Isepamicin: Difference between revisions
Gerald Chi (talk | contribs) m (→Brand Names) |
Gerald Chi (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} | ||
{{SK}} Isepamycin | {{SK}} Isepamycin | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
==Brand Names== | ==Brand Names== | ||
EXACIN<sup>®</sup>, ISEPACIN<sup>®</sup>, ISEPACINE<sup>®</sup>, ISEPALLINE<sup>®</sup> | EXACIN<sup>®</sup>, ISEPACIN<sup>®</sup>, ISEPACINE<sup>®</sup>, ISEPALLINE<sup>®</sup> (not currently available in the U.S.) | ||
==Prescribing Information== | ==Prescribing Information== | ||
====Clinical Pharmacology==== | |||
General pharmacological properties of isepamicin sulfate (HAPA-B), a new aminoglycoside antibiotic, were studied in animals and the results obtained were summarized below. Intramuscular injections of HAPA-B at doses of 500 mg/kg inhibited the writing response induced by acetic acid, and at doses of 1,000 mg/kg, caused muscle relaxation, respiratory depression, suppression of spontaneous motor activity and prolongation of thiopental anesthesia. Anticonvulsive action and the effect on the rectal temperature were not observed. Intravenous Intravenous HAPA-B showed no significant effect on the general behavior and the function of the central nervous system at doses of 100 mg/kg. Intravenous injections of HAPA-B to anesthetized dogs resulted increases in the femoral arterial blood flow at doses of 12.5 mg/kg, decrease in the blood pressure and increase in the respiratory rate at doses of 25 mg/kg, and increase in the carotid arterial blood flow at doses of 50 mg/kg. Apparent changes were not recognized in the heart rate and electrocardiograms. In conscious rabbits, intravenous HAPA-B produced increases in the heart rate without significant changes of the blood pressure and electrocardiograms at doses of 100 mg/kg. Spontaneous beatings of isolated atria were depressed by HAPA-B in concentrations of 3 X 10(-4) to 10(-3) g/ml. The HAPA-B inhibited the gastric secretion at intramuscular doses of 500 mg/kg or intravenous doses of 100 mg/kg, and depressed charcoal transport through small intestine and the spontaneous movement of isolated ileum at intramuscular doses of 1,000 mg/kg and at concentrations of 3 X 10(-4) to 10(-3) g/ml, respectively. No irritative effect was found on the gastric mucous membrane. Intravenous HAPA-B inhibited the response of nictitating membrane to pre and post ganglionic stimulations of cervical sympathetic nerve at doses of 100 mg/kg. In in vitro test, HAPA-B inhibited nonspecifically the constrictive responses of trachea, aorta, stomach, ileum and vas deferens to various agonists in concentrations of 3 X 10(-4) to 10(-3) g/ml. Spontaneous movements of uteri of estrous or pregnant animals were depressed by HAPA-B at intravenous doses of 50 to 100 mg/kg and in in vitro at concentrations of 10(-4) to 3 X 10(-4) g/ml. Antidiuretic effect was also observed at intramuscular doses of 250 mg/kg. HAPA-B increased the length of the whole blood clotting time and raised the plasma glucose level at intramuscular doses of 1,000 mg/kg and inhibited the platelet aggregation induced by ADP in vitro at concentrations of 10(-3) g/ml. | |||
====Chemical Structure==== | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Isepamycin01.jpg|400px|thumb]] | |||
|} | |||
Molecular Formula: C22H45N5O16S | |||
''' | |||
====Reported Use==== | |||
Treatment of susceptible bacterial infections | |||
====Dosage==== | |||
* '''Adults''': I.M., I.V.: 8-15 mg/kg daily in 2 divided doses; maximum: 1.5 g/day | |||
====Dosage Forms==== | |||
Injection, solution: 250 mg/mL (1 mL, 2 mL) | |||
==Mechanism of Action== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
Revision as of 15:16, 6 January 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Synonyms and keywords: Isepamycin
Overview
Isepamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic.
Category
Aminoglycoside
Brand Names
EXACIN®, ISEPACIN®, ISEPACINE®, ISEPALLINE® (not currently available in the U.S.)
Prescribing Information
Clinical Pharmacology
General pharmacological properties of isepamicin sulfate (HAPA-B), a new aminoglycoside antibiotic, were studied in animals and the results obtained were summarized below. Intramuscular injections of HAPA-B at doses of 500 mg/kg inhibited the writing response induced by acetic acid, and at doses of 1,000 mg/kg, caused muscle relaxation, respiratory depression, suppression of spontaneous motor activity and prolongation of thiopental anesthesia. Anticonvulsive action and the effect on the rectal temperature were not observed. Intravenous Intravenous HAPA-B showed no significant effect on the general behavior and the function of the central nervous system at doses of 100 mg/kg. Intravenous injections of HAPA-B to anesthetized dogs resulted increases in the femoral arterial blood flow at doses of 12.5 mg/kg, decrease in the blood pressure and increase in the respiratory rate at doses of 25 mg/kg, and increase in the carotid arterial blood flow at doses of 50 mg/kg. Apparent changes were not recognized in the heart rate and electrocardiograms. In conscious rabbits, intravenous HAPA-B produced increases in the heart rate without significant changes of the blood pressure and electrocardiograms at doses of 100 mg/kg. Spontaneous beatings of isolated atria were depressed by HAPA-B in concentrations of 3 X 10(-4) to 10(-3) g/ml. The HAPA-B inhibited the gastric secretion at intramuscular doses of 500 mg/kg or intravenous doses of 100 mg/kg, and depressed charcoal transport through small intestine and the spontaneous movement of isolated ileum at intramuscular doses of 1,000 mg/kg and at concentrations of 3 X 10(-4) to 10(-3) g/ml, respectively. No irritative effect was found on the gastric mucous membrane. Intravenous HAPA-B inhibited the response of nictitating membrane to pre and post ganglionic stimulations of cervical sympathetic nerve at doses of 100 mg/kg. In in vitro test, HAPA-B inhibited nonspecifically the constrictive responses of trachea, aorta, stomach, ileum and vas deferens to various agonists in concentrations of 3 X 10(-4) to 10(-3) g/ml. Spontaneous movements of uteri of estrous or pregnant animals were depressed by HAPA-B at intravenous doses of 50 to 100 mg/kg and in in vitro at concentrations of 10(-4) to 3 X 10(-4) g/ml. Antidiuretic effect was also observed at intramuscular doses of 250 mg/kg. HAPA-B increased the length of the whole blood clotting time and raised the plasma glucose level at intramuscular doses of 1,000 mg/kg and inhibited the platelet aggregation induced by ADP in vitro at concentrations of 10(-3) g/ml.
Chemical Structure
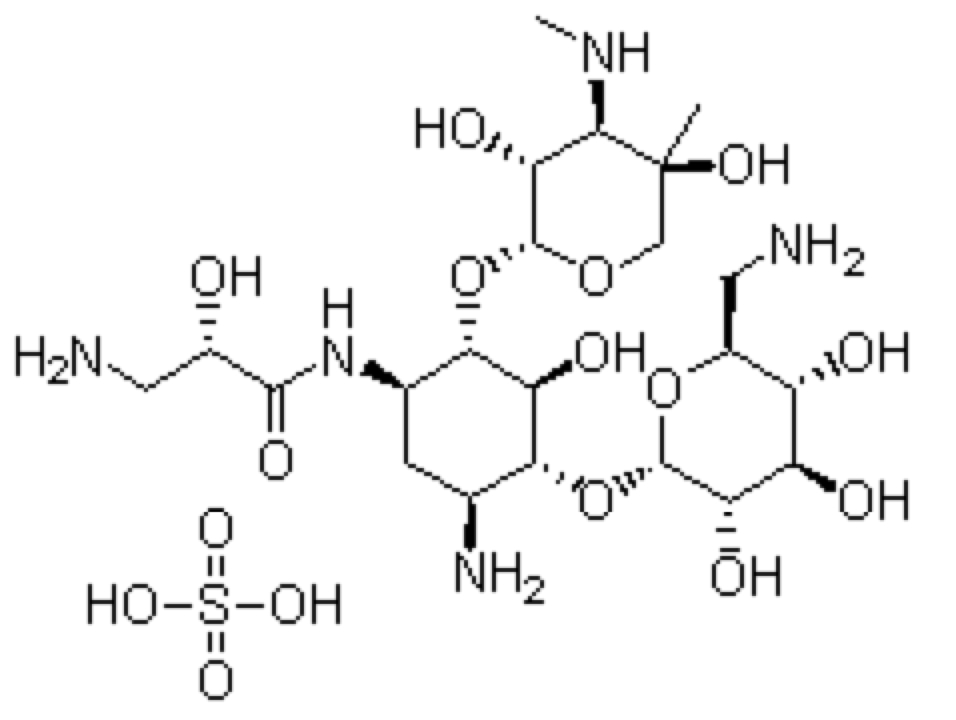 |
Molecular Formula: C22H45N5O16S
Reported Use
Treatment of susceptible bacterial infections
Dosage
- Adults: I.M., I.V.: 8-15 mg/kg daily in 2 divided doses; maximum: 1.5 g/day
Dosage Forms
Injection, solution: 250 mg/mL (1 mL, 2 mL)