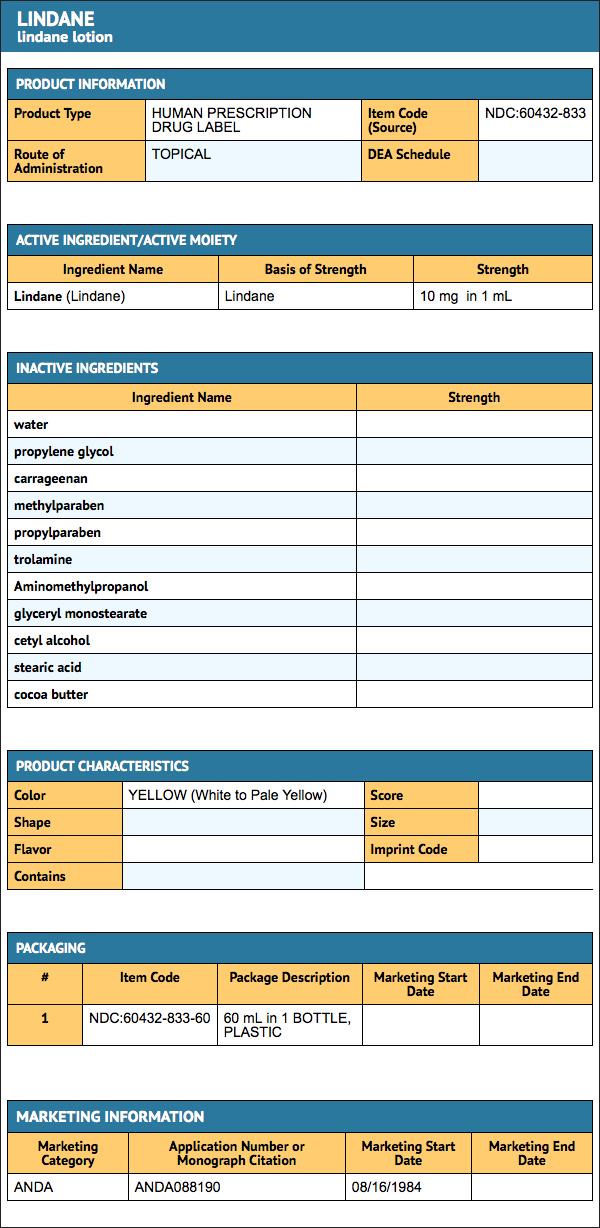
Lindane
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alberto Plate [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNINGS
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
Lindane Lotion should only be used in patients who cannot tolerate or have failed first-line treatment with safer medications for the treatment of scabies.
Neurologic Toxicity: Seizures and deaths have been reported following Lindane Lotion use with repeat or prolonged application, but also in rare cases following a single application used according to directions. Lindane Lotion should be used with caution for infants, children, the elderly, and individuals with other skin conditions (e.g., atopic dermatitis, psoriasis) and in those who weigh < 110 lbs (50 kg) as they may be at risk of serious neurotoxicity. Contraindications: Lindane Lotion is contraindicated in premature infants and individuals with known uncontrolled seizure disorders. Proper Use: Instruct patients on the proper use of Lindane Lotion, the amount to apply, how long to leave it on, and avoiding retreatment. Inform patients that itching occurs after the successful killing of scabies and is not necessarily an indication for retreatment with Lindane Lotion. |
Overview
Lindane is an ectoparasiticide and ovicide. that is FDA approved for the treatment of Scabies (infestations of Sarcoptes scabei ) only in patients who cannot tolerate other approved therapies or have failed treatment with other approved therapies. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include pruritus, post-treatment, dizziness, insomnia, anxiety.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- Apply a thin layer of Lindane Lotion over all skin from the neck down. One ounce is sufficient for an average adult. Do not prescribe more than 2 ounces for larger adults. Apply only once. Wash off in 8 to 12 hours. Do not retreat.
- Patients should be provided specific information on use of product.
- Patients should be instructed on proper use of Lindane Lotion, especially the amount to apply, how long to leave on and the need to avoid retreatment. Patients should be informed that itching occurs after the successful killing of scabies (mites) and continued itching is not necessarily an indication for retreatment with Lindane Lotion.
- A Lindane Lotion Medication Guide must be given to the patient each time Lindane Lotion is dispensed, as required by law. The Lindane Lotion Medication Guide is an important part of the risk management program for the patient.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Lindane in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Lindane in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Apply a thin layer of Lindane Lotion over all skin from the neck down. One ounce is sufficient for an average adult. Do not prescribe more than 2 ounces for larger adults. Apply only once. Wash off in 8 to 12 hours. Do not retreat.
- Patients should be provided specific information on use of product.
- Patients should be instructed on proper use of Lindane Lotion, especially the amount to apply, how long to leave on and the need to avoid retreatment. Patients should be informed that itching occurs after the successful killing of scabies (mites) and continued itching is not necessarily an indication for retreatment with Lindane Lotion.
- A Lindane Lotion Medication Guide must be given to the patient each time Lindane Lotion is dispensed, as required by law. The Lindane Lotion Medication Guide is an important part of the risk management program for the patient.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Lindane in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Lindane in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Lindane Lotion is contraindicated for premature infants because their skin may be more permeable than that of full term infants and their liver enzymes may not be sufficiently developed to metabolize Lindane. Lindane Lotion is also contraindicated for patients with crusted (Norwegian) scabies and other skin conditions (e.g., atopic dermatitis, psoriasis) that may increase systemic absorption of the drug. Lindane Lotion is contraindicated for patients with known uncontrolled seizure disorders and for individuals with a known sensitivity to the product or any of its components.
Warnings
|
WARNINGS
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
Lindane Lotion should only be used in patients who cannot tolerate or have failed first-line treatment with safer medications for the treatment of scabies.
Neurologic Toxicity: Seizures and deaths have been reported following Lindane Lotion use with repeat or prolonged application, but also in rare cases following a single application used according to directions. Lindane Lotion should be used with caution for infants, children, the elderly, and individuals with other skin conditions (e.g., atopic dermatitis, psoriasis) and in those who weigh < 110 lbs (50 kg) as they may be at risk of serious neurotoxicity. Contraindications: Lindane Lotion is contraindicated in premature infants and individuals with known uncontrolled seizure disorders. Proper Use: Instruct patients on the proper use of Lindane Lotion, the amount to apply, how long to leave it on, and avoiding retreatment. Inform patients that itching occurs after the successful killing of scabies and is not necessarily an indication for retreatment with Lindane Lotion. |
- Seizures and deaths have been reported following Lindane Lotion's use with repeat or prolonged application, but also in rare cases following a single application reportedly used according to directions. It is not known how soon after application of a single dose of Lindane Lotion that a second dose of Lindane Lotion can be safely applied.
- There have been cases of adverse events reported for Lindane Lotion and Lindane Shampoo in which a serious outcome (hospitalization, disability or death) has occurred.4 In approximately 20% of the total reported cases, Lindane Lotion and Shampoo were reported to have been used according to the labeled directions. Of these cases, thirteen deaths were reported, many cases which were remote from the time of actual Lindane use. Lindane toxicity, verified by autopsy was the cause of one infant's death, was the cause of death reported for an adult who ingested it orally in a successful suicide. The direct causes of death for the other cases were attributed to reasons other than Lindane. Most of these adverse events occurred with Lindane Lotion.
- Infants, children, the elderly, and individuals with other skin conditions and those who weigh < 110 lbs (50 kg) may be at greater risk of serious neurotoxicity. Animal studies have shown increased susceptibility to neurologic adverse events in younger animals. Children have a larger body surface area to volume ratio that may result in a proportionately larger systemic exposure.
- Careful consideration should be given before prescribing Lindane Lotion to patients with conditions that may increase the risk of seizure, such as HIV infection, history of head trauma or a prior seizure, CNS tumor, the presence of severe hepatic cirrhosis, excessive use of alcohol, abrupt withdrawal from alcohol or sedatives, as well as concomitant use of medications known to lower seizure threshold.
- Patients should be instructed on proper use of Lindane Lotion, especially the amount to apply, how long to leave the lotion on, and the need to avoid retreatment. Patients should be informed that itching may occur, and even worsen, after the successful killing of scabies. Repeat treatment is usually not necessary.
- A Lindane Lotion Medication Guide must be given to the patient each time Lindane Lotion is dispensed, as required by law.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Lindane Lotion has been reported to cause central nervous system stimulation ranging from dizziness to seizures. Although seizures were almost always associated with ingestion or misuse of the product (to include repeat treatment), seizures and deaths have been reported when Lindane Lotion was used according to directions. Irritant dermatitis from contact with this product has also been reported
Postmarketing Experience
- The following adverse reactions reflect additional postmarketing experience of Lindane Lotion. These events include alopecia, dermatitis, headache, pain, paresthesia, pruritus and urticaria. The relationship of some of these events to Lindane therapy is unknown.
Drug Interactions
Oils may enhance absorption of Lindane, therefore, patients or caregivers applying Lindane Lotion should be warned about simultaneous use of creams, ointments, or oils. In addition, there are many drugs that may lower the seizure threshold, and Lindane Lotion should be prescribed with caution in patients taking these medications. Drugs that may lower the seizure threshold include, but are not limited to the following:
- Antipsychotics
- Antidepressants
- Theophylline
- Cyclosporine
- Mycophenolate mofetil
- Tacrolimus capsules
- Penicillins, imipenem, quinolone antibiotics
- Chloroquine sulfate, pyrimethamine
- Isoniazid
- Meperidine
- Radiographic contrast agents
- Centrally active anticholinesterases
- Methocarbamol
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- All pregnancies have a risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse event regardless of drug exposure. Predictions of fetal risk from drug exposure rely heavily on animal data. However, animal studies may fail to predict effects in humans or may overstate such risks. Even if human data are available, the data may not be sufficient to determine whether there is an increased risk to the fetus, and individual reports of adverse outcomes in pregnancy in association with a drug may not reflect a causal relationship.
- Lindane Lotion should be given to pregnant women only if clearly needed. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of Lindane Lotion in pregnant women. There are no known maternal or fetal health risks if the scabies is not treated. Lindane is lipophilic and may accumulate in the placenta. There has been a single case report of a stillborn infant following multiple maternal exposures to lindane during pregnancy. The relationship of the maternal exposures to the fetal outcome is unknown.
- Animal data suggest that lindane exposure of the fetus may increase the likelihood of neurologic developmental abnormalities, based on findings at systemic exposures close to that expected in humans when Lindane Lotion is used to treat scabies. The immature central nervous system (as in the fetus) may have increased susceptibility to the effects of the drug.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Lindane in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Lindane during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Lindane is lipophilic and is present in human breast milk, but exact quantities are not known. There may be a risk of toxicity if lindane is ingested from breast milk, or from skin absorption from mother to baby in the course of breast-feeding when Lindane Lotion is applied topically to the chest area. Nursing mothers who require treatment with Lindane Lotion should be advised of the potential risks and be counseled to avoid large areas of skin-to-skin contact with the infant while Lindane Lotion is applied, as well as to interrupt breast-feeding, with expression and discarding of milk, for at least 24 hours following use.
Pediatric Use
- Animal data demonstrated increased risk of adverse events in the young across species. Pediatric patients have a higher surface to volume ratio and may be at risk of greater systemic exposure when Lindane Lotion is applied to the body. Infants and children may be at an even higher risk due to immaturity of organ systems such as skin and liver. Lindane Lotion should be used with extreme caution in patients who weigh less than approximately 110 lbs (50 kg) and especially in infants. Lindane Lotion is indicated only for the treatment of scabies; patients with lice should use Lindane Shampoo according to the labeled instructions.
Geriatic Use
- There have been no studies of Lindane Lotion in the elderly. There are four postmarketing reports of deaths in elderly patients who were treated for scabies with Lindane Lotion. Two patients died within 24 hours of Lindane Lotion application, and the third patient died 41 days after application of Lindane Lotion, having suffered a seizure on the day of death. A fourth patient died of an unreported cause of death on the same day that Lindane Lotion treatment for scabies was administered.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lindane with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lindane with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lindane in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lindane in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
- Although no studies have been conducted with Lindane Lotion, numerous long-term feeding studies have been conducted in mice and rats to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of the technical grade of hexachlorocyclohexane as well as the alpha, beta, gamma (lindane) and delta isomers. Both oral and topical applications have been evaluated. Increased incidences of neoplasms were not clearly related to administration of lindane. The results of mutagenicity tests in bacteria do not indicate that lindane is mutagenic. Lindane did not cause sister chromatid exchange in an in vivo assay. The number of spermatids in the testes of rats 2 weeks after oral administration of a single dose of 30 mg/kg body weight (12 times the estimated human exposure for scabies on a body surface area comparison and assuming 50% rat oral bioavailability and 10% human bioavailability) was significantly reduced compared to the control rats.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Lindane in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Lindane Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Lindane Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Lindane and IV administrations.
Overdosage
Contact the closest Poison Control Center in the event of suspected overdosage with Lindane Lotion.
- If accidental ingestion occurs, prompt gastric lavage should be instituted. However, since oils enhance absorption, saline cathartics for intestinal evacuation should be given rather than oil laxatives. If central nervous system (CNS) manifestations occur, they may be antagonized by the administration of pentobarbital, phenobarbital, or diazepam.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Lindane Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
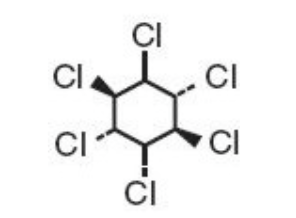
Structure
- Lindane is the gamma isomer of 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane having the following structural formula:
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Lindane Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- Lindane Lotion, USP 1%, is an ectoparasiticide and ovicide effective against Sarcoptes scabiei (scabies). Lindane exerts its parasiticidal action by being directly absorbed into the parasites and their ova. Feldmann and Maibach1 reported approximately 10% systemic absorption of a lindane acetone solution when applied to the forearm of human subjects and left in place for 24 hours. This vehicle was different from the approved product and the percutaneous penetration of lindane is dependent on the vehicle. Therefore, the clinical significance of these observations is unknown. Dale, et al2 reported a blood level of 290 ng/mL associated with convulsions following the accidental ingestion of a lindane-containing product. Ginsburg 3 found the greatest peak blood level of 64 ng/mL, 6 hours after total body application of Lindane Lotion in 1 of 8 non-scabietic pediatric patients. The half-life in blood was determined to be approximately 18 hours.
- Data available in the literature suggest that lindane has a rapid distribution phase followed by a longer β-elimination phase.1, 2, 3
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Lindane Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Lindane Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
- Lindane Lotion, USP 1% is supplied in patient-size 2 fl oz (60 mL) bottles.
Storage
- Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F)
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Lindane |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Lindane |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Lindane Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Lindane interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Lindane Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Report of the Conference of the Parties of the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants on the work of its fourth meeting. Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants. Fourth meeting, Geneva, 4–8 May 2009. http://chm.pops.int/Portals/0/Repository/COP4/UNEP-POPS-COP.4-38.English.pdf
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Lindane |Label Name=Lindane box.png
}}