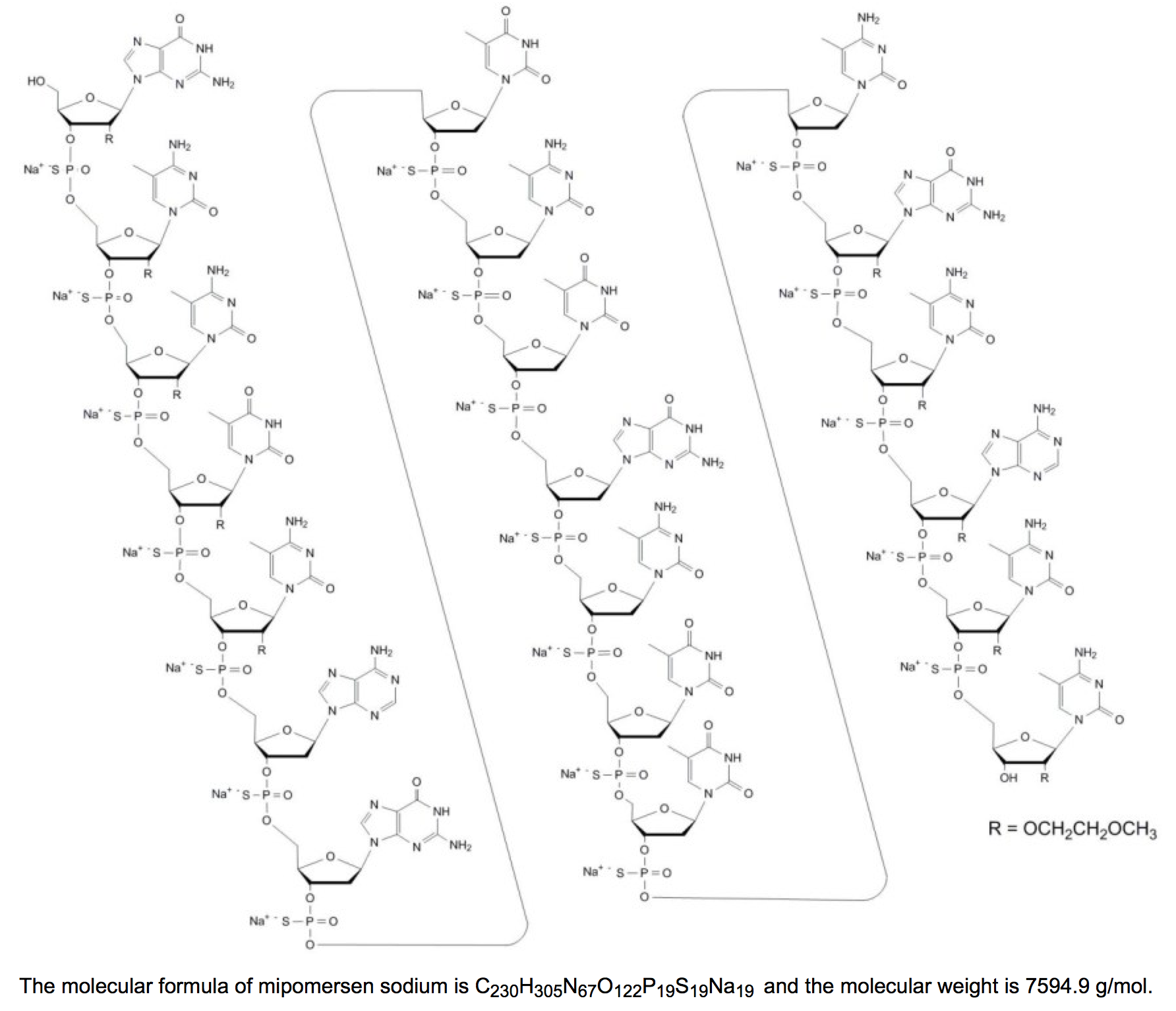
Mipomersen
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNING: RISK OF HEPATOTOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* KYNAMRO can cause elevations in transaminases. In the KYNAMRO clinical trial in patients with HoFH, 4 (12%) of the 34 patients treated with KYNAMRO compared with 0% of the 17 patients treated with placebo had at least one elevation in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) ≥ 3x upper limit of normal (ULN). There were no concomitant clinically meaningful elevations of total bilirubin, international normalized ratio (INR) or partial thromboplastin time (PTT).
|
Overview
Mipomersen is a lipid-lowering medication that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of hypercholesterolemia. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include injection site reactions, flu-like symptoms, nausea, headache, and elevations in serum transaminases, specifically ALT.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)
- KYNAMROTM is indicated as an adjunct to lipid-lowering medications and diet to reduce low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C), apolipoprotein B (apo B), total cholesterol (TC), and non-high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (non-HDL-C) in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH).
- Limitations of Use
- The safety and effectiveness of KYNAMRO have not been established in patients with hypercholesterolemia who do not have HoFH.
- The effect of KYNAMRO on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined.
- The safety and effectiveness of KYNAMRO as an adjunct to LDL apheresis have not been established; therefore, the use of KYNAMRO as an adjunct to LDL apheresis is not recommended.
- Dosing Information
- Before beginning treatment with KYNAMRO, measure transaminases (ALT, AST), alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin.
- The recommended dose of KYNAMRO is 200 milligrams (mg) once weekly as a subcutaneous injection.
- KYNAMRO is intended for subcutaneous use only. Do not administer intramuscularly or intravenously.
- The injection should be given on the same day every week, but if a dose is missed, the injection should be given at least 3 days from the next weekly dose.
- After initiation of KYNAMRO therapy lipid levels should be monitored at least every 3 months for the first year. Maximal reduction of LDL-C may be seen with KYNAMRO therapy after approximately 6 months (based on the time to steady state seen in clinical studies). Health care providers should assess the patient’s LDL-C level after 6 months to determine if the LDL-C reduction achieved with KYNAMRO is sufficiently robust to warrant the potential risk of liver toxicity.
- Administration
- Each vial or pre-filled syringe of KYNAMRO provides 200 mg of mipomersen sodium in a deliverable volume of 1 milliliter (mL) of solution and is intended for single-use only.
- The KYNAMRO vial or pre-filled syringe should be removed from 2-8°C (36-46°F) refrigerated storage and allowed to reach room temperature for at least 30 minutes prior to administration.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually prior to administration. If the solution is cloudy or contains visible particulate matter, the contents must not be injected and the product should be returned to the pharmacy.
- The first injection administered by the patient or caregiver should be performed under the guidance and supervision of an appropriately qualified health care professional.
- KYNAMRO should be injected into the abdomen, thigh region, or outer area of the upper arm. KYNAMRO should not be injected in areas of active skin disease or injury such as sunburns, skin rashes, inflammation, skin infections, active areas of psoriasis, etc. Areas of tattooed skin and scarring should also be avoided.
- Adjustments for Patients Developing Transaminase Elevations
- Table 1 summarizes recommendations for monitoring for patients who develop elevated transaminases during therapy with KYNAMRO.
- If transaminase elevations are accompanied by clinical symptoms of liver injury (e.g., nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, jaundice, lethargy, flu-like symptoms), increases in bilirubin ≥ 2x ULN, or active liver disease, discontinue treatment with KYNAMRO and investigate to identify the probable cause.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Mipomersen in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Hypercholesterolemia
- Dosing Information
- Mipomersen 200 mg subQ once weekly.[1]
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Safety and effectiveness have not been established in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Mipomersen in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Mipomersen in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B or C) or active liver disease, including unexplained persistent elevations of serum transaminases.
- Patients with a known hypersensitivity to any component of this product.
Warnings
|
WARNING: RISK OF HEPATOTOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* KYNAMRO can cause elevations in transaminases. In the KYNAMRO clinical trial in patients with HoFH, 4 (12%) of the 34 patients treated with KYNAMRO compared with 0% of the 17 patients treated with placebo had at least one elevation in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) ≥ 3x upper limit of normal (ULN). There were no concomitant clinically meaningful elevations of total bilirubin, international normalized ratio (INR) or partial thromboplastin time (PTT).
|
Risk of Hepatotoxicity
- KYNAMRO can cause elevations in transaminases and hepatic steatosis, as described below. To what extent KYNAMRO-associated hepatic steatosis promotes the elevations in transaminases is unknown. There is concern that KYNAMRO could induce steatohepatitis, which can progress to cirrhosis over several years. The clinical studies supporting the safety and efficacy of KYNAMRO in HoFH would have been unlikely to detect this adverse outcome given their size and duration.
Elevation of Transaminases
- KYNAMRO can cause increases in serum transaminases (alanine aminotransferase [ALT] and/or aspartate aminotransferase [AST]). In the clinical trial, 4 (12%) of the 34 subjects with HoFH treated with KYNAMRO compared to 0% of the 17 subjects treated with placebo had an elevation in ALT ≥ 3x ULN, and 3 (9%) of those treated with KYNAMRO compared to 0% treated with placebo had at least one elevation in ALT ≥ 5x ULN.
- Measure a full liver panel to include ALT, AST, total bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase before initiation of treatment with KYNAMRO. KYNAMRO is contraindicated in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment, or active liver disease, including unexplained persistent elevations of serum transaminases. If the baseline liver-related tests are abnormal, consider initiating KYNAMRO after an appropriate work-up and the baseline abnormalities are explained or resolved. During the first year, conduct liver-related tests monthly (ALT and AST, at a minimum). After the first year, conduct these tests at least every 3 months. Discontinue KYNAMRO for persistent or clinically significant elevations.
- If transaminase elevations are accompanied by clinical symptoms of liver injury (e.g., nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, jaundice, lethargy, flu-like symptoms), increases in bilirubin ≥ 2x ULN, or active liver disease, discontinue treatment with KYNAMRO and identify the probable cause.
Hepatic Steatosis
- KYNAMRO increases hepatic fat (steatosis) with or without concomitant increases in transaminases. Hepatic steatosis is a risk factor for advanced liver disease, including steatohepatitis and cirrhosis. The long-term consequences of hepatic steatosis associated with KYNAMRO therapy are unknown. During the clinical trials in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) and hyperlipidemia, the median absolute increase in hepatic fat was 10% after 26 weeks of treatment, from 0% at baseline, measured by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Alcohol may increase levels of hepatic fat and induce or exacerbate liver injury. It is recommended that patients taking KYNAMRO should consume no more than one alcoholic drink per day.
- Caution should be exercised when KYNAMRO is used with other medications known to have potential for hepatotoxicity, for example isotretinoin, amiodarone, acetaminophen (>4 g/day for ≥ 3 days/week), methotrexate, tetracyclines, and tamoxifen. The effect of concomitant administration of KYNAMRO with other hepatotoxic medications is unknown. More frequent monitoring of liver-related tests may be warranted.
- Mipomersen has not been studied concomitantly with other LDL-lowering agents that can also increase hepatic fat. Therefore, the combined use of such agents is not recommended.
KYNAMRO REMS
- Because of the risk of hepatotoxicity, KYNAMRO is available only through a limited program under the REMS. Under the KYNAMRO REMS, only certified healthcare providers and pharmacies may prescribe and distribute KYNAMRO. Further information is available at www.KynamroREMS.com or by telephone at 1-877-KYNAMRO (1-877-596-2676).
Injection Site Reactions
- Injection site reactions have been reported in 84% of patients receiving KYNAMRO therapy. These local reactions typically consist of one or more of the following: erythema, pain, tenderness, pruritus and local swelling. Injection site reactions do not occur with all injections but resulted in discontinuation of therapy in 5% of patients in pooled Phase 3 trials. To minimize the potential for injection site reactions, proper technique for subcutaneous administration should be followed.
Flu-Like Symptoms
- Flu-like symptoms have been reported in 30% of patients receiving KYNAMRO therapy and include one or more of the following: influenza-like illness, pyrexia, chills, myalgia, arthralgia, malaise or fatigue. Flu-like symptoms, which typically occur within 2 days after an injection, do not occur with all injections but resulted in discontinuation of therapy in 3% of patients in pooled Phase 3 trials.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Mipomersen in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Mipomersen in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Mipomersen in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Mipomersen during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mipomersen with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mipomersen with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mipomersen with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mipomersen with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mipomersen with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mipomersen in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mipomersen in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mipomersen in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Mipomersen in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Mipomersen in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Mipomersen in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Mipomersen in the drug label.
Pharmacology
Mipomersen
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-P-thioguanylyl-(3'→5')-2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-5-methyl-P-thiocytidylyl-(3'→5')-2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-5-methyl-P-thiocytidylyl-(3'→5')-2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-5-methyl-P-thiouridylyl-(3'→5')-2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-5-methyl-P-thiocytidylyl-(3'→5')-2'-deoxy-P-thioadenylyl-(3'→5')-2'-deoxy-Pthioguanylyl-(3'→5')P-thiothymidylyl-(3'→5')-2'-deoxy-5-methyl-P-thiocytidylyl-(3'→5')-P-thiothymidylyl-(3'→5')-2'-deoxy-P-thioguanylyl-(3'→5')-2'-deoxy-5-methyl-P-thiocytidylyl-(3'→5')-P-thiothymidylyl-(3'→5')-P-thiothymidylyl-(3'→5')-2'-deoxy-5-methyl-P-thiocytidylyl-(3'→5')-2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-Pthioguanylyl-(3'→5')-2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-5-methyl-P-thiocytidylyl-(3'→5')-2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-P-thioadenylyl-(3'→5')-2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-5-methyl-P-thiocytidylyl-(3'→5')-2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl)-5-methylcytidine nonadecasodiumsalt | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | C10 |
| PubChem | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 7594.80 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | Injection |
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Mipomersen in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Mipomersen in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Mipomersen in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Mipomersen in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Mipomersen Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Mipomersen |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Mipomersen |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Mipomersen in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Mipomersen interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Kynamro®[2]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- N/A[3]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Thomas, Gregory S. (2013-12-10). "Mipomersen, an apolipoprotein B synthesis inhibitor, reduces atherogenic lipoproteins in patients with severe hypercholesterolemia at high cardiovascular risk: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 62 (23): 2178–2184. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.081. ISSN 1558-3597. PMID 24013058. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ "KYNAMRO (mipomersen sodium) injection, solution".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Mipomersen |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Mipomersen |Label Name=Mipomersen11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Mipomersen |Label Name=Mipomersen11.png
}}