recommended that the patient be observed for 24 hours. Based on human and animal studies, systemic effects attributable to the lipase-inhibiting properties of XENICAL should be rapidly reversible. |drugBox=
| |
Orlistat
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
|mechAction=* Orlistat is a reversible inhibitor of gastrointestinal lipases. It exerts its therapeutic activity in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine by forming a covalent bond with the active serine residue site of gastric and pancreatic lipases. The inactivated enzymes are thus unavailable to hydrolyze dietary fat in the form of triglycerides into absorbable free fatty acids and monoglycerides. As undigested triglycerides are not absorbed, the resulting caloric deficit may have a positive effect on weight control. |structure=* XENICAL (orlistat) is a gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor for obesity management that acts by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fats.
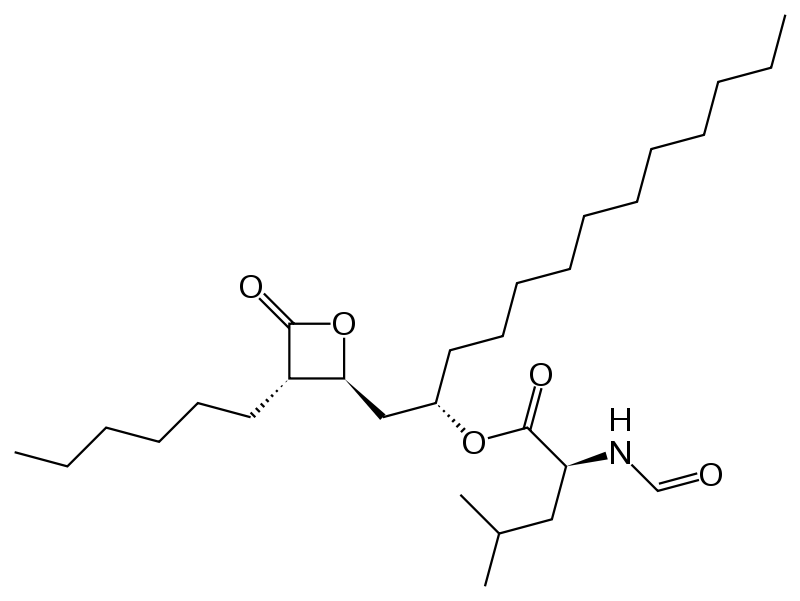
- Orlistat is (S)-2-formylamino-4-methyl-pentanoic acid (S)-1-[[(2S, 3S)-3-hexyl-4-oxo-2-oxetanyl] methyl]-dodecyl ester. Its empirical formula is C29H53NO5, and its molecular weight is 495.7. It is a single diastereomeric molecule that contains four chiral centers, with a negative optical rotation in ethanol at 529 nm. The structure is:

- Orlistat is a white to off-white crystalline powder. Orlistat is practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in chloroform, and very soluble in methanol and ethanol. Orlistat has no pKa within the physiological pH range.
- XENICAL is available for oral administration as a turquoise hard-gelatin capsule. The capsule is imprinted with black. Each capsule contains a pellet formulation consisting of 120 mg of the active ingredient, orlistat, as well as the inactive ingredients microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, sodium lauryl sulfate, povidone, and talc. The capsule shell contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, and FD&C Blue No. 2 with black printing ink containing pharmaceutical grade shellac, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, strong ammonium solution, potassium hydroxide and black iron oxide.
|PK=(Description) |nonClinToxic=(Description) |clinicalStudies======Condition 1=====
(Description)
Condition 2
(Description)
Condition 3
(Description) |howSupplied=XENICAL is a turquoise, hard-gelatin capsule containing pellets of powder.
XENICAL 120 mg Capsules: Turquoise, two-piece, No. 1 opaque hard-gelatin capsule imprinted with ROCHE and XENICAL 120 in black ink — bottle of 90 (NDC 0004-0257-52). |storage=Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep bottle tightly closed.
XENICAL should not be used after the given expiration date. |fdaPatientInfo=(Patient Counseling Information) |alcohol=Alcohol-Orlistat interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. |lookAlike=* (Paired Confused Name 1a) — (Paired Confused Name 1b)
- (Paired Confused Name 2a) — (Paired Confused Name 2b)
- (Paired Confused Name 3a) — (Paired Confused Name 3b)
|nlmPatientInfo=(Link to patient information page) |drugShortage=Drug Shortage }}
- ↑ Anderson JW, Schwartz SM, Hauptman J, Boldrin M, Rossi M, Bansal V; et al. (2006). "Low-dose orlistat effects on body weight of mildly to moderately overweight individuals: a 16 week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial". Ann Pharmacother. 40 (10): 1717–23. doi:10.1345/aph.1H234. PMID 16940406 PMID: 16940406 Check
|pmid=value (help).