Hypereosinophilic syndrome: Difference between revisions
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
'''Hypereosinophilic syndrome''' (HES) is a type of [[Myeloproliferative disease|myeloproliferative disorder]] characterized by a persistently [[Eosinophilia|elevated eosinophil count]] (≥ 1500 [[eosinophils]]/mm³) in the [[blood]] for at least six months without any recognizable cause, with involvement of either the [[heart]], [[nervous system]], or [[bone marrow]]. Hypereosinophilic syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion, after clonal [[eosinophilia]] (such as [[leukemia]]) and reactive [[eosinophilia]] (in response to [[infection]], [[autoimmune disease]], [[atopy]], [[Adrenal insufficiency|hypoadrenalism]], [[Eosinophilia|tropical eosinophilia]], or cancer) have been ruled out. Hypereosinophilic syndrome may be classified into 3 categories: primary, secondary, and idiopathic. Hypereosinophilic syndrome may be caused by either [[stem cell]], [[myeloid]], or [[eosinophilic]] [[Neoplasm|neoplasms]]. Hypereosinophilic syndrome is mainly caused by [[Mutation|mutations]] in the BCR-ABL, PDGFRA, PDGFRβ, and KIT genes. There are some associations with [[chronic eosinophilic leukemia]] as it shows similar characteristics and [[genetic]] defects. [[Patient|Patients]] with hypereosinophilic syndrome may be initially [[asymptomatic]]. Early clinical features include [[fatigue]], [[diarrhea]], and [[rash]]. [[Prognosis]] is generally poor, and the 3-year [[Survival analysis|survival]] rate of patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome is approximately 12%. Findings related with poor [[prognosis]] in hypereosinophilic syndrome, include: presence of [[anemia]], thrombocytopenia, [[Blood cell|white blood cell]] count greater than 100,000 cells/cm3, abnormal [[Bone marrow|marrow]] and/or [[basophils]], elevated serum levels of [[vitamin B12]], serum [[tryptase]], and abnormal levels of [[leukocyte alkaline phosphatase]]. If left untreated, hypereosinophilic syndrome is progressively fatal. Treatment will depend on the presence of [[Mutation|mutations]]. Treatment of choice for patients with FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]] is [[imatinib]] and first line treatment for [[Patient|patients]] without FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]] is [[Glucocorticoid|glucocorticoid therapy]]. The addition of the [[Monoclonal antibodies|monoclonal antibody]] [[mepolizumab]] may reduce the dose of [[glucocorticoids]]. Once diagnosed and successfully treated, [[Patient|patients]] with hypereosinophilic syndrome are followed-up periodically every 6 or 12 months depending on the clinical progression. Follow-up testing includes the following tests: [[complete blood count]], [[biochemical]] profile ([[liver enzymes]], [[creatine kinase]], [[renal function]], and [[troponin]]), [[electrocardiogram]], and [[Biopsy|tissue biopsies]]. | '''Hypereosinophilic syndrome''' (HES) is a type of [[Myeloproliferative disease|myeloproliferative disorder]] characterized by a persistently [[Eosinophilia|elevated eosinophil count]] (≥ 1500 [[eosinophils]]/mm³) in the [[blood]] for at least six months without any recognizable cause, with involvement of either the [[heart]], [[nervous system]], or [[bone marrow]]. Hypereosinophilic syndrome is a [[diagnosis]] of exclusion, after [[Clonal colony|clonal]] [[eosinophilia]] (such as [[leukemia]]) and reactive [[eosinophilia]] (in response to [[infection]], [[autoimmune disease]], [[atopy]], [[Adrenal insufficiency|hypoadrenalism]], [[Eosinophilia|tropical eosinophilia]], or cancer) have been ruled out. Hypereosinophilic syndrome may be classified into 3 categories: primary, secondary, and [[idiopathic]]. Hypereosinophilic syndrome may be caused by either [[stem cell]], [[myeloid]], or [[eosinophilic]] [[Neoplasm|neoplasms]]. Hypereosinophilic syndrome is mainly caused by [[Mutation|mutations]] in the BCR-ABL, PDGFRA, PDGFRβ, and KIT genes. There are some associations with [[chronic eosinophilic leukemia]] as it shows similar characteristics and [[genetic]] defects. [[Patient|Patients]] with hypereosinophilic syndrome may be initially [[asymptomatic]]. Early clinical features include [[fatigue]], [[diarrhea]], and [[rash]]. [[Prognosis]] is generally poor, and the 3-year [[Survival analysis|survival]] rate of patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome is approximately 12%. Findings related with poor [[prognosis]] in hypereosinophilic syndrome, include: presence of [[anemia]], thrombocytopenia, [[Blood cell|white blood cell]] count greater than 100,000 cells/cm3, abnormal [[Bone marrow|marrow]] and/or [[basophils]], elevated serum levels of [[vitamin B12]], serum [[tryptase]], and abnormal levels of [[leukocyte alkaline phosphatase]]. If left untreated, hypereosinophilic syndrome is progressively [[fatal]]. Treatment will depend on the presence of [[Mutation|mutations]]. Treatment of choice for [[Patient|patients]] with FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]] is [[imatinib]] and first line treatment for [[Patient|patients]] without FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]] is [[Glucocorticoid|glucocorticoid therapy]]. The addition of the [[Monoclonal antibodies|monoclonal antibody]] [[mepolizumab]] may reduce the dose of [[glucocorticoids]]. Once [[Diagnosis|diagnosed]] and successfully treated, [[Patient|patients]] with hypereosinophilic syndrome are followed-up periodically every 6 or 12 months depending on the clinical progression. Follow-up testing includes the following [[Test|tests]]: [[complete blood count]], [[biochemical]] profile ([[liver enzymes]], [[creatine kinase]], [[renal function]], and [[troponin]]), [[electrocardiogram]], and [[Biopsy|tissue biopsies]]. | ||
==Historical Perspective== | ==Historical Perspective== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
::*Also known as reactive hypereosinophilic syndrome | ::*Also known as reactive hypereosinophilic syndrome | ||
:* '''Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome''' | :* '''Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome''' | ||
*Other variants of hypereosinophilic syndrome may include [[Myeloproliferative disease|myeloproliferative]], [[T lymphocyte|T lymphocytic]], familiar, idiopathic, and [[Organ (anatomy)|organ]]-restricted hypereosinophilic syndrome variants. | *Other variants of hypereosinophilic syndrome may include [[Myeloproliferative disease|myeloproliferative]], [[T lymphocyte|T lymphocytic]], familiar, [[idiopathic]], and [[Organ (anatomy)|organ]]-restricted hypereosinophilic syndrome variants. | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
==Differentiating Hypereosinophilic Syndrome from Other Diseases== | ==Differentiating Hypereosinophilic Syndrome from Other Diseases== | ||
*Hypereosinophilic syndrome must be differentiated from other diseases that cause [[skin rash]], [[fatigue]], and [[hypereosinophilia]], such as:<ref name="pmid19243381">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gleich GJ, Leiferman KM |title=The hypereosinophilic syndromes: current concepts and treatments |journal=Br. J. Haematol. |volume=145 |issue=3 |pages=271–85 |year=2009 |pmid=19243381 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.07599.x |url=}}</ref> | *Hypereosinophilic syndrome must be differentiated from other [[Disease|diseases]] that cause [[skin rash]], [[fatigue]], and [[hypereosinophilia]], such as:<ref name="pmid19243381">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gleich GJ, Leiferman KM |title=The hypereosinophilic syndromes: current concepts and treatments |journal=Br. J. Haematol. |volume=145 |issue=3 |pages=271–85 |year=2009 |pmid=19243381 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.07599.x |url=}}</ref> | ||
:*[[Allergy differential diagnosis|Allergic diseases]] | :*[[Allergy differential diagnosis|Allergic diseases]] | ||
:*[[Atopic dermatitis]] | :*[[Atopic dermatitis]] | ||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
:*[[Eosinophilic pneumonia]] | :*[[Eosinophilic pneumonia]] | ||
:*[[Hypersensitivities|Hypersensitivity diseases]] | :*[[Hypersensitivities|Hypersensitivity diseases]] | ||
:*Malignancy with secondary eosinophilia | :*[[Malignancy]] with secondary [[eosinophilia]] | ||
==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
=== Medical Therapy === | === Medical Therapy === | ||
*The [[Medical management company|medical management]] of hypereosinophilic syndrome is divided into 2 categories: presence of FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]], and absence of FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]].<ref name="lupdate">Hypereosinophilic syndrome: an update. http://www.pneumonologia.gr/articlefiles/20070228_Hypereosinophilic_Syndrome_An_Update.pdf Accessed on April 4, 2016</ref> | *The [[Medical management company|medical management]] of hypereosinophilic syndrome is divided into 2 categories: presence of FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]], and absence of FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]].<ref name="lupdate">Hypereosinophilic syndrome: an update. http://www.pneumonologia.gr/articlefiles/20070228_Hypereosinophilic_Syndrome_An_Update.pdf Accessed on April 4, 2016</ref> | ||
::*Treatment of choice for patients with FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]] is [[imatinib]] | ::*Treatment of choice for [[Patient|patients]] with FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]] is [[imatinib]] | ||
::*First line treatment for patients without FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]] is [[Glucocorticoids|glucocorticoid therapy]]. | ::*[[First-line treatment|First line treatment]] for [[Patient|patients]] without FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]] is [[Glucocorticoids|glucocorticoid therapy]]. | ||
::*Initial high-dose [[prednisone]] is typically initiated at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day | ::*Initial high-dose [[prednisone]] is typically initiated at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day | ||
::*Second line treatment for [[Patient|patients]] without FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]] include [[interferon alpha]] and [[hydroxyurea]]. | ::*Second line treatment for [[Patient|patients]] without FIP1L1/PDGFRA [[mutation]] include [[interferon alpha]] and [[hydroxyurea]]. | ||
| Line 157: | Line 157: | ||
*There are no [[Primary prevention|primary preventive]] measures available for hypereosinophilic syndrome.<ref name="lupdate">Hypereosinophilic syndrome: an update. http://www.pneumonologia.gr/articlefiles/20070228_Hypereosinophilic_Syndrome_An_Update.pdf Accessed on April 4, 2016</ref> | *There are no [[Primary prevention|primary preventive]] measures available for hypereosinophilic syndrome.<ref name="lupdate">Hypereosinophilic syndrome: an update. http://www.pneumonologia.gr/articlefiles/20070228_Hypereosinophilic_Syndrome_An_Update.pdf Accessed on April 4, 2016</ref> | ||
*There are no effective measures for the [[primary prevention]] of hypereosinophilic syndrome. | *There are no effective measures for the [[primary prevention]] of hypereosinophilic syndrome. | ||
*Once [[Diagnosis|diagnosed]] and successfully treated, patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome are followed-up periodically every 6 or 12 months depending on the clinical progression. | *Once [[Diagnosis|diagnosed]] and successfully treated, [[Patient|patients]] with hypereosinophilic syndrome are followed-up periodically every 6 or 12 months depending on the clinical progression. | ||
*Follow-up testing includes the following tests: complete blood count, biochemical profile (liver enzymes, [[creatine kinase]], [[renal function]], and [[troponin]]), | *Follow-up testing includes the following [[Test|tests]]: [[complete blood count]], [[Biochemistry|biochemical profile]] ([[Liver function tests|liver enzymes]], [[creatine kinase]], [[renal function]], and [[troponin]]), [[electrocardiogram]], and [[Biopsy|tissue biopsies]]. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 13:51, 11 April 2019
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Maria Fernanda Villarreal, M.D. [2]
Synonyms and keywords: HES; Hypereosinophilic disease; Primary hypereosinophilic syndrome; Secondary hypereosinophilic syndrome; Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome
Overview
Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is a type of myeloproliferative disorder characterized by a persistently elevated eosinophil count (≥ 1500 eosinophils/mm³) in the blood for at least six months without any recognizable cause, with involvement of either the heart, nervous system, or bone marrow. Hypereosinophilic syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion, after clonal eosinophilia (such as leukemia) and reactive eosinophilia (in response to infection, autoimmune disease, atopy, hypoadrenalism, tropical eosinophilia, or cancer) have been ruled out. Hypereosinophilic syndrome may be classified into 3 categories: primary, secondary, and idiopathic. Hypereosinophilic syndrome may be caused by either stem cell, myeloid, or eosinophilic neoplasms. Hypereosinophilic syndrome is mainly caused by mutations in the BCR-ABL, PDGFRA, PDGFRβ, and KIT genes. There are some associations with chronic eosinophilic leukemia as it shows similar characteristics and genetic defects. Patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome may be initially asymptomatic. Early clinical features include fatigue, diarrhea, and rash. Prognosis is generally poor, and the 3-year survival rate of patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome is approximately 12%. Findings related with poor prognosis in hypereosinophilic syndrome, include: presence of anemia, thrombocytopenia, white blood cell count greater than 100,000 cells/cm3, abnormal marrow and/or basophils, elevated serum levels of vitamin B12, serum tryptase, and abnormal levels of leukocyte alkaline phosphatase. If left untreated, hypereosinophilic syndrome is progressively fatal. Treatment will depend on the presence of mutations. Treatment of choice for patients with FIP1L1/PDGFRA mutation is imatinib and first line treatment for patients without FIP1L1/PDGFRA mutation is glucocorticoid therapy. The addition of the monoclonal antibody mepolizumab may reduce the dose of glucocorticoids. Once diagnosed and successfully treated, patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome are followed-up periodically every 6 or 12 months depending on the clinical progression. Follow-up testing includes the following tests: complete blood count, biochemical profile (liver enzymes, creatine kinase, renal function, and troponin), electrocardiogram, and tissue biopsies.
Historical Perspective
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome was first described by Hardy and Anderson in 1968.[1]
- In 2003, PDGFRA and FIP1L1 gene mutations were first identified in the pathogenesis of hypereosinophilic syndrome.[2]
Classification
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome may be classified into 3 categories:.[3]
- Primary hypereosinophilic syndrome
- Also known as neoplasic hypereosinophilic syndrome
- Secondary hypereosinophilic syndrome
- Also known as reactive hypereosinophilic syndrome
- Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome
- Other variants of hypereosinophilic syndrome may include myeloproliferative, T lymphocytic, familiar, idiopathic, and organ-restricted hypereosinophilic syndrome variants.
Pathophysiology
- The pathogenesis of hypereosinophilic syndrome is characterized by the constitutive activation of tyrosine kinases induced by eosinophils.[4][5]
- Other mechanisms of hypereosinophilic syndrome pathogenesis, include: clonal eosinophilic proliferation, and overproduction of eosinophilopoietic cytokines.[4]
- The overproduction of eosinophilopoietic cytokines (eg. IL-5) will induce epithelial cell and tissue damage.[4]
- Genes associated with the development of hypereosinophilic syndrome, include:[4]
- PDGFRA gene
- PDGFRB gene
- FGFR1 gene
- On gross pathology, there are no are characteristic findings of hypereosinophilic syndrome.
- In some cases, eosinophilia causes infiltration of the myocardium, findings include:
- Fibrotic thickening of portions of the heart.
- May involve the mitral or tricuspid valves.
- The cavity of the ventricles of the heart diminish in size
- Ventricular mural thrombi may develop.
- On microscopic histopathological analysis, hypercellular marrow, and increased eosinophilic precursors are characteristic findings of hypereosinophilic syndrome.
Gallery
Microscopic Pathology
Images shown below are courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
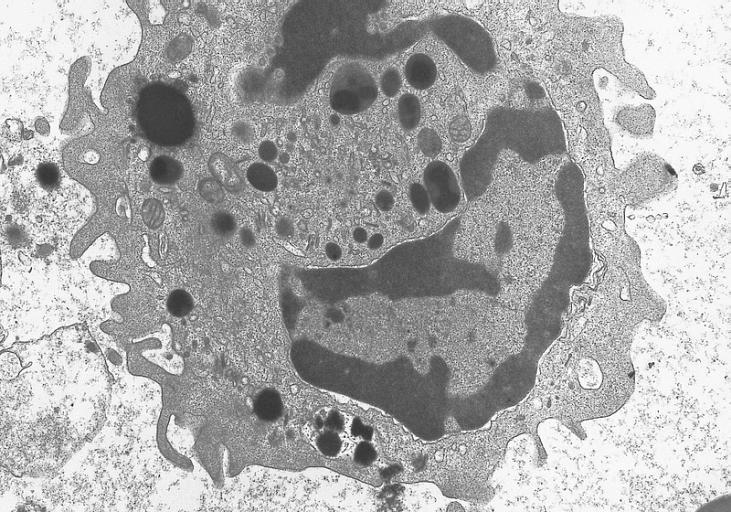
Electron micrograph of an abnormal eosinophil from the specimen in figure 274B. There is a decreased number of granules. The majority of the granules present are homogeneous in contrast to normal eosinophil granules which have a dense core surrounded by a less dense capsule. (Uranyl acetate-lead citrate stains, X20,000)
-
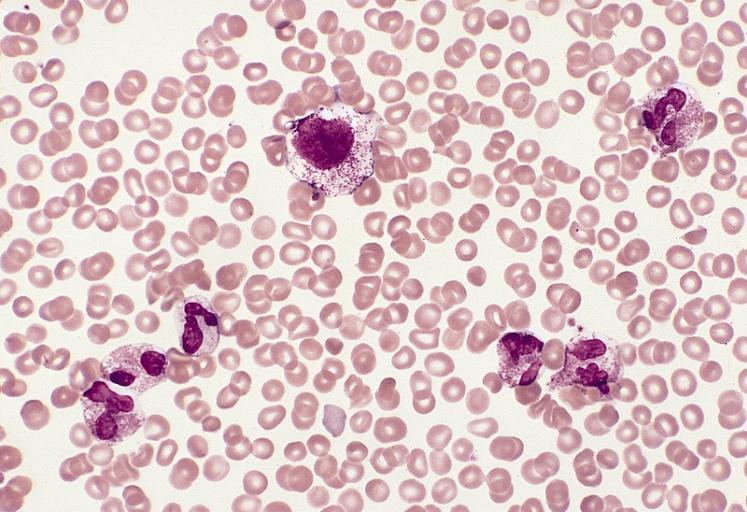
A blood smear from a young woman with mast cell leukemia and marked eosinophilia. There are five eosinophils, one neutrophil, and a large atypical-appearing mast cell with relatively sparse small granules and a slightly lobulated nucleus. This patient had eosinophilia as a presenting feature and was initially thought to have a hypereosinophilic syndrome. Eosinophilia is observed in approximately one third of patients with systemic mast cell disease. (Wright-Giemsa stain)
-
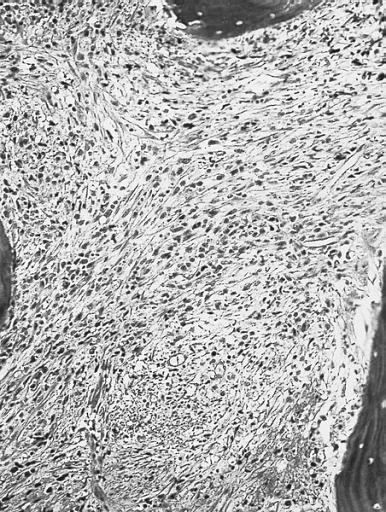
Bone marrow biopsy. The marrow is markedly fibrotic. (Hematoxylin and eosin stain)
-
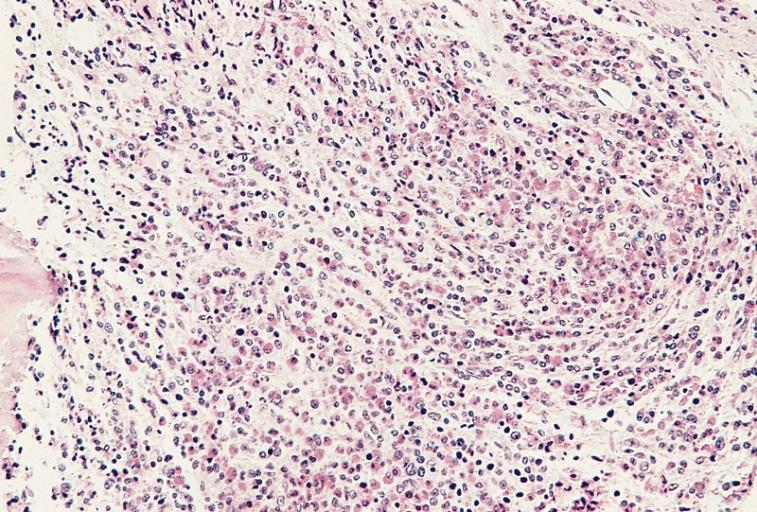
High magnification of the specimen on the left. Blasts and immature cells are scattered throughout the fibrotic tissue. (Hematoxylin and eosin stain)
-
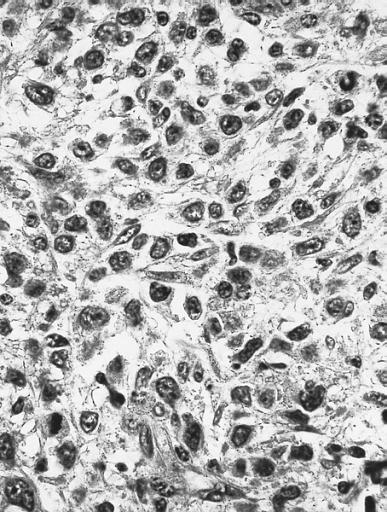
Bone marrow biopsy showing marked hypercellularity due primarily to an increase in eosinophils and precursors. Megakaryocytes are markedly reduced. Increased reticulin fibers are present. Despite intensive chemotherapy there was a progressive increase in marrow fibrosis and number of blasts. The patient died of central nervous system failure 17 months after this specimen was obtained. (Hematoxylin and eosin stain)
-
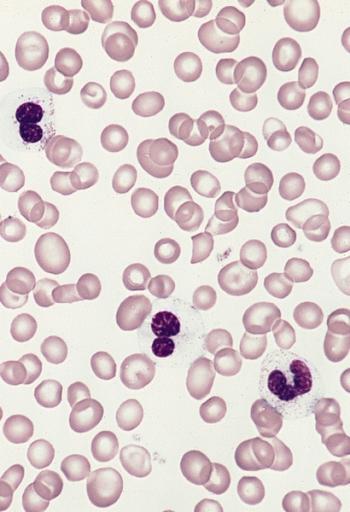
Blood smear from a 50-year-old male with a 3-year history of hypereosinophilic syndrome with progressive bone marrow failure and multiple organ involvement. The three eosinophils show marked hypogranulation. (Wright-Giemsa stain)
-
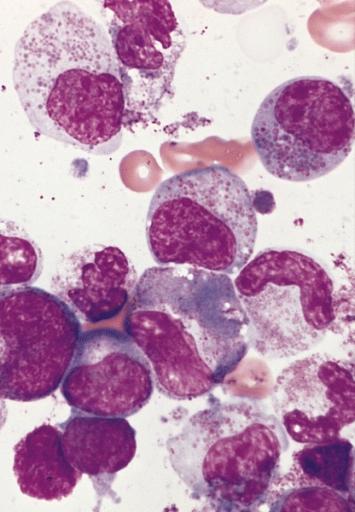
Bone marrow smear from the patient in A showing a marked increase in eosinophils at all stages of maturation. Some of the granules in immature eosinophils have a basophilic color and two of the eosinophil myelocytes have a diminished number of granules. (Wright-Giemsa stain)
Gross Pathology
Images shown below are courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
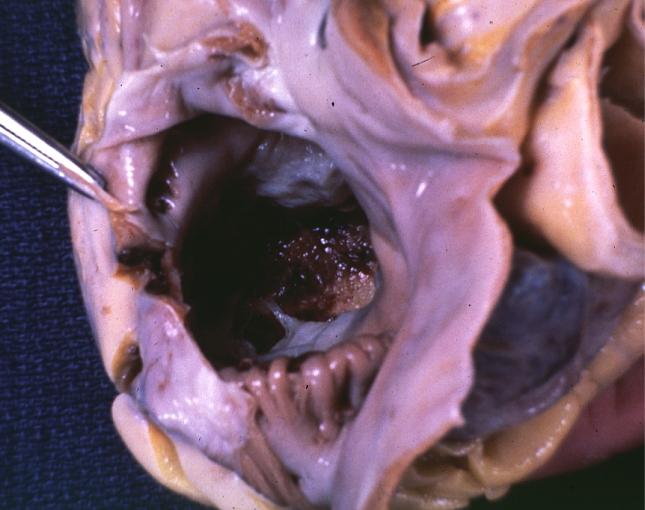
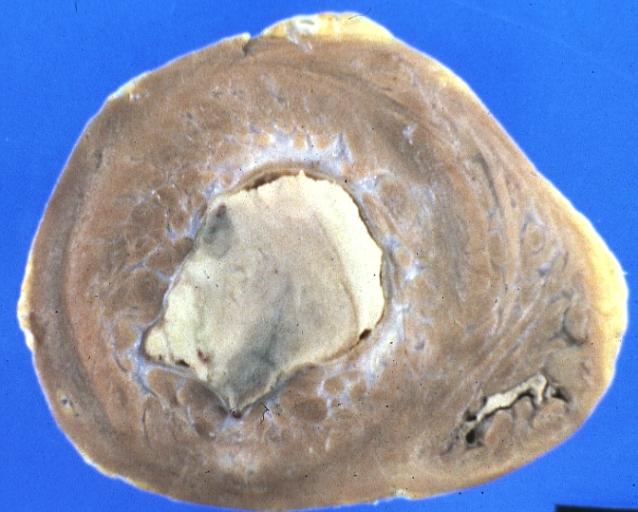
Endomyocardial Fibrosis With Ventricular Thrombosis: Gross fixed tissue good color view from right atrium into right ventricle showing top of thrombus in right ventricle strange case of 43yo F with thrombi filling both ventricles cause completely unknown
-
Endomyocardial Fibrosis With Ventricular Thrombosis: Gross fixed tissue good color horizontal section of ventricles endocardial fibrosis thrombus and focal myocardial fibrosis are evident strange case with no evident cause
Causes
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome may be caused by either stem cell, myeloid, or eosinophilic neoplasms.
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome is caused by a mutation in the BCR-ABL, PDGFRA, PDGFRβ, and KIT gene.[3]
Differentiating Hypereosinophilic Syndrome from Other Diseases
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome must be differentiated from other diseases that cause skin rash, fatigue, and hypereosinophilia, such as:[3]
Epidemiology and Demographics
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome is a very rare disease.
- The prevalence of hypereosinophilic syndrome is approximately 0.36 to 6.3 per 100,000 individuals worldwide.
Age
- Patients of all age groups may develop hypereosinophilic syndrome.
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome is more commonly observed among adults.
Gender
- Males are more likely to be affected from hypereosinophilic syndrome than females, with male to female ratio of 5:1[6]
Race
Risk Factors
- Common risk factors in the development of hypereosinophilic syndrome are previous history of cancer, presence of primary cancer, and history of previous allergic hypersensitivity
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
- Patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome may be initially asymptomatic.
- Early clinical features include fatigue, diarrhea, and rash.
- If left untreated, the majority of patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome may progress to develop thromboembolism, acute respiratory failure, and death.
- Common complications of hypereosinophilic syndrome include chronic heart failure, myocardial fibrosis, and death.
- Prognosis is generally poor, and the 3 year survival rate of patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome is approximately 12%
- Findings related with poor prognosis in hypereosinophilic syndrome, include: presence of anemia, thrombocytopenia, white blood cell count greater than 100,000 cells/cm3, abnormal marrow and/or basophils, elevated serum levels of vitamin B12, serum tryptase, and abnormal levels of leukocyte alkaline phosphatase.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Criteria
- Persistently elevated eosinophil count (≥ 1500 eosinophils/mm³) in the blood
- At least six months without any recognizable cause
- Involvement of either the heart, nervous system, or bone marrow
Symptoms
Physical Examination
- Patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome usually have a normal appearance.
- Physical examination may be remarkable for:[3]
-
- Thickening of the skin (lichenification)
- Eczema (flexural areas)
- Dermographism
Laboratory Findings
- Laboratory findings consistent with the diagnosis of hypereosinophilic syndrome include the following:[6]
- Elevated serum IgE immunoglobulin
- Elevated serum vitamin B12
- Elevated serum tryptase
Imaging Findings
- There are no imaging findings associated with hypereosinophilic syndrome.
Other Diagnostic Studies
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome may also be diagnosed using bone marrow biopsy and molecular testing.[3]
Treatment
Medical Therapy
- The medical management of hypereosinophilic syndrome is divided into 2 categories: presence of FIP1L1/PDGFRA mutation, and absence of FIP1L1/PDGFRA mutation.[6]
- Treatment of choice for patients with FIP1L1/PDGFRA mutation is imatinib
- First line treatment for patients without FIP1L1/PDGFRA mutation is glucocorticoid therapy.
- Initial high-dose prednisone is typically initiated at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day
- Second line treatment for patients without FIP1L1/PDGFRA mutation include interferon alpha and hydroxyurea.
- Medical therapies for hypereosinophilic syndrome, include: corticosteroids, cytotoxic agents (eg. hydroxyurea, vincristine), biological response modifers (eg. interferon-alpha), targeted therapy, and mepolizumab.
Surgery
- Surgical intervention is not recommended for the management of hypereosinophilic syndrome.
- In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to reduce pain in patients with spleen enlargement due to hypereosinophilic syndrome.
Prevention
- There are no primary preventive measures available for hypereosinophilic syndrome.[6]
- There are no effective measures for the primary prevention of hypereosinophilic syndrome.
- Once diagnosed and successfully treated, patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome are followed-up periodically every 6 or 12 months depending on the clinical progression.
- Follow-up testing includes the following tests: complete blood count, biochemical profile (liver enzymes, creatine kinase, renal function, and troponin), electrocardiogram, and tissue biopsies.
References
- ↑ Hardy WR, Anderson RE (1968). "The hypereosinophilic syndromes". Ann. Intern. Med. 68 (6): 1220–9. PMID 5653621.
- ↑ Cools J, DeAngelo DJ, Gotlib J, et al. (2003). "A tyrosine kinase created by fusion of the PDGFRA and FIP1L1 genes as a therapeutic target of imatinib in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome". N. Engl. J. Med. 348 (13): 1201–14. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa025217. PMID 12660384.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Gleich GJ, Leiferman KM (2009). "The hypereosinophilic syndromes: current concepts and treatments". Br. J. Haematol. 145 (3): 271–85. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.07599.x. PMID 19243381.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Weller PF (1991). "The immunobiology of eosinophils". N. Engl. J. Med. 324 (16): 1110–8. doi:10.1056/NEJM199104183241607. PMID 2008184.
- ↑ Chusid MJ, Dale DC, West BC, Wolff SM (1975). "The hypereosinophilic syndrome: analysis of fourteen cases with review of the literature". Medicine (Baltimore). 54 (1): 1–27. doi:10.1097/00005792-197501000-00001. PMID 1090795.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Hypereosinophilic syndrome: an update. http://www.pneumonologia.gr/articlefiles/20070228_Hypereosinophilic_Syndrome_An_Update.pdf Accessed on April 4, 2016