Numbering aberrant rhythms: Difference between revisions
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
*Bigeminal Couplets: Normal, Normal, PVC, PVC, Normal, Normal, PVC, PVC... | *Bigeminal Couplets: Normal, Normal, PVC, PVC, Normal, Normal, PVC, PVC... | ||
*NS-VT: Normal, Normal, PVC, PVC, PVC, PVC, Normal, Normal, PVC... | *NS-VT: Normal, Normal, PVC, PVC, PVC, PVC, Normal, Normal, PVC... | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
Revision as of 14:20, 24 October 2012
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Synonyms and keywords: Bigeminy, trigeminy
Overview
Bigeminy (Latin: Bi-Two Gemini-twins) is a descriptor for a heart arrhythmia in which abnormal heart beats occur every other concurrent beat. A typical example is with bigeminal premature ventricular beats, also known as a premature ventricular contractions/complexes (PVC). Following the PVC there is a pause and then the normal beat returns - only to be followed by another PVC. The continuation of this pairing of beats is an example of bigeminy.
These descriptors can increase depending on the number of beats involved in the abnormal system. If every other beat is abnormal, you can describe it as bigeminal. If every third beat is aberrant, it is trigeminal; every fourth would be quadrigeminal. Typically, if every fifth or more beat is abnormal, the aberrant beat would be termed occasional.
Bigeminy is contrasted with couplets, which are paired abnormal beats. If these concurrent beats number three, they are called triplets and are considered as a brief run of non-sustained Ventricular tachycardia or NS-VT.
PVC's are not the only aberrant beat that makes use of these adjectives; others are premature atrial contractions, parasystole, and escape complexes.
Diagnosis
EKG Examples
Shown below is an EKG depicting atrial bigeminy. The EKG shows a regularly irregular rhythm at a rate of about 75/minute. There are two P wave morphologies best seen in lead V1.
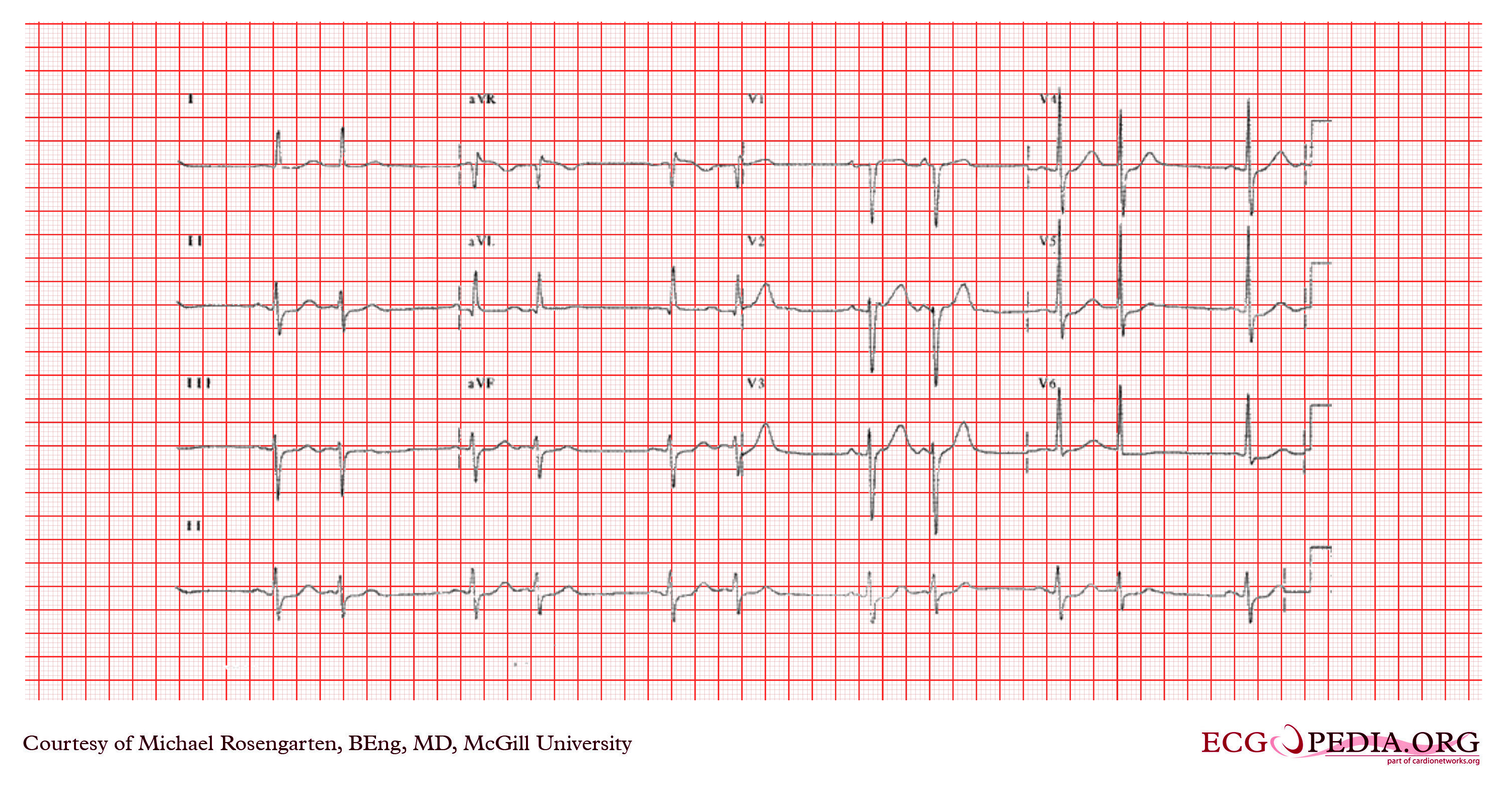
Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia,http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
Shown below is an EKG depicting bigemini. The pacemaker is an atrial pacer set at 30/min. Note the marker channel documenting (labels should be AP and AS) atrial pacing and then sensing of the QRS in the refractory period of the pacemaker. The tracing is curious as the paced atrial beats seem to stimulate a normal sinus beat and hence create the bigeminal rhythm.

Copyleft image obtained courtesy of ECGpedia,http://en.ecgpedia.org/wiki/Main_Page
Examples
- Bigeminal premature ventricular contractions = Normal, PVC, Normal, PVC...
- Trigeminal premature atrial contractions = Normal, Normal, PAC, Normal, Normal, PAC...
- Quadrageminal premature ventricular contractions = Normal, Normal, Normal, PVC; Normal, Normal, Normal, PVC...
- Occasional escape complexes: Normal, Normal, Normal, Normal, Pause, Escape...
- Bigeminal Couplets: Normal, Normal, PVC, PVC, Normal, Normal, PVC, PVC...
- NS-VT: Normal, Normal, PVC, PVC, PVC, PVC, Normal, Normal, PVC...