Multiple sclerosis physical examination
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia
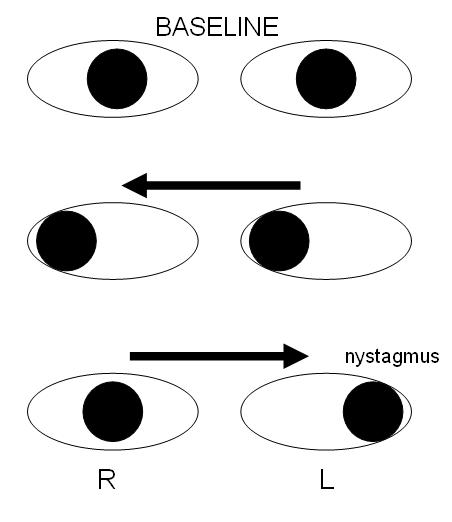
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia is a disorder of conjugate lateral gaze. The affected eye shows impairment of adduction. The partner eye diverges from the affected eye during abduction, producing diplopia; during extreme abduction, compensatorynystagmus can be seen in the partner eye. Diplopia means double vision while nystagmus is involuntary eye movementcharacterized by alternating smooth pursuit in one direction and a saccadic movement in the other direction.
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia occurs when MS affects a part of the brain stem called the medial longitudinal fasciculus, which is responsible for communication between the two eyes by connecting the abducens nucleus of one side to the oculomotor nucleus of the opposite side. This results in the failure of the medial rectus muscle to contract appropriately, so that the eyes do not move equally (called disconjugate gaze).