Ketoconazole (gel)
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Adeel Jamil, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Ketoconazole (gel) is a antifungal agent that is FDA approved for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in immunocompetent adults. Common adverse reactions include application site burning, dermatitis, discharge, dryness, erythema, irritation, pain, pruritus, and pustule.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- XOLEGEL is indicated for the topical treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in immunocompetent adults and children 12 years of age and older.
- Safety and efficacy of XOLEGEL for treatment of fungal infections have not been established.
Dosing Information
- XOLEGEL is for topical use only, and not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
- XOLEGEL should be applied once daily to the affected area for 2 weeks.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ketoconazole (gel) in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Ketoconazole (gel) in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Ketoconazole (gel) FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ketoconazole (gel) in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Ketoconazole (gel) in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
There is limited information regarding Ketoconazole (gel) Contraindications in the drug label.
Warnings
Flammable Contents
- XOLEGEL is flammable. Avoid being near fire, flame, or smoking during and immediately following application of XOLEGEL.
Systemic Effects
- Hepatitis and, at high doses, lowered testosterone and ACTH induced corticosteroid serum levels have been seen with orally administered ketoconazole; these effects have not been seen with topically administered ketoconazole.
Local Effects
- XOLEGEL can cause local irritation at the application site. If irritation occurs or if the disease worsens, use of the medication should be discontinued and the health care provider should be contacted.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Clinical Trial Experiences=
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
- In the 3 safety and efficacy trials, 65 of 933 subjects (7%) experienced at least one treatment-related adverse event. The most common treatment-related adverse reaction was application site burning (4%). Treatment-related application site reactions that were reported in < 1% of subjects were: dermatitis, discharge, dryness, erythema, irritation, pain, pruritus, and pustules. Other treatment-related adverse reactions that were reported in < 1% of subjects were: eye irritation, eye swelling, keratoconjunctivitis sicca, impetigo, pyogenic granuloma, dizziness, headache, paresthesia, acne, nail discoloration, facial swelling.
Postmarketing Experience
- Adverse events identified during post approval use with XOLEGEL include burning sensation, pain, skin irritation, and erythema. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Drug Interactions
- Formal drug interaction studies with XOLEGEL have not been performed. Coadministration of oral ketoconazole with CYP3A4 metabolized HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors such as simvastatin, lovastatin and atorvastatin, may increase the risk of skeletal muscle toxicity, including rhabdomyolysis. These effects have not been observed with topically administered ketoconazole.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- There are no adequate and well controlled trials in pregnant women. XOLEGEL should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
- Reproductive toxicity studies have not been performed with XOLEGEL. Ketoconazole was tested for its effects on offspring in the rat at oral doses of 10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 mg/kg. Ketoconazole was teratogenic (syndactylia and oligodactylia) at 80 mg/kg/day and embryotoxic at 160 mg/kg/day (76 and 152 times the human dose, respectively). However, these effects may be related to maternal toxicity, which was also seen at these dose levels.
- Oral doses of 10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 mg/kg were studied in pre- and postnatal development studies in rats. Doses of 40 mg/kg (38 times the human dose) and above were associated with maternal toxicity, an increase in the length of gestation, and an increase in the number of stillborn fetuses. These doses of ketoconazole were also toxic to the offspring, resulting in a decrease in fetal/pup weights and viability.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Ketoconazole (gel) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Ketoconazole (gel) during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether XOLEGEL is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when XOLEGEL is administered to a nursing woman.
- If used during lactation and XOLEGEL is applied to the chest, care should be taken to avoid accidental ingestion by the infant.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ketoconazole (gel) in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
- Of the 933 subjects in the three safety and efficacy trials, 193 (20.7%) were 65 and older, while 61 (6.5%) were 75 and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ketoconazole (gel) with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ketoconazole (gel) with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ketoconazole (gel) in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ketoconazole (gel) in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ketoconazole (gel) in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Ketoconazole (gel) in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Topical
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Ketoconazole (gel) Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Ketoconazole (gel) and IV administrations.
Overdosage
- XOLEGEL is intended for topical use only.
- There has been no experience of overdose with XOLEGEL. No incidents of accidental ingestion have been reported. A health care provider or poison control center should be contacted in the event of accidental ingestion.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Ketoconazole (gel) Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- The mechanism of action of ketoconazole in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis is unknown.
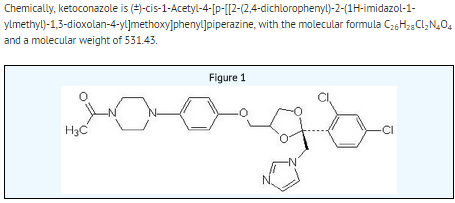
Structure
- XOLEGEL contains the antifungal agent ketoconazole USP at 2% in a topical anhydrous gel vehicle for topical administration.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Ketoconazole (gel) Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- In a pharmacokinetic absorption trial, eighteen subjects, both males and females
- The plasma levels from an oral dose of 200 mg ketoconazole taken with a meal are approximately 250 times higher than the resulting plasma levels of ketoconazole following topical application of XOLEGEL.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- The carcinogenic potential of ketoconazole gel has been evaluated in a 2-year dermal carcinogenicity study in CD-1 mice. Ketoconazole gel applied topically at doses up to 80 mg ketoconazole/kg/day (76 times the human dose) exhibited no evidence of dermal or systemic tumorigenic effects attributable to ketoconazole or the gel vehicle. A long-term feeding study in Swiss Albino mice and in Wistar rats showed no evidence of oncogenic activity. Ketoconazole gel at a dosage up to 5 mg/kg/dose is not photocarcinogenic when topically applied to hairless mice five days per week for a period of 40 weeks. Ketoconazole produced no evidence of mutagenicity in the dominant lethal mutation test in male and female mice at single oral doses up to 80 mg/kg. When tested in the Ames assay, ketoconazole was found to be non-mutagenic to Salmonella typhimurium in the presence and absence of metabolic activation. Ketoconazole, in combination with another drug, gave equivocal results in the mouse micronucleus test. At oral doses of 75 to 80 mg/kg/day (71 to 76 times the human dose) ketoconazole impaired the reproductive performance in female (decreased pregnancy and implantation rates) and male (increased abnormal sperm and decreased sperm motility) rats.
Clinical Studies
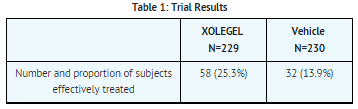
- Study 1 was a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, vehicle-controlled trial which enrolled 459 subjects 12 years of age and older with moderate to severe seborrheic dermatitis. A total of 229 subjects were treated with XOLEGEL, and 230 subjects were treated with vehicle. All subjects were treated once daily for 14 days, and efficacy was assessed at Day 28 (i.e., 2 weeks after end of treatment). Effective Treatment was defined as:
- an Investigator's Global Assessment score of ≤ 1 (completely clear or almost clear) and
erythema and scaling scores of 0 (none) if the baseline score was 2, or 1 (mild) if the baseline score was 3.
- The proportion of subjects effectively treated is shown in Table 1.
- Two additional double-blind, randomized, vehicle-controlled, parallel, and multicenter trials that included a total of 316 subjects treated with XOLEGEL provided supportive evidence of the efficacy of XOLEGEL for treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. Subjects applied either XOLEGEL or vehicle study treatment to the affected area(s) once daily for 14 days and were followed through Day 28. Efficacy was assessed by the proportion of subjects who were completely clear at Day 28.
- The contribution to efficacy of individual components of the vehicle has not been established.
How Supplied
XOLEGEL® (ketoconazole) Gel, 2% is supplied in 45-gram (NDC 16110-080-45) white-coated aluminum tubes with white caps, and is dispensed with FDA-Approved Patient Labeling.
Storage
- Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° - 30°C (59° - 86°F).
- Contents are flammable.
- Keep out of reach of children.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Ketoconazole (gel) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 45 g Carton
NDC 16110-080-45
Xolegel® (ketoconazole) Gel, 2%
AQUA PHARMACEUTICALS
45 grams Rx only. For topical use only.
{{#ask: Label Page::Ketoconazole (gel) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- This medication is to be used as directed by the health care provider. It is for external use only.
- XOLEGEL may be irritating to mucus membranes. Contact with the eyes, nostrils, and mouth should be avoided.
- As with any topical medication, patients should wash their hands after application.
- This medication should not be used for any disorder other than that for which it has been prescribed.
- Patients should report any signs of adverse reactions to their health care provider.



Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Ketoconazole (gel) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Ketoconazole (gel) Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Ketoconazole (gel) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.