Inotuzumab ozogamicin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 223: | Line 223: | ||
|othersTitle=Others | |othersTitle=Others | ||
|useInOthers=(Description) | |useInOthers=(Description) | ||
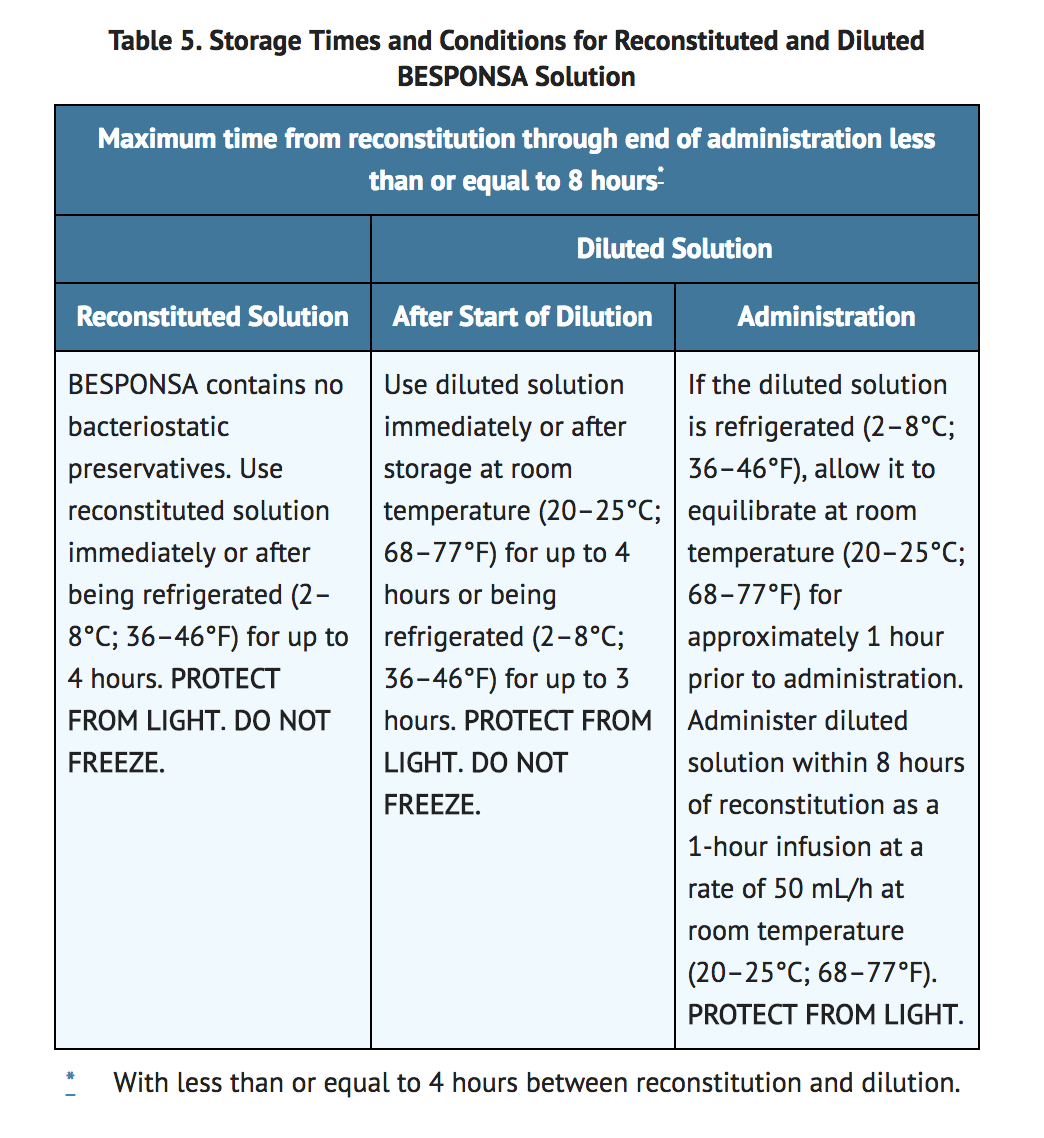
|administration=( | |administration=*See TABLE 5 for storage times and conditions for prior to and during administration of the diluted solution. | ||
*Filtration of the diluted solution is not required. However, if the diluted solution is filtered, polyethersulfone (PES)-, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)-,or hydrophilic polysulfone (HPS)-based filters are recommended. Do not use filters made of nylon or mixed cellulose ester (MCE). | |||
*Infuse the diluted solution for 1 hour at a rate of 50 mL/h at room temperature (20–25°C; 68–77°F). Infusion lines made of PVC (DEHP- or non-DEHP-containing), polyolefin (polypropylene and/or polyethylene), or polybutadiene are recommended. | |||
=====Do not mix BESPONSA or administer as an infusion with other medicinal products.===== | |||
*Table 5 shows the storage times and conditions for reconstitution, dilution, and administration of BESPONSA. | |||
[[image:Inotuzumab_Ozogamicin_Administration_Table.png|none|thumb|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
|monitoring======Condition 1===== | |monitoring======Condition 1===== | ||
| Line 236: | Line 247: | ||
(Description regarding monitoring, from ''Warnings'' section) | (Description regarding monitoring, from ''Warnings'' section) | ||
|overdose | |overdose= | ||
|drugBox= | |drugBox= | ||
Revision as of 13:37, 18 July 2018
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Yashasvi Aryaputra[2];
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
HEPATOTOXICITY, INCLUDING HEPATIC VENO-OCCLUSIVE DISEASE (VOD) (ALSO KNOWN AS SINUSOIDAL OBSTRUCTION SYNDROME AND INCREASED RISK OF POST-HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANT (HSCT) NON-RELAPSE MORTALITY
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
HEPATOTOXICITY, INCLUDING VOD:
INCREASED RISK OF POST-HSCT NON-RELAPSE MORTALITY:
|
Overview
Inotuzumab ozogamicin is a Acetylcholine release inhibitor, Adrenergic receptor agonist that is FDA approved for the (type of indication of drug) of a list of indications, separated by commas.. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include a list of adverse reactions, separated by commas..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Contraindications
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Warnings
|
HEPATOTOXICITY, INCLUDING HEPATIC VENO-OCCLUSIVE DISEASE (VOD) (ALSO KNOWN AS SINUSOIDAL OBSTRUCTION SYNDROME AND INCREASED RISK OF POST-HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANT (HSCT) NON-RELAPSE MORTALITY
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
HEPATOTOXICITY, INCLUDING VOD:
INCREASED RISK OF POST-HSCT NON-RELAPSE MORTALITY:
|
Conidition 1
(Description)
Conidition 2
(Description)
Conidition 3
(Description)
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Condition 2
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Postmarketing Experience
(Description)
Drug Interactions
- Drug 1
- Drug 2
- Drug 3
- Drug 4
- Drug 5
Drug 1
(Description)
Drug 2
(Description)
Drug 3
(Description)
Drug 4
(Description)
Drug 5
(Description)
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
(Description)
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Inotuzumab ozogamicin in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
(Description)
Nursing Mothers
(Description)g
Pediatric Use
(Description)
Geriatic Use
(Description)
Gender
(Description)
Race
(Description)
Renal Impairment
(Description)
Hepatic Impairment
(Description)
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
(Description)
Immunocompromised Patients
(Description)
Others
(Description)
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- See TABLE 5 for storage times and conditions for prior to and during administration of the diluted solution.
- Filtration of the diluted solution is not required. However, if the diluted solution is filtered, polyethersulfone (PES)-, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)-,or hydrophilic polysulfone (HPS)-based filters are recommended. Do not use filters made of nylon or mixed cellulose ester (MCE).
- Infuse the diluted solution for 1 hour at a rate of 50 mL/h at room temperature (20–25°C; 68–77°F). Infusion lines made of PVC (DEHP- or non-DEHP-containing), polyolefin (polypropylene and/or polyethylene), or polybutadiene are recommended.
Do not mix BESPONSA or administer as an infusion with other medicinal products.
- Table 5 shows the storage times and conditions for reconstitution, dilution, and administration of BESPONSA.
Monitoring
Condition 1
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 2
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 3
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Inotuzumab ozogamicin and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Inotuzumab ozogamicin overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
Inotuzumab ozogamicin?
| |
| Therapeutic monoclonal antibody | |
| Source | zu/o |
| Target | CD22 |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | L01 |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 150,000 g/mol |
| Synonyms | CMC-544 |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Protein binding | 97% (cytotoxic agent) |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | 12.3 days |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status |
[[Prescription drug|Template:Unicode-only]](US) |
| Routes | Intravenous infusion |
Mechanism of Action
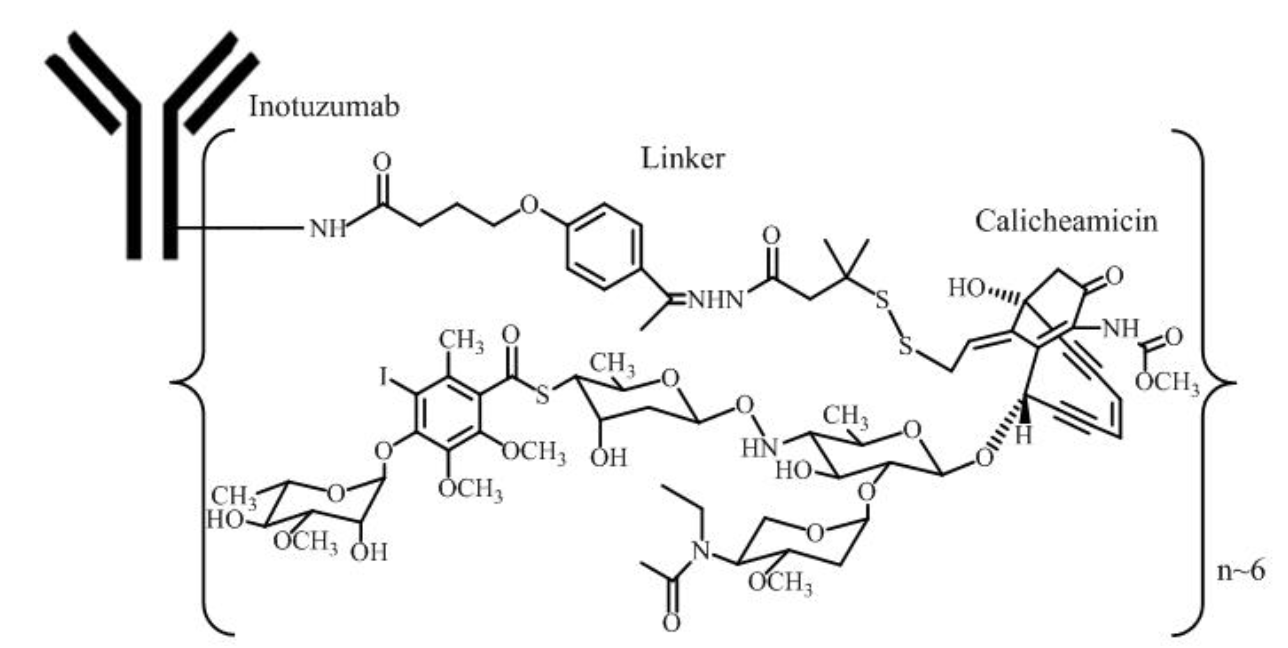
- Inotuzumab ozogamicin is a CD22-directed antibody-drug conjugate (ADC). Inotuzumab recognizes human CD22. The small molecule, N-acetyl-gamma-calicheamicin, is a cytotoxic agent that is covalently attached to the antibody via a linker. Nonclinical data suggest that the anticancer activity of inotuzumab ozogamicin is due to the binding of the ADC to CD22-expressing tumor cells, followed by internalization of the ADC-CD22 complex, and the intracellular release of N-acetyl-gamma-calicheamicin dimethylhydrazide via hydrolytic cleavage of the linker. Activation of N-acetyl-gamma-calicheamicin dimethylhydrazide induces double-strand DNA breaks, subsequently inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death.
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
- During the treatment period, the pharmacodynamic response to BESPONSA was characterized by the depletion of CD22-positive leukemic blasts.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
- In a randomized clinical study in patients with relapsed or refractory ALL, increases in QTcF of ≥ 60 msec from baseline were measured in 4/162 patients (3%) in the BESPONSA arm and 3/124 patients (2%) in the Investigator's choice of chemotherapy arm. Increases in QTcF of > 500 msec were observed in none of the patients in the BESPONSA arm and 1/124 patients (1%) in the Investigator's choice of chemotherapy arm. Central tendency analysis of the QTcF interval changes from baseline showed that the highest mean (upper bound of the 2-sided 90% CI) for QTcF was 15.3 (21.1) msec, which was observed at Cycle 4/Day 1/1 hour in the BESPONSA arm.
Pharmacokinetics
- The mean Cmax of inotuzumab ozogamicin was 308 ng/mL. The mean simulated total AUC per cycle was 100,000 ng∙h/mL. In patients with relapsed or refractory ALL, steady-state drug concentration was achieved by Cycle 4. Following administration of multiple doses, a 5.3 times accumulation of inotuzumab ozogamicin was predicted by Cycle 4.
Distribution
- N-acetyl-gamma-calicheamicin dimethylhydrazide is approximately 97% bound to human plasma proteins in vitro. In humans, the total volume of distribution of inotuzumab ozogamicin was approximately 12 L.
Elimination
- The pharmacokinetics of inotuzumab ozogamicin was well characterized by a 2-compartment model with linear and time-dependent clearance components. In 234 patients with relapsed or refractory ALL, the clearance of inotuzumab ozogamicin at steady state was 0.0333 L/h and the terminal half-life (t½) was 12.3 days. Following administration of multiple doses, a 5.3 times accumulation of inotuzumab ozogamicin was predicted by Cycle 4.
Metabolism
- In vitro, N-acetyl-gamma-calicheamicin dimethylhydrazide was primarily metabolized via nonenzymatic reduction. In humans, N-acetyl-gamma-calicheamicin dimethylhydrazide serum levels were typically below the limit of quantitation.
Specific Populations
- The effect of intrinsic factors on inotuzumab ozogamicin pharmacokinetics was assessed using a population pharmacokinetic analysis unless otherwise specified. Age (18 to 92 years of age), sex, and race (Asian versus non-Asian [Caucasian, Black, and Unspecified]) had no clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of inotuzumab ozogamicin. Body surface area was found to significantly affect inotuzumab ozogamicin disposition. BESPONSA is dosed based on body surface area.
Patients with Renal Impairment
- The clearance of inotuzumab ozogamicin in patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr; based on the Cockcroft-Gault formula] 60–89 mL/min; n=237), moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30–59 mL/min; n=122), or severe renal impairment (CLcr 15–29 mL/min; n=4) was similar to patients with normal renal function (CLcr ≥90 mL/min; n=402). The safety and efficacy of inotuzumab ozogamicin in patients with end stage renal disease with or without hemodialysis is unknown.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
- The clearance of inotuzumab ozogamicin in patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ULN and AST > ULN, or total bilirubin >1.0–1.5 × ULN and AST any level; n=150) was similar to patients with normal hepatic function (total bilirubin/AST ≤ULN; n=611). There is insufficient data in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >1.5 ULN).
Drug Interactions
- In vitro
- Effect of Metabolic Pathways and Transporter Systems on BESPONSA
- N-acetyl-gamma-calicheamicin dimethylhydrazide is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp).
- At clinically relevant concentrations, N-acetyl-gamma-calicheamicin dimethylhydrazide had a low potential to:
- Inhibit cytochrome P450 (CYP 450) Enzymes: CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4/5.
- Induce CYP450 Enzymes: CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4.
- Inhibit UGT Enzymes: UGT1A1, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, and UGT2B7.
- Inhibit Drug Transporters: P-gp, breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), organic anion transporter (OAT)1 and OAT3, organic cation transporter (OCT)2, and organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP)1B1 and OATP1B3.
- At clinically relevant concentrations, inotuzumab ozogamicin had a low potential to:
- Inhibit CYP450 Enzymes: CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4/5.
- Induce CYP450 Enzymes: CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Formal carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with inotuzumab ozogamicin. In toxicity studies, rats were dosed weekly for 4 or 26 weeks with inotuzumab ozogamicin at doses up to 4.1 mg/m2 and 0.73 mg/m2, respectively. After 26 weeks of dosing, rats developed hepatocellular adenomas in the liver at 0.73 mg/m2 (approximately 2 times the exposure in patients at the maximum recommended dose, based on AUC).
- Inotuzumab ozogamicin was clastogenic in vivo in the bone marrow of male mice that received single doses ≥1.1 mg/m2. This is consistent with the known induction of DNA breaks by calicheamicin. N-acetyl-gamma-calicheamicin dimethylhydrazide (the cytotoxic agent released from inotuzumab ozogamicin) was mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay.
- In a female fertility and early embryonic development study, female rats were administered daily intravenous doses of inotuzumab ozogamicin up to 0.11 mg/m2 for 2 weeks before mating through Day 7 of pregnancy. An increase in the proportion of resorptions and decrease in the number of viable embryos and gravid uterine weights were observed at the 0.11 mg/m2 dose level (approximately 2 times the exposure in patients at the maximum recommended dose, based on AUC). Additional findings in female reproductive organs occurred in repeat-dose toxicology studies and included decreased ovarian and uterine weights, and ovarian and uterine atrophy. Findings in male reproductive organs occurred in repeat-dose toxicology studies and included decreased testicular weights, testicular degeneration, hypospermia, and prostatic and seminal vesicle atrophy. Testicular degeneration and hypospermia were nonreversible following a 4-week nondosing period. In the chronic studies of 26-weeks duration, adverse effects on reproductive organs occurred at ≥0.07 mg/m2 in male rats and at 0.73 mg/m2 in female monkeys.
Clinical Studies
Patients With Relapsed or Refractory ALL – INO-VATE ALL
- The safety and efficacy of BESPONSA were evaluated in INO-VATE ALL (NCT01564784) a randomized (1:1), open-label, international, multicenter study in patients with relapsed or refractory ALL. Patients were stratified at randomization based on duration of first remission (< 12 months or ≥ 12 months, salvage treatment (Salvage 1 or 2) and patient age at randomization (< 55 or ≥ 55 years). Eligible patients were ≥ 18 years of age with Philadelphia chromosome-negative or Philadelphia chromosome-positive relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor ALL. All patients were required to have ≥ 5% bone marrow blasts and to have received 1 or 2 previous induction chemotherapy regimens for ALL. Patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive B-cell precursor ALL were required to have disease that failed treatment with at least 1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor and standard chemotherapy. Table 1 shows the dosing regimen used to treat patients.
- Among all 326 patients who were randomized to receive BESPONSA (N=164) or Investigator's choice of chemotherapy (N=162), 215 patients (66%) had received 1 prior treatment regimen for ALL and 108 patients (33%) had received 2 prior treatment regimens for ALL. The median age was 47 years (range: 18–79 years), 276 patients (85%) had Philadelphia chromosome-negative ALL, 206 patients (63%) had a duration of first remission < 12 months, and 55 patients (17%) had undergone a HSCT prior to receiving BESPONSA or Investigator's choice of chemotherapy. The two treatment groups were generally balanced with respect to the baseline demographics and disease characteristics.
- All evaluable patients had B-cell precursor ALL that expressed CD22, with ≥ 90% of evaluable patients exhibiting ≥ 70% leukemic blast CD22 positivity prior to treatment, as assessed by flow cytometry performed at a central laboratory.
- The efficacy of BESPONSA was established on the basis of CR, the duration of CR, and proportion of MRD-negative CR (< 1 × 10-4 of bone marrow nucleated cells by flow cytometry) in the first 218 patients randomized. CR, duration of remission (DoR), and MRD results in the initial 218 randomized patients were consistent with those seen in all 326 randomized patients.
- Among the initial 218 randomized patients, 64/88 (73%) and 21/88 (24%) of responding patients per EAC achieved CR/CRi in Cycles 1 and 2, respectively, in the BESPONSA arm, and 29/32 (91%) and 1/32 (3%) of responding patients per EAC achieved a CR/CRi in Cycles 1 and 2, respectively, in the Investigator's choice of chemotherapy arm.
- Table 8 shows the efficacy results from this study.
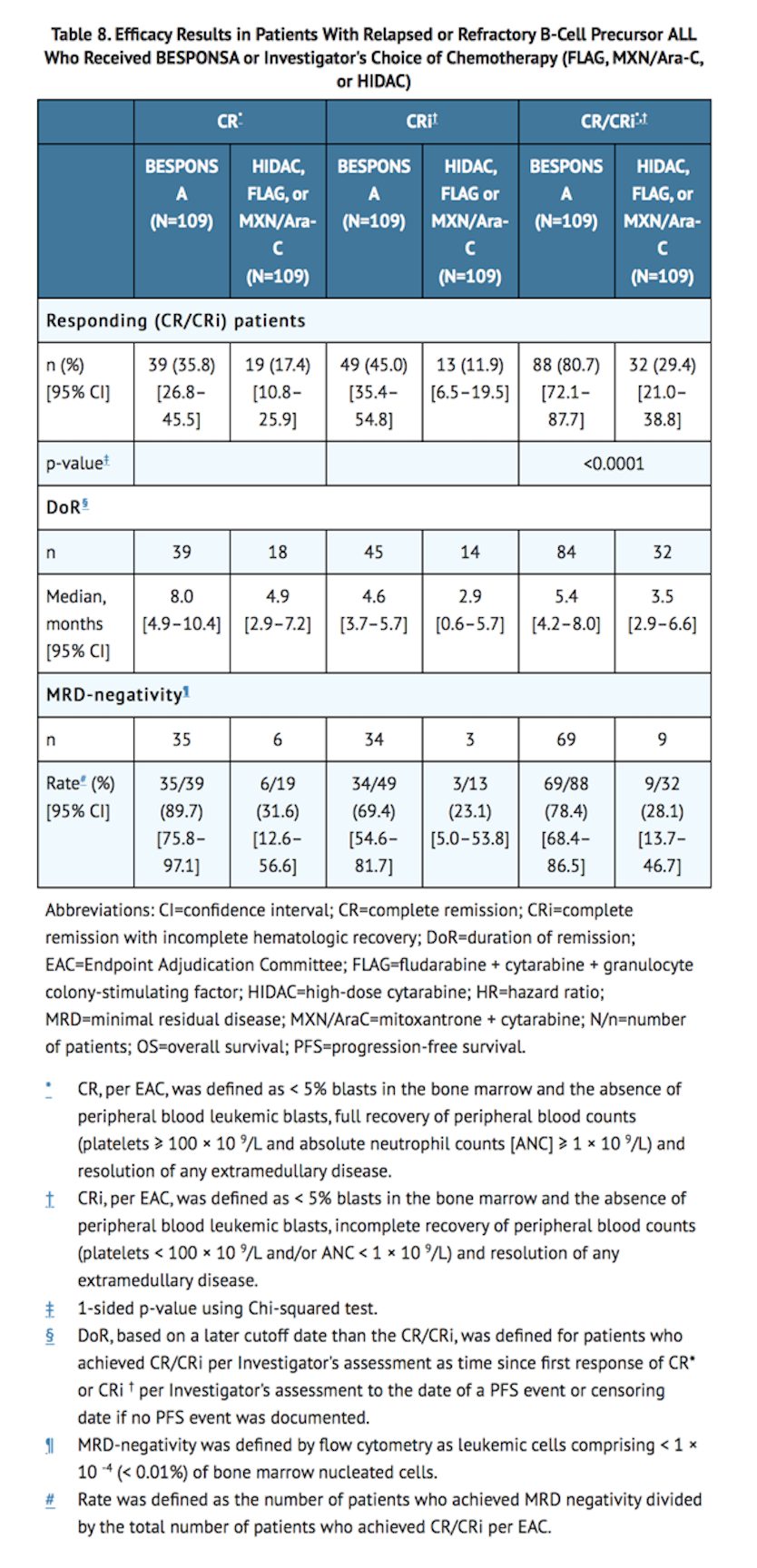
- Among the initial 218 patients, as per EAC assessment, 32/109 patients (29%) in the BESPONSA arm achieved complete remission with partial hematologic recovery (CRh; defined as <5% blasts in the bone marrow, ANC > 0.5 × 109/L, and platelet counts > 50 × 109/L but not meeting full recovery of peripheral blood counts) versus 6/109 patients (6%) in the Investigator's choice of chemotherapy arm, and 71/109 patients (65%) in the BESPONSA arm achieved CR/CRh versus 25/109 patients (23%) in the Investigator's choice of chemotherapy arm.
- Overall, 79/164 patients (48%) in the BESPONSA arm and 35/162 patients (22%) in the Investigator's choice of chemotherapy arm had a follow-up HSCT.
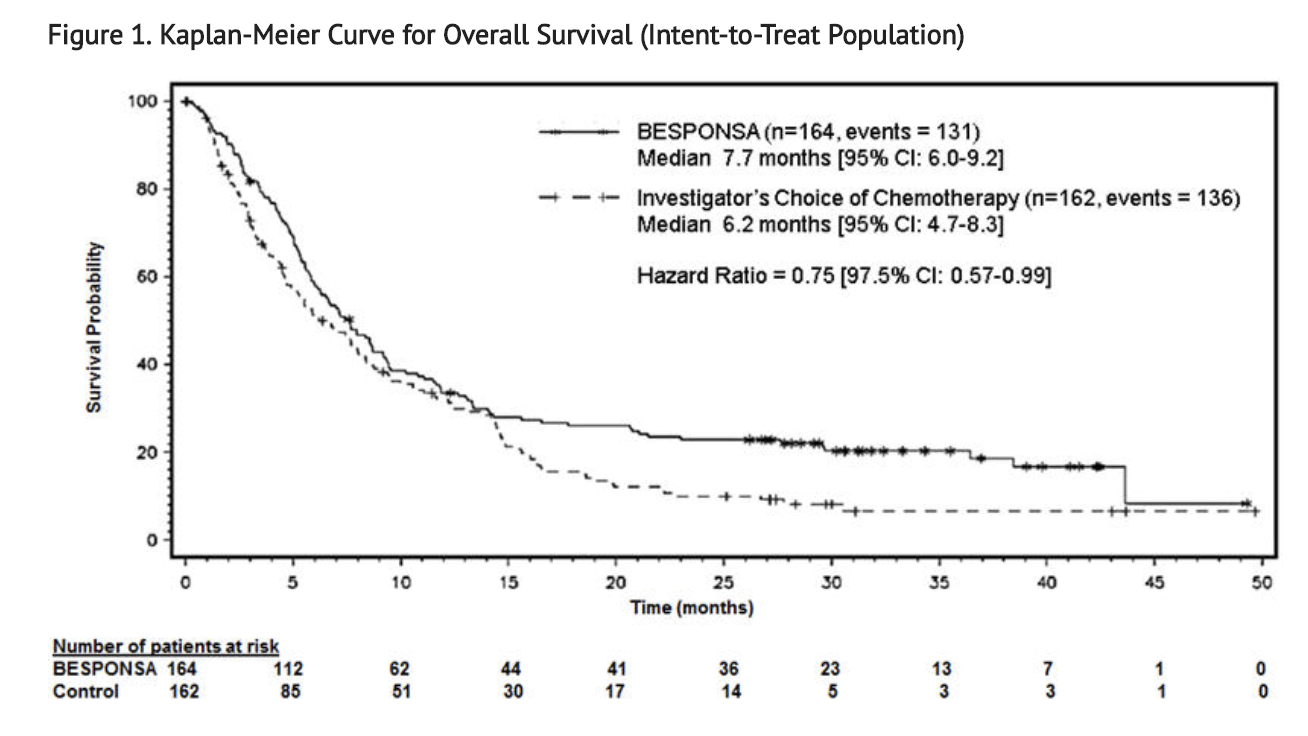
- Figure 1 shows the analysis of overall survival (OS). The analysis of OS did not meet the pre-specified boundary for statistical significance.
How Supplied
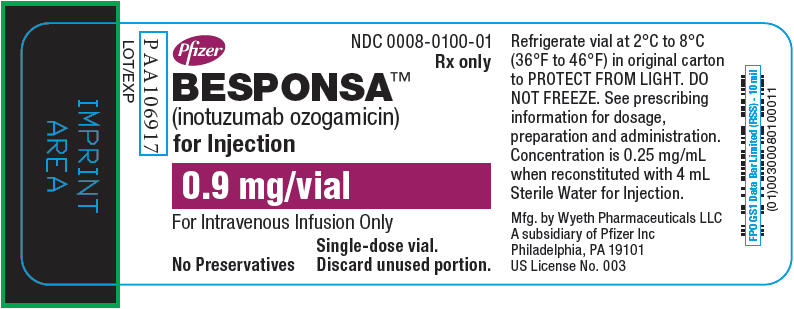
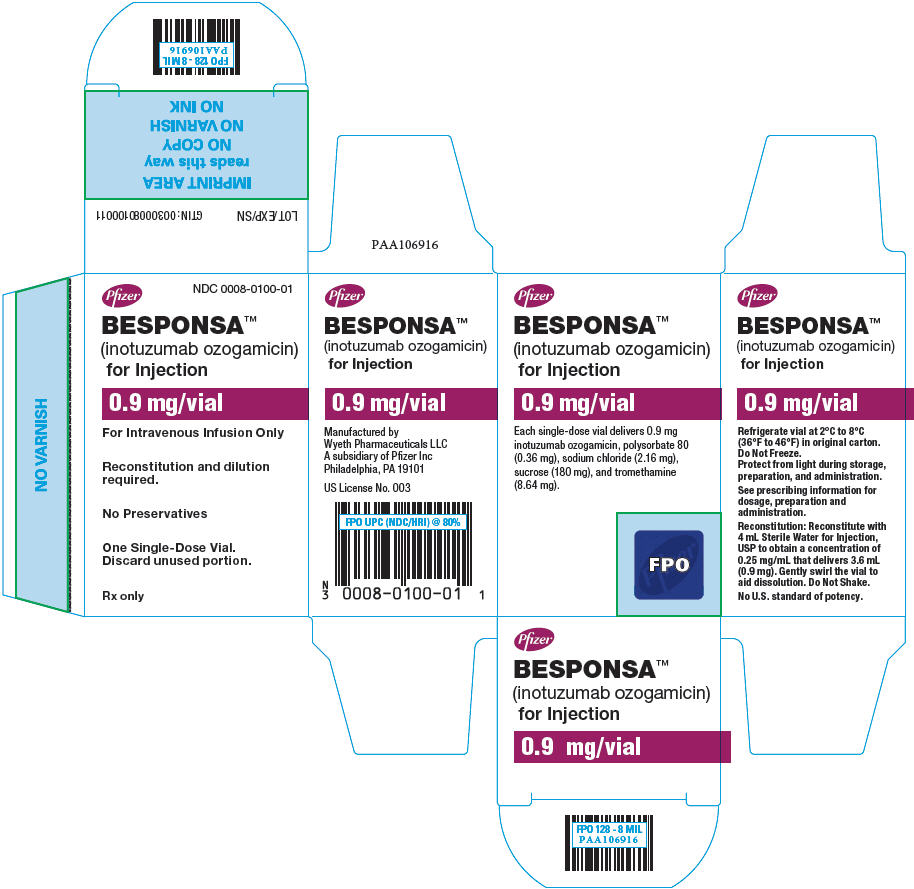
- BESPONSA (inotuzumab ozogamicin) for Injection is supplied as a white to off-white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution and further dilution. Each vial delivers 0.9 mg inotuzumab ozogamicin. Each carton (NDC 0008-0100-01) contains one single-dose vial.
Storage
- Refrigerate (2–8°C; 36–46°F) BESPONSA vials and store in the original carton to protect from light. Do not freeze.
- BESPONSA is a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Inotuzumab ozogamicin |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Inotuzumab ozogamicin |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Hepatotoxicity, Including Hepatic Veno-occlusive Disease (VOD) (also known as Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome)
- Inform patients that liver problems, including severe, life-threatening, or fatal VOD, and increases in liver tests may develop during BESPONSA treatment. Inform patients that they should seek immediate medical advice if they experience symptoms of VOD, which may include elevated bilirubin, rapid weight gain, and abdominal swelling that may be painful. Inform patients that they should carefully consider the benefit/risk of BESPONSA treatment if they have a prior history of VOD or serious ongoing liver disease.
Increased Risk of Post-HSCT Non-Relapse Mortality
- Inform patients that there is an increased risk of post-HSCT non-relapse mortality after receiving BESPONSA, that the most common causes of post-HSCT non-relapse mortality included infection and VOD. Advise patients to report signs and symptoms of infection.
Myelosuppression
- Inform patients that decreased blood counts, which may be life-threatening, may develop during BESPONSA treatment and that complications associated with decreased blood counts may include infections, which may be life-threatening or fatal, and bleeding/hemorrhage events. Inform patients that signs and symptoms of infection, bleeding/hemorrhage, or other effects of decreased blood counts should be reported during treatment with BESPONSA.
Infusion Related Reactions
- Advise patients to contact their health care provider if they experience symptoms such as fever, chills, rash, or breathing problems during the infusion of BESPONSA.
QT Interval Prolongation
- Inform patients of symptoms that may be indicative of significant QTc prolongation including dizziness, lightheadedness, and syncope. Advise patients to report these symptoms and the use of all medications to their healthcare provider.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Advise males and females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during BESPONSA treatment and for at least 5 and 8 months after the last dose, respectively. Advise females of reproductive potential to avoid becoming pregnant while receiving BESPONSA. Advise women to contact their healthcare provider if they become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected, during treatment with BESPONSA. Inform the patient of the potential risk to the fetus.
Lactation
- Advise women against breastfeeding while receiving BESPONSA and for 2 months after the last dose.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Inotuzumab ozogamicin interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Besponsa
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Inotuzumab ozogamicin Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.