Inferior thyroid veins
| Cardiology Network |
 Discuss Inferior thyroid veins further in the WikiDoc Cardiology Network |
| Adult Congenital |
|---|
| Biomarkers |
| Cardiac Rehabilitation |
| Congestive Heart Failure |
| CT Angiography |
| Echocardiography |
| Electrophysiology |
| Cardiology General |
| Genetics |
| Health Economics |
| Hypertension |
| Interventional Cardiology |
| MRI |
| Nuclear Cardiology |
| Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| Prevention |
| Public Policy |
| Pulmonary Embolism |
| Stable Angina |
| Valvular Heart Disease |
| Vascular Medicine |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
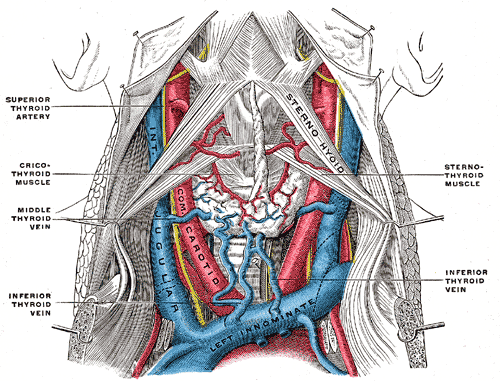
The inferior thyroid veins two, frequently three or four, in number, arise in the venous plexus on the thyroid gland, communicating with the middle and superior thyroid veins.
They form a plexus in front of the trachea, behind the Sternothyreoidei.
From this plexus, a left vein descends and joins the left innominate trunk, and a right vein passes obliquely downward and to the right across the innominate artery to open into the right innominate vein, just at its junction with the superior vena cava; sometimes the right and left veins open by a common trunk in the latter situation.
These veins receive esophageal tracheal, and inferior laryngeal veins, and are provided with valves at their terminations in the innominate veins.
Additional images
-
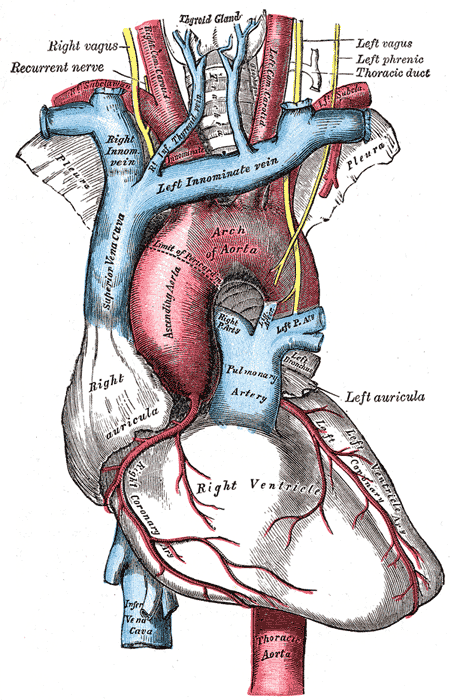
The arch of the aorta, and its branches.
-
The fascia and middle thyroid veins.
-
The thymus of a full-time fetus, exposed in situ.