Mecamylamine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Protected "Mecamylamine": Bot: Protecting all pages from category Drug ([Edit=Allow only administrators] (indefinite) [Move=Allow only administrators] (indefinite))) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<!--Overview--> | <!--Overview--> | ||
|genericName= | |genericName= | ||
Mecamylamine | Mecamylamine | ||
|aOrAn= | |aOrAn= | ||
a | a | ||
|drugClass= | |drugClass= | ||
[[Ganglionic blocker|autonomic ganglionic blocker]] | [[Ganglionic blocker|autonomic ganglionic blocker]] | ||
|indication= | |indication= | ||
moderately severe to severe [[essential hypertension]] and uncomplicated cases of [[malignant hypertension]] | moderately severe to severe [[essential hypertension]] and uncomplicated cases of [[malignant hypertension]] | ||
|hasBlackBoxWarning= | |hasBlackBoxWarning= | ||
|adverseReactions= | |adverseReactions= | ||
| Line 29: | Line 23: | ||
<!--Black Box Warning--> | <!--Black Box Warning--> | ||
|blackBoxWarningTitle= | |blackBoxWarningTitle= | ||
Title | Title | ||
|blackBoxWarningBody= | |blackBoxWarningBody= | ||
<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span></i> | <i><span style="color:#FF0000;">ConditionName: </span></i> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 33: | ||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | <!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | ||
|fdaLIADAdult= | |fdaLIADAdult= | ||
=====Essential Hypertension and Malignant Hypertension===== | =====Essential Hypertension and Malignant Hypertension===== | ||
* Administration of Mecamylamine HCl after meals may cause a more gradual absorption and smoother control of excessively high [[blood pressure]]. The timing of doses in relation to meals should be consistent. Since the [[blood pressure]] response to antihypertensive drugs is increased in the early morning, the larger dose should be given at noontime and perhaps in the evening. The morning dose, as a rule, should be relatively small and in some instances may even be omitted. | |||
* Administration of Mecamylamine HCl after meals may cause a more gradual absorption and smoother control of excessively high blood pressure. The timing of doses in relation to meals should be consistent. Since the blood pressure response to antihypertensive drugs is increased in the early morning, the larger dose should be given at noontime and perhaps in the evening. The morning dose, as a rule, should be relatively small and in some instances may even be omitted. | |||
* The initial regulation of dosage should be determined by blood pressure readings in the erect position at the time of maximal effect of the drug, as well as by other signs and symptoms of orthostatic hypotension. | * The initial regulation of dosage should be determined by [[blood pressure]] readings in the erect position at the time of maximal effect of the drug, as well as by other signs and symptoms of orthostatic hypotension. | ||
* The effective maintenance dosage should be regulated by blood pressure readings in the erect position and by limitation of dosage to that which causes slight faintness or dizziness in this position. If the patient or a relative can use a sphygmomanometer, instructions may be given to reduce or omit a dose if readings fall below a designated level or if faintness or lightheadedness occurs. However, no change should be instituted without the knowledge of the physician. | * The effective maintenance dosage should be regulated by [[blood pressure]] readings in the erect position and by limitation of dosage to that which causes slight [[faintness]] or [[dizziness]] in this position. If the patient or a relative can use a sphygmomanometer, instructions may be given to reduce or omit a dose if readings fall below a designated level or if faintness or lightheadedness occurs. However, no change should be instituted without the knowledge of the physician. | ||
* Close supervision and education of the patient, as well as critical adjustment of dosage, are essential to successful therapy. | * Close supervision and education of the patient, as well as critical adjustment of dosage, are essential to successful therapy. | ||
* Other Antihypertensive Agents | * Other Antihypertensive Agents | ||
:* When Mecamylamine HCl is given with other antihypertensive drugs, the dosage of these other agents, as well as that of Mecamylamine HCl, should be reduced to avoid excessive hypotension. However, | :* When Mecamylamine HCl is given with other [[antihypertensive]] drugs, the dosage of these other agents, as well as that of Mecamylamine HCl, should be reduced to avoid excessive [[hypotension]]. However, [[thiazide]]s should be continued in their usual dosage, while that of Mecamylamine HCl is decreased by at least 50 percent. | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* '''''Initial Dosage''''': '''2.5 mg PO bid''' | |||
:* | ::* This initial dosage should be modified by increments of one 2.5 mg tablet at intervals of not less than 2 days until the desired blood pressure response occurs (the criterion being a dosage just under that which causes signs of mild [[postural hypotension]]). | ||
:* However, as little as 2.5 mg daily may be sufficient to control hypertension in some patients. A range of two to four or even more doses may be required in severe cases when smooth control is difficult to obtain. In severe or urgent cases, larger increments at smaller intervals may be needed. Partial tolerance may develop in certain patients, requiring an increase in the daily dosage of Mecamylamine HCl. | :* '''''Maintenance Dosage''''': '''25 mg/day PO tid''' | ||
::* However, as little as 2.5 mg daily may be sufficient to control [[hypertension]] in some patients. A range of two to four or even more doses may be required in severe cases when smooth control is difficult to obtain. In severe or urgent cases, larger increments at smaller intervals may be needed. Partial tolerance may develop in certain patients, requiring an increase in the daily dosage of Mecamylamine HCl. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | <!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | ||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | <!--Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | ||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | |offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | ||
| Line 73: | Line 62: | ||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | <!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | ||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= | |offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= | ||
| Line 81: | Line 69: | ||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | <!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | ||
|fdaLIADPed= | |fdaLIADPed= | ||
| Line 89: | Line 76: | ||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | <!--Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | ||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport= | |offLabelPedGuideSupport= | ||
| Line 95: | Line 81: | ||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | <!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | ||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | |offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | ||
| Line 101: | Line 86: | ||
<!--Contraindications--> | <!--Contraindications--> | ||
|contraindications= | |contraindications= | ||
* Mild, moderate, labile hypertension | * Mild, moderate, labile [[hypertension]] | ||
:* Mecamylamine HCl should not be used in mild, moderate, labile hypertension and may prove unsuitable in uncooperative patients. | :* Mecamylamine HCl should not be used in mild, moderate, labile [[hypertension]] and may prove unsuitable in uncooperative patients. | ||
* [[Coronary insufficiency]] or recent [[myocardial infarction]] | |||
:* It is contraindicated in [[coronary insufficiency]] or recent [[myocardial infarction]]. | |||
* | * [[Uremia]] | ||
:* Mecamylamine HCl should be given with great discretion, if at all, when [[renal insufficiency]] is manifested by a rising or elevated [[BUN]]. The drug is contraindicated in [[uremia]]. | |||
* | * Use of [[antibiotic]]s and [[sulfonamide]]s | ||
:* Patients receiving [[antibiotic]]s and [[sulfonamide]]s should generally not be treated with [[ganglionic blocker]]s. | |||
* Hypersensitivity | * [[Glaucoma]] | ||
* Organic [[pyloric stenosis]] | |||
* [[Hypersensitivity]] | |||
<!--Warnings--> | <!--Warnings--> | ||
|warnings= | |warnings= | ||
* Mecamylamine, a secondary amine, readily penetrates into the brain and thus may produce central nervous system effects. Tremor, choreiform movements, mental aberrations, and | * Mecamylamine, a secondary amine, readily penetrates into the [[brain]] and thus may produce [[central nervous system]] effects. [[Tremor]], choreiform movements, mental aberrations, and [[convulsion]]s may occur rarely. These have occurred most often when large doses of Mecamylamine HCl were used, especially in patients with cerebral or [[renal insufficiency]]. | ||
* When | * When [[ganglionic blocker]]s or other potent [[antihypertensive]] drugs are discontinued suddenly, hypertensive levels return. In patients with [[malignant hypertension]] and others, this may occur abruptly and may cause fatal [[cerebral vascular accident]]s or acute [[congestive heart failure]]. When Mecamylamine HCl is withdrawn, this should be done gradually and other [[antihypertensive]] therapy usually must be substituted. On the other hand, the effects of Mecamylamine HCl sometimes may last from hours to days after therapy is discontinued. | ||
====Precautions==== | ====Precautions==== | ||
| Line 136: | Line 115: | ||
* The patient's condition should be evaluated carefully, particularly as to renal and cardiovascular function. When renal, cerebral, or coronary blood flow is deficient, any additional impairment, which might result from added hypotension, must be avoided. The use of Mecamylamine HCl in patients with marked cerebral and coronary arteriosclerosis or after a recent cerebral accident requires caution. | * The patient's condition should be evaluated carefully, particularly as to renal and cardiovascular function. When renal, cerebral, or coronary blood flow is deficient, any additional impairment, which might result from added hypotension, must be avoided. The use of Mecamylamine HCl in patients with marked cerebral and coronary arteriosclerosis or after a recent cerebral accident requires caution. | ||
* The action of Mecamylamine HCl may be potentiated by excessive heat, fever, infection, hemorrhage, pregnancy, anesthesia, surgery, vigorous exercise, other antihypertensive drugs, alcohol, and salt depletion as a result of diminished intake or increased excretion due to diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating, or | * The action of Mecamylamine HCl may be potentiated by excessive heat, [[fever]], [[infection]], [[hemorrhage]], [[pregnancy]], [[anesthesia]], [[surgery]], vigorous exercise, other [[antihypertensive]] drugs, alcohol, and salt depletion as a result of diminished intake or increased excretion due to [[diarrhea]], [[vomiting]], excessive sweating, or [[diuretic]]s. | ||
* During therapy with Mecamylamine HCl, sodium intake should not be restricted but, if necessary, the dosage of the | * During therapy with Mecamylamine HCl, sodium intake should not be restricted but, if necessary, the dosage of the [[ganglionic blocker]] must be adjusted. | ||
* Since urinary retention may occur in patients on | * Since [[urinary retention]] may occur in patients on [[ganglionic blocker]]s, caution is required in patients with [[prostate gland|prostatic]] [[hypertrophy]], bladder neck obstruction, and [[urethra]]l stricture. | ||
* Frequent loose bowel movements with abdominal distention and decreased borborygmi may be the first signs of paralytic ileus. If these are present, Mecamylamine HCl should be discontinued immediately and remedial steps taken. | * Frequent loose bowel movements with abdominal distention and decreased borborygmi may be the first signs of paralytic [[ileus]]. If these are present, Mecamylamine HCl should be discontinued immediately and remedial steps taken. | ||
<!--Adverse Reactions--> | <!--Adverse Reactions--> | ||
<!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | <!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | ||
|clinicalTrials= | |clinicalTrials= | ||
| Line 153: | Line 131: | ||
<!--Postmarketing Experience--> | <!--Postmarketing Experience--> | ||
|postmarketing= | |postmarketing= | ||
* The following adverse reactions have been reported and within each category are listed in order of decreasing severity. | * The following adverse reactions have been reported and within each category are listed in order of decreasing severity. | ||
======Neurologic====== | ======Neurologic====== | ||
[[Convulsion]]s, choreiform movements, mental aberrations, [[tremor]], and [[paresthesia]]s | |||
======Cardiovascular====== | ======Cardiovascular====== | ||
Orthostatic dizziness and syncope, postural hypotension. | [[Orthostasis|Orthostatic]] [[dizziness]] and [[syncope]], [[postural hypotension]]. | ||
======Respiratory====== | ======Respiratory====== | ||
Interstitial pulmonary edema and fibrosis. | Interstitial [[pulmonary edema]] and [[fibrosis]]. | ||
======Gastrointestinal====== | ======Gastrointestinal====== | ||
Ileus, constipation (sometimes preceded by small, frequent liquid stools), vomiting, nausea, anorexia, glossitis and dryness of mouth. | [[Ileus]], [[constipation]] (sometimes preceded by small, frequent liquid stools), [[vomiting]], [[nausea]], [[anorexia]], [[glossitis]] and dryness of mouth. | ||
======Urogenital====== | ======Urogenital====== | ||
Urinary retention, impotence, decreased libido. | [[Urinary retention]], [[impotence]], decreased [[libido]]. | ||
======Special Senses====== | ======Special Senses====== | ||
Blurred vision, dilated pupils. | [[Blurred vision]], [[mydriasis|dilated pupils]]. | ||
======Miscellaneous====== | ======Miscellaneous====== | ||
Weakness, fatigue, sedation. | [[Weakness]], [[fatigue]], [[sedation]]. | ||
<!--Drug Interactions--> | <!--Drug Interactions--> | ||
|drugInteractions= | |drugInteractions= | ||
* | * [[Sulfonamide]]s | ||
:* Patients receiving | :* Patients receiving [[antibiotic]]s and [[sulfonamide]]s generally should not be treated with [[ganglionic blocker]]s. | ||
* Anesthesia, other antihypertensive drugs and alcohol | * [[Anesthesia]], other [[antihypertensive]] drugs, and [[alcohol]] | ||
:* The action of Mecamylamine HCl may be potentiated by anesthesia, other antihypertensive drugs and alcohol. | :* The action of Mecamylamine HCl may be potentiated by [[anesthesia]], other [[antihypertensive]] drugs and [[alcohol]]. | ||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | <!--Use in Specific Populations--> | ||
|useInPregnancyFDA= | |useInPregnancyFDA= | ||
* '''Pregnancy Category C''' | * '''Pregnancy Category C''' | ||
:* Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Mecamylamine HCl. It is not known whether Mecamylamine HCl can cause fetal harm when given to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Mecamylamine HCl should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed. | :* Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Mecamylamine HCl. It is not known whether Mecamylamine HCl can cause fetal harm when given to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Mecamylamine HCl should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed. | ||
|useInPregnancyAUS= | |useInPregnancyAUS= | ||
* '''Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category''' | * '''Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category''' | ||
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of {{PAGENAME}} in women who are pregnant. | There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of {{PAGENAME}} in women who are pregnant. | ||
|useInLaborDelivery= | |useInLaborDelivery= | ||
There is no FDA guidance on use of {{PAGENAME}} during labor and delivery. | There is no FDA guidance on use of {{PAGENAME}} during labor and delivery. | ||
|useInNursing= | |useInNursing= | ||
* Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Mecamylamine HCl, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. | * Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Mecamylamine HCl, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. | ||
|useInPed= | |useInPed= | ||
* Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. | * Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. | ||
|useInGeri= | |useInGeri= | ||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to geriatric patients. | There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to geriatric patients. | ||
|useInGender= | |useInGender= | ||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific gender populations. | There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific gender populations. | ||
|useInRace= | |useInRace= | ||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific racial populations. | There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific racial populations. | ||
|useInRenalImpair= | |useInRenalImpair= | ||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with renal impairment. | There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with renal impairment. | ||
|useInHepaticImpair= | |useInHepaticImpair= | ||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with hepatic impairment. | There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients with hepatic impairment. | ||
|useInReproPotential= | |useInReproPotential= | ||
There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in women of reproductive potentials and males. | There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in women of reproductive potentials and males. | ||
|useInImmunocomp= | |useInImmunocomp= | ||
There is no FDA guidance one the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients who are immunocompromised. | There is no FDA guidance one the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients who are immunocompromised. | ||
<!--Administration and Monitoring--> | <!--Administration and Monitoring--> | ||
|administration= | |administration= | ||
* | * Oral | ||
|monitoring= | |monitoring= | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | ||
<!--IV Compatibility--> | <!--IV Compatibility--> | ||
|IVCompat= | |IVCompat= | ||
| Line 262: | Line 218: | ||
<!--Overdosage--> | <!--Overdosage--> | ||
|overdose= | |overdose= | ||
| Line 269: | Line 224: | ||
====Signs and Symptoms==== | ====Signs and Symptoms==== | ||
* Signs of overdosage include: hypotension (which may progress to peripheral vascular collapse), postural hypotension, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, paralytic ileus, urinary retention, dizziness, anxiety, dry mouth, mydriasis, blurred vision, or palpitations. A rise in intraocular pressure may occur. | * Signs of overdosage include: [[hypotension]] (which may progress to peripheral vascular collapse), [[postural hypotension]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[diarrhea]], [[constipation]], paralytic [[ileus]], [[urinary retention]], [[dizziness]], [[anxiety]], [[dry mouth]], [[mydriasis]], [[blurred vision]], or [[palpitations]]. [[IICP|A rise in intraocular pressure]] may occur. | ||
* Pressor amines may be used to counteract excessive hypotension. Since patients being treated with | * Pressor amines may be used to counteract excessive [[hypotension]]. Since patients being treated with [[ganglionic blocker]]s are more than normally reactive to pressor amines, small doses of the latter are recommended to avoid excessive response. | ||
* The oral LD50 of Mecamylamine HCl in the mouse is 92 mg/kg. | * The oral LD50 of Mecamylamine HCl in the mouse is 92 mg/kg. | ||
| Line 280: | Line 235: | ||
<!--Drugbox2--> | <!--Drugbox2--> | ||
|drugBox= | |drugBox= | ||
| Line 333: | Line 287: | ||
<!--Mechanism of Action--> | <!--Mechanism of Action--> | ||
|mechAction= | |mechAction= | ||
* | * Mecamylamine HCl is a potent, oral [[antihypertension]] agent and [[ganglionic blocker]], and is a secondary amine. | ||
<!--Structure--> | <!--Structure--> | ||
|structure= | |structure= | ||
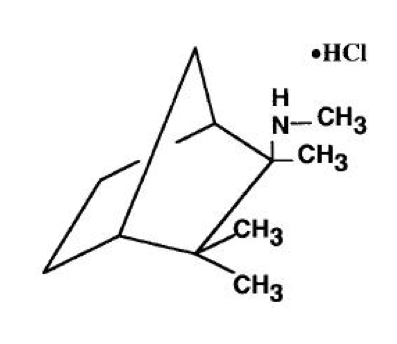
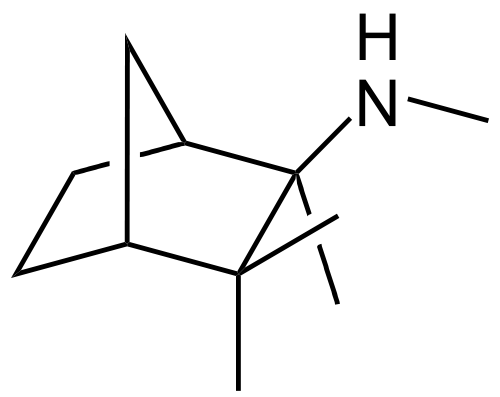
* Mecamylamine HCl | * Mecamylamine HCl is N,2,3,3-tetramethyl-bicyclo [2.2.1] heptan-2-amine hydrochloride. Its empirical formula is C11H21N • HCl and its structural formula is: | ||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb| | : [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
* It is a white, odorless, or practically odorless, crystalline powder, is highly stable, soluble in water and has a molecular weight of 203.75. | * It is a white, odorless, or practically odorless, crystalline powder, is highly stable, soluble in water and has a molecular weight of 203.75. | ||
* Mecamylamine HCl is supplied as tablets for oral use, each containing 2.5 mg mecamylamine HCl. Inactive ingredients are calcium phosphate, D&C Yellow 10, FD&C Yellow 6, lactose, magnesium stearate, cornstarch, and talc. | * Mecamylamine HCl is supplied as tablets for oral use, each containing 2.5 mg mecamylamine HCl. Inactive ingredients are calcium phosphate, D&C Yellow 10, FD&C Yellow 6, lactose, magnesium stearate, cornstarch, and talc. | ||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | <!--Pharmacodynamics--> | ||
|PD= | |PD= | ||
* Mecamylamine HCl reduces blood pressure in both normotensive and hypertensive individuals. It has a gradual onset of action (1/2 to 2 hours) and a long-lasting effect (usually 6 to 12 hours or more). A small oral dosage often produces a smooth and predictable reduction of blood pressure. Although this antihypertensive effect is predominantly orthostatic, the supine blood pressure is also significantly reduced. | * Mecamylamine HCl reduces blood pressure in both normotensive and [[hypertensive]] individuals. It has a gradual onset of action (1/2 to 2 hours) and a long-lasting effect (usually 6 to 12 hours or more). A small oral dosage often produces a smooth and predictable reduction of blood pressure. Although this [[antihypertensive]] effect is predominantly orthostatic, the supine [[blood pressure]] is also significantly reduced. | ||
<!--Pharmacokinetics--> | <!--Pharmacokinetics--> | ||
|PK= | |PK= | ||
* Mecamylamine HCl is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in consistent lowering of blood pressure in most patients with hypertensive cardiovascular disease. Mecamylamine HCl is excreted slowly in the urine in the unchanged form. The rate of its renal elimination is influenced markedly by urinary pH. Alkalinization of the urine reduces, and acidification promotes, renal excretion of mecamylamine. | * Mecamylamine HCl is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in consistent lowering of blood pressure in most patients with [[hypertensive]] cardiovascular disease. Mecamylamine HCl is excreted slowly in the urine in the unchanged form. The rate of its renal elimination is influenced markedly by urinary pH. Alkalinization of the urine reduces, and acidification promotes, renal excretion of mecamylamine. | ||
* Mecamylamine HCl crosses the blood-brain and placental barriers. | * Mecamylamine HCl crosses the blood-brain and placental barriers. | ||
<!--Nonclinical Toxicology--> | <!--Nonclinical Toxicology--> | ||
|nonClinToxic= | |nonClinToxic= | ||
* Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility | * Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility | ||
:* Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the effects upon fertility, mutagenic or carcinogenic potential of Mecamylamine HCl. | :* Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the effects upon fertility, mutagenic or carcinogenic potential of Mecamylamine HCl. | ||
<!--Clinical Studies--> | <!--Clinical Studies--> | ||
|clinicalStudies= | |clinicalStudies= | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>Clinical Studies</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | There is limited information regarding <i>Clinical Studies</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | ||
<!--How Supplied--> | <!--How Supplied--> | ||
|howSupplied= | |howSupplied= | ||
| Line 395: | Line 335: | ||
<!--Patient Counseling Information--> | <!--Patient Counseling Information--> | ||
|fdaPatientInfo= | |fdaPatientInfo= | ||
| Line 401: | Line 340: | ||
<!--Precautions with Alcohol--> | <!--Precautions with Alcohol--> | ||
|alcohol= | |alcohol= | ||
* The action of Mecamylamine may be potentiated by alcohol. | * The action of Mecamylamine may be potentiated by alcohol. | ||
| Line 410: | Line 347: | ||
<!--Brand Names--> | <!--Brand Names--> | ||
|brandNames= | |brandNames= | ||
| Line 416: | Line 352: | ||
<!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | <!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | ||
|lookAlike= | |lookAlike= | ||
| Line 422: | Line 357: | ||
<!--Drug Shortage Status--> | <!--Drug Shortage Status--> | ||
|drugShortage= | |drugShortage= | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 457: | Line 391: | ||
[[Category:Cardiovascular Drugs]] | [[Category:Cardiovascular Drugs]] | ||
[[Category:Drug]] | [[Category:Drug]] | ||
[[Category:Antihypertensive agents]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:39, 20 August 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Mecamylamine is a autonomic ganglionic blocker that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of moderately severe to severe essential hypertension and uncomplicated cases of malignant hypertension. Common adverse reactions include orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Essential Hypertension and Malignant Hypertension
- Administration of Mecamylamine HCl after meals may cause a more gradual absorption and smoother control of excessively high blood pressure. The timing of doses in relation to meals should be consistent. Since the blood pressure response to antihypertensive drugs is increased in the early morning, the larger dose should be given at noontime and perhaps in the evening. The morning dose, as a rule, should be relatively small and in some instances may even be omitted.
- The initial regulation of dosage should be determined by blood pressure readings in the erect position at the time of maximal effect of the drug, as well as by other signs and symptoms of orthostatic hypotension.
- The effective maintenance dosage should be regulated by blood pressure readings in the erect position and by limitation of dosage to that which causes slight faintness or dizziness in this position. If the patient or a relative can use a sphygmomanometer, instructions may be given to reduce or omit a dose if readings fall below a designated level or if faintness or lightheadedness occurs. However, no change should be instituted without the knowledge of the physician.
- Close supervision and education of the patient, as well as critical adjustment of dosage, are essential to successful therapy.
- Other Antihypertensive Agents
- When Mecamylamine HCl is given with other antihypertensive drugs, the dosage of these other agents, as well as that of Mecamylamine HCl, should be reduced to avoid excessive hypotension. However, thiazides should be continued in their usual dosage, while that of Mecamylamine HCl is decreased by at least 50 percent.
- Dosing Information
- Initial Dosage: 2.5 mg PO bid
- This initial dosage should be modified by increments of one 2.5 mg tablet at intervals of not less than 2 days until the desired blood pressure response occurs (the criterion being a dosage just under that which causes signs of mild postural hypotension).
- Maintenance Dosage: 25 mg/day PO tid
- However, as little as 2.5 mg daily may be sufficient to control hypertension in some patients. A range of two to four or even more doses may be required in severe cases when smooth control is difficult to obtain. In severe or urgent cases, larger increments at smaller intervals may be needed. Partial tolerance may develop in certain patients, requiring an increase in the daily dosage of Mecamylamine HCl.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Mecamylamine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Mecamylamine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Mecamylamine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Mecamylamine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Mild, moderate, labile hypertension
- Mecamylamine HCl should not be used in mild, moderate, labile hypertension and may prove unsuitable in uncooperative patients.
- Coronary insufficiency or recent myocardial infarction
- It is contraindicated in coronary insufficiency or recent myocardial infarction.
- Mecamylamine HCl should be given with great discretion, if at all, when renal insufficiency is manifested by a rising or elevated BUN. The drug is contraindicated in uremia.
- Use of antibiotics and sulfonamides
- Patients receiving antibiotics and sulfonamides should generally not be treated with ganglionic blockers.
- Glaucoma
- Organic pyloric stenosis
- Hypersensitivity
Warnings
- Mecamylamine, a secondary amine, readily penetrates into the brain and thus may produce central nervous system effects. Tremor, choreiform movements, mental aberrations, and convulsions may occur rarely. These have occurred most often when large doses of Mecamylamine HCl were used, especially in patients with cerebral or renal insufficiency.
- When ganglionic blockers or other potent antihypertensive drugs are discontinued suddenly, hypertensive levels return. In patients with malignant hypertension and others, this may occur abruptly and may cause fatal cerebral vascular accidents or acute congestive heart failure. When Mecamylamine HCl is withdrawn, this should be done gradually and other antihypertensive therapy usually must be substituted. On the other hand, the effects of Mecamylamine HCl sometimes may last from hours to days after therapy is discontinued.
Precautions
- The patient's condition should be evaluated carefully, particularly as to renal and cardiovascular function. When renal, cerebral, or coronary blood flow is deficient, any additional impairment, which might result from added hypotension, must be avoided. The use of Mecamylamine HCl in patients with marked cerebral and coronary arteriosclerosis or after a recent cerebral accident requires caution.
- The action of Mecamylamine HCl may be potentiated by excessive heat, fever, infection, hemorrhage, pregnancy, anesthesia, surgery, vigorous exercise, other antihypertensive drugs, alcohol, and salt depletion as a result of diminished intake or increased excretion due to diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating, or diuretics.
- During therapy with Mecamylamine HCl, sodium intake should not be restricted but, if necessary, the dosage of the ganglionic blocker must be adjusted.
- Since urinary retention may occur in patients on ganglionic blockers, caution is required in patients with prostatic hypertrophy, bladder neck obstruction, and urethral stricture.
- Frequent loose bowel movements with abdominal distention and decreased borborygmi may be the first signs of paralytic ileus. If these are present, Mecamylamine HCl should be discontinued immediately and remedial steps taken.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Mecamylamine in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
- The following adverse reactions have been reported and within each category are listed in order of decreasing severity.
Neurologic
Convulsions, choreiform movements, mental aberrations, tremor, and paresthesias
Cardiovascular
Orthostatic dizziness and syncope, postural hypotension.
Respiratory
Interstitial pulmonary edema and fibrosis.
Gastrointestinal
Ileus, constipation (sometimes preceded by small, frequent liquid stools), vomiting, nausea, anorexia, glossitis and dryness of mouth.
Urogenital
Urinary retention, impotence, decreased libido.
Special Senses
Blurred vision, dilated pupils.
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Patients receiving antibiotics and sulfonamides generally should not be treated with ganglionic blockers.
- Anesthesia, other antihypertensive drugs, and alcohol
- The action of Mecamylamine HCl may be potentiated by anesthesia, other antihypertensive drugs and alcohol.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C
- Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Mecamylamine HCl. It is not known whether Mecamylamine HCl can cause fetal harm when given to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Mecamylamine HCl should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Mecamylamine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Mecamylamine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Mecamylamine HCl, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mecamylamine with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mecamylamine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mecamylamine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mecamylamine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mecamylamine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mecamylamine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Mecamylamine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Mecamylamine in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Mecamylamine in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Signs of overdosage include: hypotension (which may progress to peripheral vascular collapse), postural hypotension, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, paralytic ileus, urinary retention, dizziness, anxiety, dry mouth, mydriasis, blurred vision, or palpitations. A rise in intraocular pressure may occur.
- Pressor amines may be used to counteract excessive hypotension. Since patients being treated with ganglionic blockers are more than normally reactive to pressor amines, small doses of the latter are recommended to avoid excessive response.
- The oral LD50 of Mecamylamine HCl in the mouse is 92 mg/kg.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Mecamylamine in the drug label.
Pharmacology
| |
Mecamylamine
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| (1S,2R,4R)-N,2,3,3-tetramethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | C02 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 167.291 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Protein binding | 40% |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status |
Template:Unicode Prescription only |
| Routes | Oral |
Mechanism of Action
- Mecamylamine HCl is a potent, oral antihypertension agent and ganglionic blocker, and is a secondary amine.
Structure
- Mecamylamine HCl is N,2,3,3-tetramethyl-bicyclo [2.2.1] heptan-2-amine hydrochloride. Its empirical formula is C11H21N • HCl and its structural formula is:
- It is a white, odorless, or practically odorless, crystalline powder, is highly stable, soluble in water and has a molecular weight of 203.75.
- Mecamylamine HCl is supplied as tablets for oral use, each containing 2.5 mg mecamylamine HCl. Inactive ingredients are calcium phosphate, D&C Yellow 10, FD&C Yellow 6, lactose, magnesium stearate, cornstarch, and talc.
Pharmacodynamics
- Mecamylamine HCl reduces blood pressure in both normotensive and hypertensive individuals. It has a gradual onset of action (1/2 to 2 hours) and a long-lasting effect (usually 6 to 12 hours or more). A small oral dosage often produces a smooth and predictable reduction of blood pressure. Although this antihypertensive effect is predominantly orthostatic, the supine blood pressure is also significantly reduced.
Pharmacokinetics
- Mecamylamine HCl is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in consistent lowering of blood pressure in most patients with hypertensive cardiovascular disease. Mecamylamine HCl is excreted slowly in the urine in the unchanged form. The rate of its renal elimination is influenced markedly by urinary pH. Alkalinization of the urine reduces, and acidification promotes, renal excretion of mecamylamine.
- Mecamylamine HCl crosses the blood-brain and placental barriers.
Nonclinical Toxicology
- Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the effects upon fertility, mutagenic or carcinogenic potential of Mecamylamine HCl.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Mecamylamine in the drug label.
How Supplied
- Vecamyl [Mecamylamine HCl Tablet USP] are slightly yellow, round, compressed tablets, coded MP on one side and 2.5 on the other side. They are supplied as follows:
- NDC 0722-7183-01 in bottles of 100.
- Storage
- Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F)
Storage
There is limited information regarding Mecamylamine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Mecamylamine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Mecamylamine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Mecamylamine HCl may cause dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting, especially when rising from a lying or sitting position. This effect may be increased by alcoholic beverages, exercise, or during hot weather. Getting up slowly may help alleviate such a reaction.
Precautions with Alcohol
- The action of Mecamylamine may be potentiated by alcohol.
- Mecamylamine may cause dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting, especially when rising from a lying or sitting position. This effect may be increased by alcoholic beverages.
Brand Names
- Vecamyl®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- N/A[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "VECAMYL (mecamylamine hydrochloride) tablet".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Mecamylamine |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Mecamylamine |Label Name=Mecamylamine02.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Mecamylamine |Label Name=Mecamylamine03.png
}}